A panel is a flat or curved component that forms part of a surface, commonly used in construction, electronics, and design. It serves functional purposes such as insulation, structural support, or housing electronic displays and controls. Explore the rest of the article to learn how panels can enhance your projects and applications.
Table of Comparison
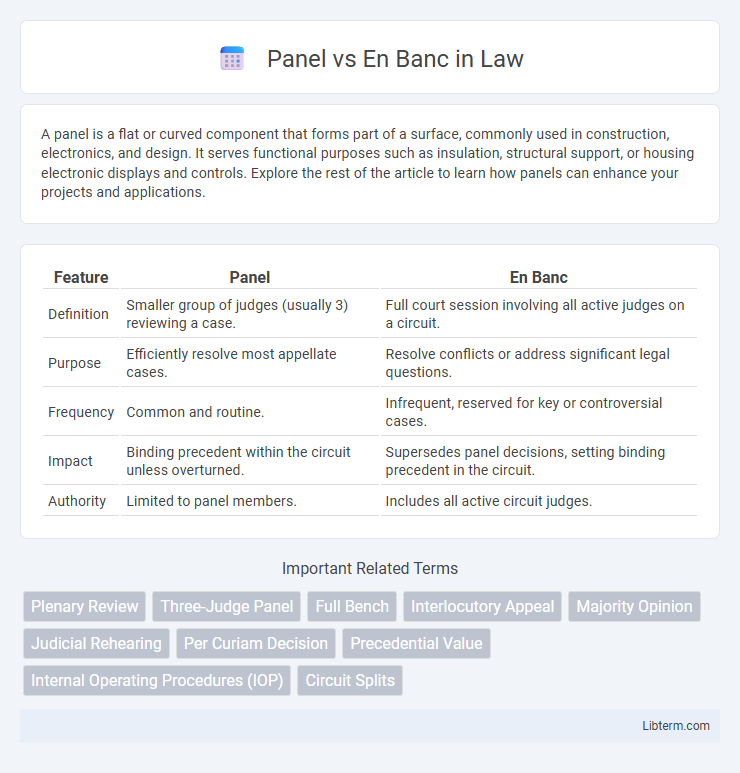
| Feature | Panel | En Banc |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Smaller group of judges (usually 3) reviewing a case. | Full court session involving all active judges on a circuit. |
| Purpose | Efficiently resolve most appellate cases. | Resolve conflicts or address significant legal questions. |
| Frequency | Common and routine. | Infrequent, reserved for key or controversial cases. |
| Impact | Binding precedent within the circuit unless overturned. | Supersedes panel decisions, setting binding precedent in the circuit. |
| Authority | Limited to panel members. | Includes all active circuit judges. |
Introduction to Panel and En Banc Hearings
Panel hearings involve a smaller group of judges, typically three, who review cases to determine the outcome based on the presented record and legal arguments. En banc hearings include all active judges of the court, reserved for cases of exceptional importance or to resolve conflicts in panel decisions. This format ensures uniformity in legal interpretations and addresses significant judicial questions.
Defining Panel Hearings in Appellate Courts
Panel hearings in appellate courts involve a small group of judges, typically three, who review and decide cases, ensuring focused evaluation and consistency in legal interpretation. These panels assess trial court decisions by examining the application of law rather than re-evaluating factual evidence, streamlining appellate process efficiency. Panel decisions establish binding precedent within their jurisdiction unless overturned by an en banc review or higher court ruling.
Understanding En Banc Review
En banc review refers to the process where a case is heard before all the judges of a court, rather than a panel of selected judges, typically used in appellate courts to resolve significant or complex legal issues. This procedure ensures uniformity in legal interpretations and corrects panel decisions that may conflict with established precedent. En banc hearings are less common than panel decisions and often involve more extensive legal argumentation and consideration.
Key Differences Between Panel and En Banc Processes
Panel decisions involve a smaller group of judges, typically three, who review and rule on cases, allowing for quicker resolutions and focused legal analysis. In contrast, en banc reviews include all active judges on the court, providing a broader judicial consensus on complex or significant legal issues. The en banc process serves to ensure uniformity in rulings and address conflicts arising from panel decisions, often leading to more authoritative and precedent-setting outcomes.
Criteria for Granting En Banc Review
En banc review is granted when a case presents questions of exceptional importance or conflicts in circuit court decisions, ensuring uniformity in federal law interpretation. The criteria include the need to resolve inter-panel disagreements, correct a panel decision that conflicts with Supreme Court precedent, or address issues of significant public interest or legal uncertainty. Typically, at least a majority of active judges in the circuit must agree to rehear the case en banc, reflecting the judiciary's commitment to consistency and authoritative guidance.
Advantages of Panel Decisions
Panel decisions offer the advantage of faster resolution by relying on a smaller group of judges, typically three, which streamlines the review process compared to en banc hearings involving all judges. They promote judicial efficiency and consistency by allowing more cases to be decided without the need for full court deliberation, reducing caseload backlogs. Panel opinions also provide a mechanism for diverse viewpoints within the judiciary, as different panels may issue varying interpretations that contribute to legal evolution over time.
Benefits of En Banc Hearings
En banc hearings allow all judges of a court to participate, providing a comprehensive review that enhances consistency in legal interpretations and mitigates panel-based discrepancies. This broader judicial consideration increases the likelihood of correcting significant errors and shaping precedent, fostering uniformity across circuit rulings. En banc sessions also reinforce the authority of court decisions by involving a collective judicial perspective, lending greater weight to their outcomes in future cases.
Impact on Case Law and Legal Precedent
Panel decisions, typically issued by a smaller group of appellate judges, establish legal precedent that binds lower courts within their jurisdiction but may be more narrowly focused in scope. En banc reviews, involving the full bench of appellate judges, carry greater authoritative weight and often signify pivotal shifts or clarifications in case law. The impact of en banc rulings on legal precedent is more substantial, frequently resolving conflicts within panel decisions and setting binding standards for future cases.
Famous Cases: Panel vs En Banc Outcomes
Panel decisions often resolve most federal appellate cases, such as the landmark Microsoft v. i4i dispute where a three-judge panel affirmed patent infringement, while en banc review can overturn or modify those rulings, exemplified by the Seventh Circuit en banc reversal in United States v. Apple Inc. which reshaped antitrust interpretations. En banc hearings, involving all active judges on a circuit, tend to address cases with significant legal questions or conflicting panel decisions, providing greater precedential authority compared to individual panel outcomes. Famous en banc cases like NFL v. NFL Players Association demonstrate how en banc courts clarify complex statutory interpretations, often resulting in influential shifts in legal standards initially established by panel decisions.
Choosing Between Panel and En Banc: Strategic Considerations
Choosing between a panel and en banc review involves strategic considerations centered on case complexity and precedent impact. Panels, typically composed of three judges, offer quicker resolutions and focus on specific legal issues, while en banc reviews, involving a larger number of judges, address cases with significant legal questions or conflicts among panel decisions. Litigators must evaluate the potential for broader legal implications, judicial workload, and the likelihood of reversal when deciding the optimal forum for appellate review.
Panel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com