Malicious prosecution occurs when someone is wrongfully subjected to legal action without probable cause, driven by malicious intent rather than legitimate grounds. Understanding the key elements and defenses of malicious prosecution can protect your rights and help you seek appropriate remedies. Continue reading to explore how malicious prosecution claims work and what steps you can take if you're affected.
Table of Comparison
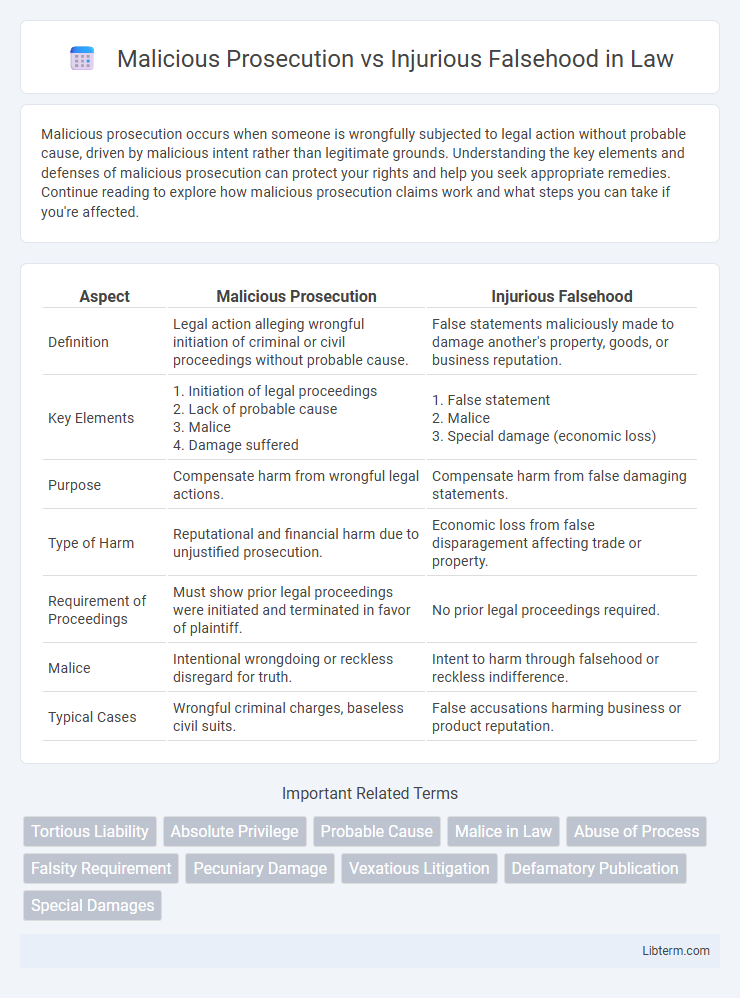
| Aspect | Malicious Prosecution | Injurious Falsehood |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal action alleging wrongful initiation of criminal or civil proceedings without probable cause. | False statements maliciously made to damage another's property, goods, or business reputation. |
| Key Elements | 1. Initiation of legal proceedings 2. Lack of probable cause 3. Malice 4. Damage suffered |
1. False statement 2. Malice 3. Special damage (economic loss) |
| Purpose | Compensate harm from wrongful legal actions. | Compensate harm from false damaging statements. |
| Type of Harm | Reputational and financial harm due to unjustified prosecution. | Economic loss from false disparagement affecting trade or property. |
| Requirement of Proceedings | Must show prior legal proceedings were initiated and terminated in favor of plaintiff. | No prior legal proceedings required. |
| Malice | Intentional wrongdoing or reckless disregard for truth. | Intent to harm through falsehood or reckless indifference. |
| Typical Cases | Wrongful criminal charges, baseless civil suits. | False accusations harming business or product reputation. |
Introduction to Malicious Prosecution and Injurious Falsehood
Malicious prosecution involves initiating a legal action without reasonable grounds, primarily intending to cause harm or harassment to the defendant, often resulting in damage to reputation or financial loss. Injurious falsehood, also known as trade libel or economic tort, pertains to the intentional publication of false statements that disparage another's goods or business, causing economic damage. Both torts protect individuals and businesses from unjust harm but differ in their focus: malicious prosecution targets wrongful legal proceedings, while injurious falsehood addresses defamatory falsehoods impacting commercial interests.
Legal Definitions: Malicious Prosecution vs Injurious Falsehood
Malicious prosecution is a legal claim arising when a party initiates a baseless lawsuit or criminal charge with malice and without probable cause, causing harm to the defendant. Injurious falsehood, also known as trade libel or commercial disparagement, involves the publication of false statements that intentionally damage another party's economic interests or reputation. Both torts require proof of malice, but malicious prosecution centers on wrongful legal proceedings, whereas injurious falsehood targets economically harmful falsehoods.
Essential Elements of Malicious Prosecution
Malicious prosecution requires the plaintiff to prove the initiation or continuation of a legal action without probable cause, malice, and a favorable termination of the prior proceeding. Essential elements include an unlawful prosecution initiated by the defendant, absence of reasonable grounds, and damage suffered by the plaintiff as a result. Unlike injurious falsehood, which focuses on false statements harming business or property interests, malicious prosecution centers on the improper use of legal processes.
Essential Elements of Injurious Falsehood
Injurious falsehood requires a publication of false statements made maliciously, causing special damages to a person's property or business interests. The essential elements include proof that the statements were false, that they were published with malice or wrongful intent, and that the claimant suffered specific damage as a direct result. Unlike malicious prosecution, which involves wrongful legal proceedings, injurious falsehood centers on defamatory falsehoods that harm economic interests rather than personal reputation.
Key Differences Between Malicious Prosecution and Injurious Falsehood
Malicious prosecution involves wrongful legal action initiated without probable cause and with malice, typically requiring proof of the case's favorable termination for the defendant. Injurious falsehood, also known as trade libel, centers on false statements damaging a person's goods, property, or business reputation, demanding proof of actual malice and specific economic loss. The key difference lies in malicious prosecution addressing improper lawsuits, while injurious falsehood pertains to harmful false statements causing financial harm outside of litigation.
Burden of Proof in Both Claims
In malicious prosecution claims, the plaintiff must prove the defendant initiated or continued a legal action without probable cause and with malice, and the prior proceeding ended in the plaintiff's favor, placing a heavy burden on the plaintiff to establish wrongful intent and favorable termination. Injurious falsehood requires proof that the defendant published false statements maliciously causing economic damage to the plaintiff's property or business interests, emphasizing the need to show both malice and demonstrable financial harm. The burden of proof in malicious prosecution centers on wrongful legal action and successful termination, whereas injurious falsehood focuses on malicious false statements and resulting quantifiable economic loss.
Typical Examples and Case Studies
Malicious prosecution involves wrongful legal action initiated with malice and lacking probable cause, often seen in cases like baseless criminal charges or unfounded civil suits; for instance, the landmark case of *Gatineau v. Mailman* demonstrated clear elements of malicious prosecution through unfounded defamation claims. Injurious falsehood, also known as trade libel or commercial disparagement, centers on false statements harming a person's economic interests, typically illustrated by cases like *Spiegel v. Globe*, where false allegations about product quality led to significant financial losses. These case studies highlight the legal nuances distinguishing malicious prosecution's focus on improper legal proceedings from injurious falsehood's emphasis on economic harm caused by false information.
Available Legal Remedies and Damages
Malicious prosecution claims focus on wrongful legal proceedings initiated without probable cause, seeking remedies such as dismissal of the case, compensation for legal costs, and damages for reputational harm and emotional distress. Injurious falsehood involves the publication of false statements causing economic loss, with available remedies including injunctions, general damages for loss of reputation, and special damages for quantifiable financial harm. Both torts allow plaintiffs to recover compensatory damages; however, malicious prosecution often requires proving malice and termination in the plaintiff's favor, while injurious falsehood emphasizes malice and actual economic loss to secure remedies.
Common Defenses in Malicious Prosecution and Injurious Falsehood
Common defenses in malicious prosecution include lack of malice, absence of probable cause, and termination of prior proceedings in the plaintiff's favor. In injurious falsehood, defenses often involve justification or truth, absence of malice, and privilege, each aiming to negate the intent or falsity underlying the claim. Both torts require proving malice and damage, making substantiating these defenses critical for successful litigation outcomes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Legal Action
Selecting the appropriate legal action between malicious prosecution and injurious falsehood hinges on the specific nature of the wrongful act and the type of harm suffered. Malicious prosecution addresses wrongful criminal or civil proceedings initiated without probable cause, whereas injurious falsehood targets false statements damaging a person's business or property interests. Understanding the distinct legal elements and evidentiary requirements of each tort ensures effective pursuit of remedies and compensation.
Malicious Prosecution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com