Laches is an equitable defense in legal cases that prevents a claimant from asserting a right due to an unreasonable delay in pursuing it, which causes prejudice to the opposing party. Understanding how laches operates is crucial for protecting your rights against stale claims and ensuring timely justice. Explore the rest of this article to learn how laches might affect your legal strategies and outcomes.
Table of Comparison
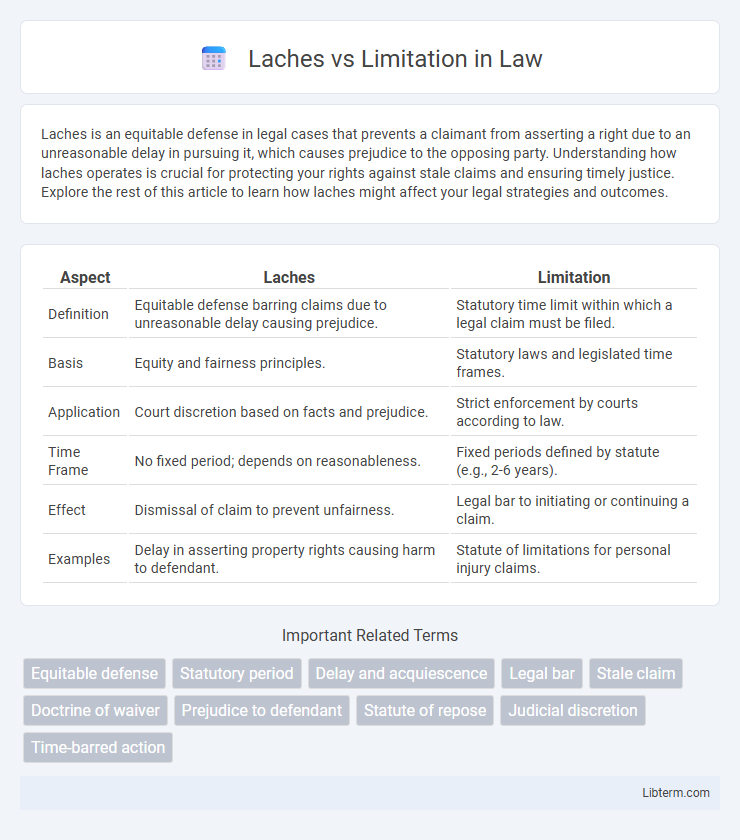
| Aspect | Laches | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Equitable defense barring claims due to unreasonable delay causing prejudice. | Statutory time limit within which a legal claim must be filed. |
| Basis | Equity and fairness principles. | Statutory laws and legislated time frames. |
| Application | Court discretion based on facts and prejudice. | Strict enforcement by courts according to law. |
| Time Frame | No fixed period; depends on reasonableness. | Fixed periods defined by statute (e.g., 2-6 years). |
| Effect | Dismissal of claim to prevent unfairness. | Legal bar to initiating or continuing a claim. |
| Examples | Delay in asserting property rights causing harm to defendant. | Statute of limitations for personal injury claims. |
Introduction to Laches vs Limitation
Laches and limitation are critical doctrines in equity and law that govern the timeliness of legal claims. Laches is an equitable defense that bars a claim when a plaintiff unreasonably delays enforcing a right, causing prejudice to the defendant, while limitation refers to statutory time periods within which a legal action must be initiated. Understanding the differences between laches and limitation is essential for assessing the viability of claims in property disputes, contract enforcement, and intellectual property cases.
Definition of Laches in Law
Laches is an equitable defense in law that bars a claimant from seeking relief if they have unreasonably delayed in asserting their rights, causing prejudice to the opposing party. Unlike statutes of limitation, which are fixed legal time limits, laches depends on the plaintiff's lack of diligence and resulting harm. Courts apply laches to prevent unfairness when a claim is made after an excessive lapse of time without valid justification.
Understanding Legal Limitation Periods
Legal limitation periods define the maximum time frame within which a claim or lawsuit must be filed, ensuring timely justice and legal certainty. Unlike laches, which is an equitable defense based on unreasonable delay causing prejudice, limitation periods are statutory deadlines strictly enforced by courts. Understanding these limitations prevents forfeiture of rights and helps litigants assess the viability of their legal actions within prescribed time frames.
Key Differences Between Laches and Limitation
Laches is an equitable defense based on unreasonable delay in asserting a right, causing prejudice to the opposing party, while limitation refers to statutory time limits set by law for filing claims. The key difference lies in laches requiring proof of both delay and resulting harm, whereas limitation involves strict deadlines regardless of prejudice. Courts apply laches flexibly based on fairness, but limitation periods are rigid and codified by legislation.
Legal Principles Underpinning Laches
Laches is an equitable defense grounded in the principle that undue delay in asserting a right can cause prejudice to the opposing party, emphasizing fairness and justice over strict legal rules. Unlike statutes of limitation, which impose fixed time limits for filing claims based on legislative enactments, laches relies on the court's discretion to assess reasonableness of the delay and related harm. The core legal concept underpinning laches is that equity aids the vigilant, not those who sleep on their rights, ensuring timeliness in pursuing claims to prevent injustice.
Statutory Basis of Limitation Periods
Laches is an equitable defense based on unreasonable delay in pursuing a claim, lacking specific statutory deadlines, while limitation periods are strictly defined by statutes that prescribe exact timeframes for bringing legal actions. Statutory limitation periods vary by jurisdiction and type of claim, such as contracts, torts, or property disputes, ensuring legal certainty and finality. Courts generally prioritize statutory limitations over laches when clear legislative time limits exist, emphasizing legal compliance over equitable considerations.
Applicability of Laches in Various Legal Systems
Laches is an equitable defense that bars claims where a plaintiff unreasonably delays asserting a right, causing prejudice to the defendant, and is predominantly recognized in common law jurisdictions such as the United States and the United Kingdom. In contrast, limitation refers to statutory time limits for filing claims, enforced universally across various legal systems including civil law countries like France and Germany, where laches has limited or no application. Laches is generally inapplicable in legal systems that strictly adhere to codified statutes of limitations, emphasizing fixed deadlines over equitable discretion.
Case Law Illustrating Laches and Limitation
Laches, an equitable defense based on unreasonable delay causing prejudice, is illustrated in *Petrella v. Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer, Inc.*, where the U.S. Supreme Court emphasized timeliness in asserting rights. Limitation periods, governed by statutes such as the Copyright Act's three-year limitation, are strictly enforced, as seen in *Godfrey v. Dobrowski*, where claims dismissed after statutory deadlines upheld. Courts differentiate laches from statutory limitation by assessing fairness and prejudice beyond mere lapse of time, ensuring equitable justice in cases like *Daniels v. City of Arlington*.
Practical Implications for Litigants
Laches prevents recovery when a plaintiff unreasonably delays asserting a right, causing prejudice to the defendant, focusing on fairness rather than strict timing. Statutes of limitation set fixed legal deadlines for filing claims, after which cases are barred regardless of prejudice. Litigants benefit from understanding that laches can excuse delays within limitation periods, while reliance on statutes of limitation offers more predictable, enforceable timeframes for initiating lawsuits.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Laches and Limitation
Selecting between laches and limitation hinges on the nature of the claim and the defendant's circumstances; laches applies to equitable claims where unreasonable delay causes prejudice, while limitation statutes impose fixed deadlines for filing legal actions. Courts often prefer limitation periods due to their clear, statute-based timeframes offering predictability, whereas laches is more flexible, focusing on fairness in equity. Strategic consideration should assess statutory time bars against evidentiary prejudice to determine the optimal defense.
Laches Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com