Enforce means to ensure compliance with laws, rules, or regulations through authoritative measures or actions. It involves applying penalties or corrective steps to maintain order and uphold standards effectively. Discover how enforcement impacts various sectors and why it's crucial for your understanding in the detailed article ahead.
Table of Comparison
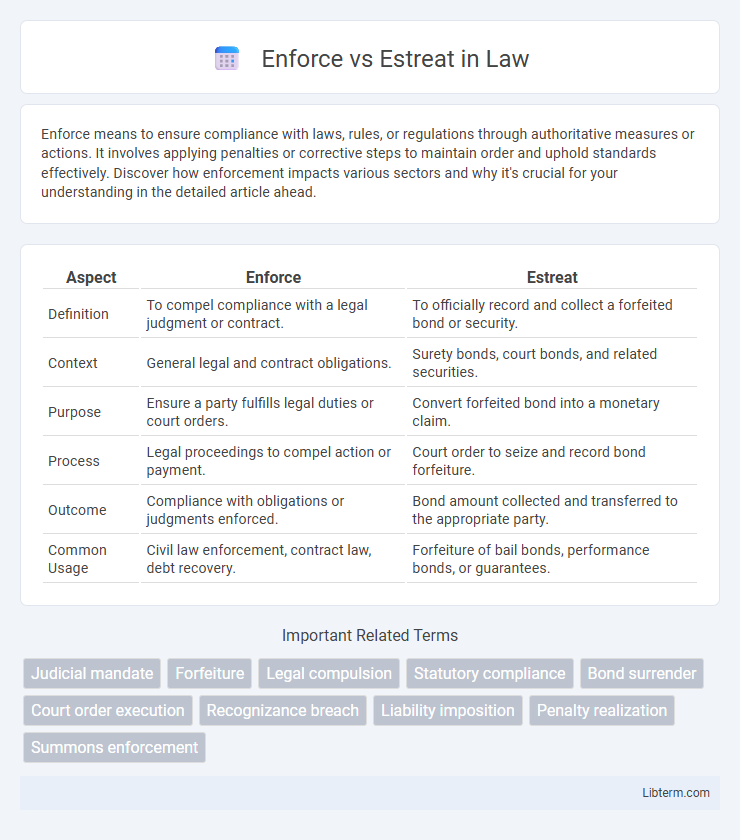
| Aspect | Enforce | Estreat |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | To compel compliance with a legal judgment or contract. | To officially record and collect a forfeited bond or security. |
| Context | General legal and contract obligations. | Surety bonds, court bonds, and related securities. |
| Purpose | Ensure a party fulfills legal duties or court orders. | Convert forfeited bond into a monetary claim. |
| Process | Legal proceedings to compel action or payment. | Court order to seize and record bond forfeiture. |
| Outcome | Compliance with obligations or judgments enforced. | Bond amount collected and transferred to the appropriate party. |
| Common Usage | Civil law enforcement, contract law, debt recovery. | Forfeiture of bail bonds, performance bonds, or guarantees. |
Understanding the Terms: Enforce vs Estreat
Enforce refers to the act of compelling compliance with a law, rule, or obligation, often through legal or administrative measures to ensure performance or adherence. Estreat specifically involves the process of legally seizing or forfeiting a bond, deposit, or surety as a penalty for failing to meet a condition or obligation. Understanding enforce highlights broader enforcement actions, while estreat zeroes in on financial penalties linked to breach of contract or court orders.
Legal Definitions and Contexts
Enforce refers to the act of compelling compliance with a law, regulation, or court order through legal authority, ensuring that obligations or judgments are fulfilled. Estreat involves the legal process of converting a bond or recognizance into a monetary penalty when a party fails to meet a stipulated condition, often used in court forfeitures. Both terms operate within judicial contexts but differ as enforce pertains to executing legal mandates, while estreat focuses specifically on forfeiting financial guarantees due to non-compliance.
Historical Background of Enforce and Estreat
Enforcement and estreat have origins in English common law, where estreat referred to the official process of extracting a bond's forfeited sum recorded in legal pleadings or court records. Historically, enforcement evolved as a broader legal mechanism to compel compliance with court orders, including the collection of debts or penalties. The term estreat is now largely archaic but was crucial in medieval and early modern legal systems for converting bond defaults into monetary judgments.
Key Differences Between Enforce and Estreat
Enforce refers to the act of compelling compliance with a law, rule, or obligation through legal or authoritative means, while Estreat specifically involves the formal process of converting a bond or recognizance into a sum of money due to non-compliance or breach. Enforce is a broader concept encompassing various enforcement actions, whereas Estreat is a specialized legal procedure typically used in bond forfeiture. Understanding the key differences lies in Enforce's general application for ensuring adherence and Estreat's focused use for collecting penalties arising from failed obligations.
When to Use Enforce in Legal Proceedings
Enforce is used in legal proceedings to compel compliance with court orders, judgments, or contracts when a party fails to fulfill their legal obligations voluntarily. This action typically involves measures such as seizing assets, garnishing wages, or imposing fines to ensure enforcement of the court's decision. Enforce is appropriate when securing the actual execution of a legal ruling, unlike Estreat, which pertains primarily to converting a bond or recognizance into a penalty for non-performance.
Situations Requiring Estreat Actions
Situations requiring estreat actions typically involve the forfeiture of a bond or security due to failure to comply with agreed terms, such as not appearing in court or violating probation conditions. Estreat occurs to recover funds originally posted as security, converting the bond into a debt owed to the court. This process enforces accountability while ensuring the penal system retains the necessary financial remedies for non-compliance.
Impact on Legal Outcomes: Enforce vs Estreat
The impact on legal outcomes between enforce and estreat lies in their procedural functions where enforce involves compelling compliance with a court order or judgment, directly affecting case resolution by ensuring obligations are met. Estreat specifically refers to the process of converting a bond or recognizance into a fine or penalty due to non-compliance, leading to financial consequences enforced by the court. Understanding the distinction influences legal strategies, as enforcement secures performance while estreat triggers monetary sanctions for breaches.
Common Misconceptions Explained
Enforce refers to the act of compelling compliance with laws, rules, or agreements, while estreat involves legally demanding the forfeiture of a bond or deposit due to non-compliance. A common misconception is that estreat is simply a synonym for enforcement, but estreat specifically concerns the recovery of pledged money following a breach. Understanding that enforcement encompasses broader regulatory actions whereas estreat applies strictly to financial penalties helps clarify their distinct legal functions.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Enforce and Estreat serve distinct functions in financial and legal contexts, such as enforcing court judgments or forfeiting bonds. For instance, in a real-world case, courts enforce judgments by compelling payment through wage garnishments, while estreat is applied when a surety bond is forfeited due to the principal's failure to comply with legal obligations, leading to the bond amount being collected by the court. Case studies in bail bond scenarios illustrate estreat actions causing forfeiture of the bail bond, whereas enforcement examples include the execution of liens to collect unpaid debts.
Conclusion: Choosing the Correct Legal Term
Enforce refers to the act of compelling compliance with a law or court order, while estreat involves the formal process of converting a bond forfeiture into a monetary judgment. Correctly distinguishing between enforce and estreat ensures precise legal communication and effective case management. Selecting the appropriate term hinges on whether the goal is to implement a court decision (enforce) or to execute a financial penalty linked to bond forfeiture (estreat).
Enforce Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com