The warranty of merchantability ensures that a product you purchase meets basic standards of quality and reliability, functioning as expected for its intended use. This implied warranty protects your rights when a product is defective or fails to perform adequately without needing explicit guarantees. Explore the rest of this article to understand how this warranty influences your consumer protection.
Table of Comparison
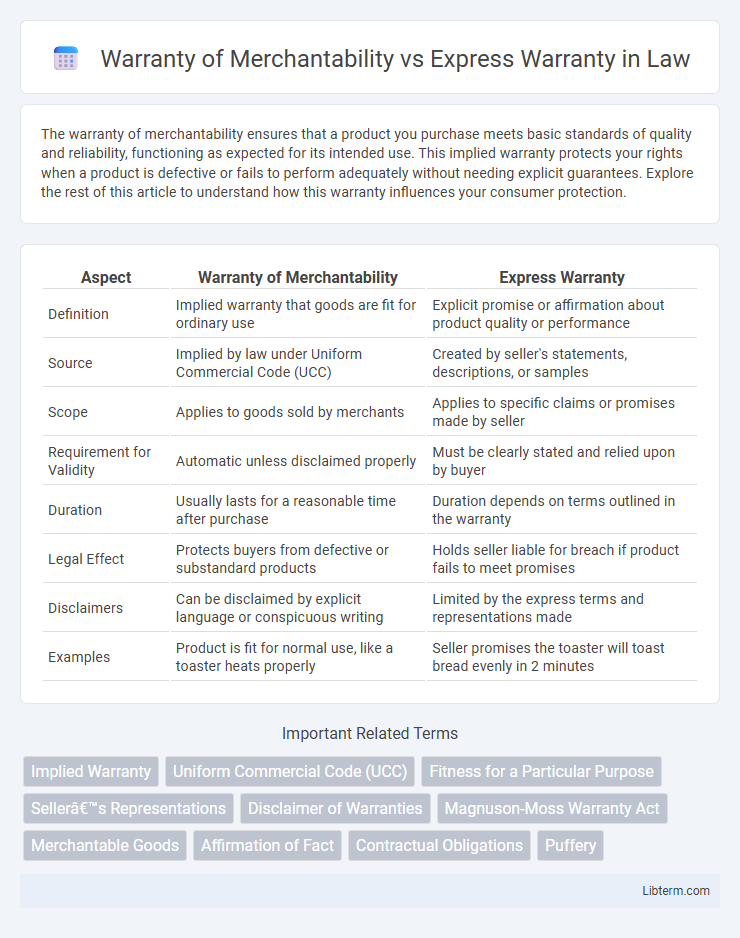
| Aspect | Warranty of Merchantability | Express Warranty |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Implied warranty that goods are fit for ordinary use | Explicit promise or affirmation about product quality or performance |
| Source | Implied by law under Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) | Created by seller's statements, descriptions, or samples |
| Scope | Applies to goods sold by merchants | Applies to specific claims or promises made by seller |
| Requirement for Validity | Automatic unless disclaimed properly | Must be clearly stated and relied upon by buyer |
| Duration | Usually lasts for a reasonable time after purchase | Duration depends on terms outlined in the warranty |
| Legal Effect | Protects buyers from defective or substandard products | Holds seller liable for breach if product fails to meet promises |
| Disclaimers | Can be disclaimed by explicit language or conspicuous writing | Limited by the express terms and representations made |
| Examples | Product is fit for normal use, like a toaster heats properly | Seller promises the toaster will toast bread evenly in 2 minutes |
Introduction to Warranties in Sales
In sales, warranties guarantee the quality and reliability of products, protecting buyers by setting expectations. The warranty of merchantability ensures that a product meets ordinary standards and is fit for general use, implied by law in most sales contracts. Express warranties, created through explicit promises or descriptions by the seller, offer specific guarantees about product performance or features beyond standard quality.
Defining the Warranty of Merchantability
The Warranty of Merchantability guarantees that a product will meet ordinary standards and function as expected for its typical purpose, ensuring it is fit for sale and use. It is an implied warranty under the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) that applies automatically to goods sold by merchants. In contrast, an Express Warranty is explicitly stated by the seller, detailing specific promises or representations about the product's quality or performance.
Understanding Express Warranties
Express warranties are explicit promises made by a seller regarding the quality, condition, or performance of a product, often stated in writing or verbally to assure buyers of specific attributes. Unlike the implied warranty of merchantability, which guarantees that a product meets basic standards of quality and functionality, express warranties provide clear, detailed commitments tailored to the item sold. Understanding express warranties is crucial because they create legally binding obligations that can override general expectations and directly influence consumer protection and product liability claims.
Key Differences: Merchantability vs Express Warranty
Warranty of merchantability guarantees that a product is fit for ordinary use, meeting basic quality and performance standards implied by law. Express warranty involves specific promises or affirmations made by the seller about the product's characteristics or functionality, explicitly stated in writing or verbally. The key difference lies in merchantability being an implied warranty covering general condition, while express warranty is a clearly defined, intentional assurance regarding particular attributes or performance.
Legal Basis: UCC and Warranty Law
The Warranty of Merchantability, governed by the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) Section 2-314, implies that goods sold by a merchant meet basic quality standards and are fit for ordinary use, even without explicit statements. In contrast, an Express Warranty arises from the seller's specific promises or affirmations about the product, as outlined in UCC Section 2-313, creating legally binding commitments based on clear representations. Both warranties operate within warranty law but differ primarily in their formation: implied by law versus expressly stated by the seller.
Common Scenarios Involving Both Warranties
Common scenarios involving both warranty of merchantability and express warranty often arise in the sale of consumer goods where the seller guarantees product quality and specific features. For example, a buyer purchasing electronics may receive an express warranty promising a one-year repair service, while the merchantability warranty ensures the product is fit for ordinary use and free from defects. Disputes frequently occur when products fail to meet the express warranty's explicit promises or when they do not conform to the basic standards of merchantability implied by law.
Limitations and Exclusions of Each Warranty
The Warranty of Merchantability guarantees that a product will function as expected for a reasonable period but often includes limitations such as implied conditions of suitability that do not cover all defects or unusual uses. Express Warranty, explicitly stated by the seller or manufacturer, may include specific promises or performance standards but is subject to exclusions like damages from misuse or unauthorized modifications. Both warranties can be limited by disclaimers or time constraints under Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) provisions, affecting the scope and duration of legal protections for buyers.
Consumer Rights and Remedies
The Warranty of Merchantability guarantees that a product will function as expected for ordinary purposes, providing consumers protection if the item is defective or fails to meet basic standards. Express Warranty involves specific promises or affirmations made by the seller regarding the product's quality or performance, directly influencing consumer expectations and legal remedies. Consumers can seek remedies such as repair, replacement, or refund under both warranties, with express warranties often providing clearer grounds for claims due to documented assurances.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Warranty of Merchantability guarantees that products sold by merchants meet basic quality and functionality standards expected in the marketplace, such as a used car being operable. Express Warranty involves explicit, written or verbal promises about a product's specific qualities or performance, like a smartphone manufacturer assuring battery life of 24 hours. In real-world cases, a seller failing to fix a defective appliance under express warranty (e.g., Walmart's faulty washers) contrasts with courts enforcing merchantability when a sold vehicle repeatedly breaks down despite no explicit promises being made.
Tips for Buyers and Sellers on Navigating Warranties
Buyers should carefully review express warranty terms, ensuring clear documentation of product promises beyond the implied Warranty of Merchantability, which guarantees basic product functionality. Sellers must disclose any limitations or conditions related to express warranties to avoid legal disputes and enhance customer trust. Maintaining detailed records of warranties and communications aids both parties in resolving issues efficiently and protecting their rights.
Warranty of Merchantability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com