Joint Tenancy is a legal property ownership arrangement where two or more individuals share equal rights and responsibilities with a right of survivorship, meaning that upon the death of one owner, their interest automatically transfers to the surviving joint tenants. This structure helps avoid probate and ensures seamless ownership transition, making it popular among couples, family members, and business partners. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Joint Tenancy can impact your property rights and financial planning.
Table of Comparison
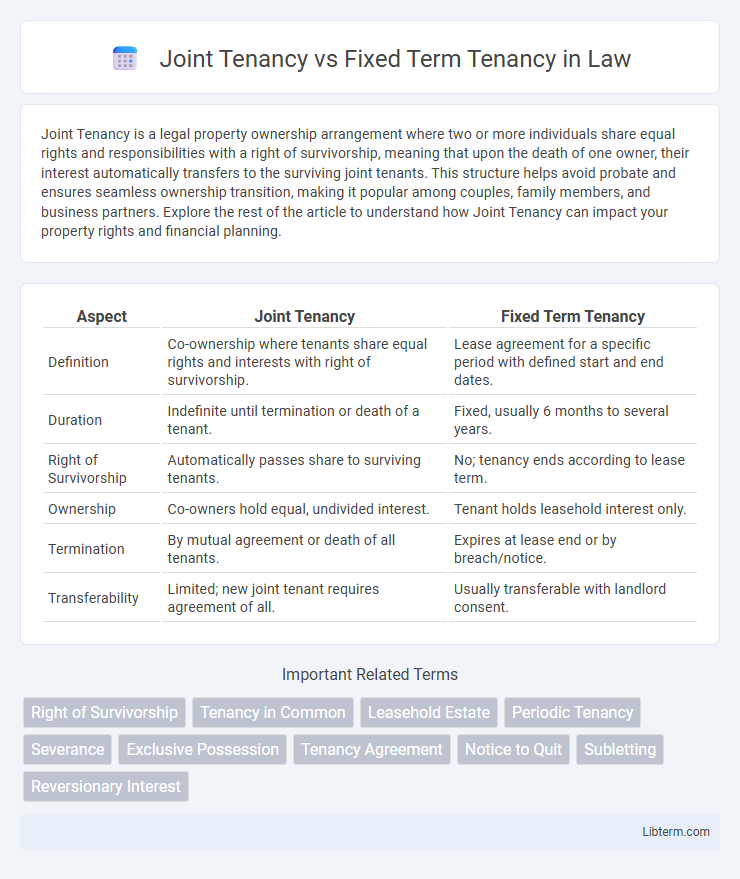
| Aspect | Joint Tenancy | Fixed Term Tenancy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Co-ownership where tenants share equal rights and interests with right of survivorship. | Lease agreement for a specific period with defined start and end dates. |
| Duration | Indefinite until termination or death of a tenant. | Fixed, usually 6 months to several years. |
| Right of Survivorship | Automatically passes share to surviving tenants. | No; tenancy ends according to lease term. |
| Ownership | Co-owners hold equal, undivided interest. | Tenant holds leasehold interest only. |
| Termination | By mutual agreement or death of all tenants. | Expires at lease end or by breach/notice. |
| Transferability | Limited; new joint tenant requires agreement of all. | Usually transferable with landlord consent. |
Overview of Joint Tenancy and Fixed Term Tenancy
Joint Tenancy is a form of property co-ownership where two or more individuals hold equal shares with rights of survivorship, meaning that upon the death of one tenant, their interest automatically passes to the surviving tenants. Fixed Term Tenancy, also known as a tenancy for a set period, involves a lease agreement that lasts for a specified duration, granting tenants possession for the agreed term with defined start and end dates. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for managing property rights, rent obligations, and succession in residential or commercial lease agreements.
Key Differences Between Joint and Fixed Term Tenancy
Joint Tenancy involves multiple tenants sharing equal rights and responsibilities over a property, with the right of survivorship allowing co-tenants to automatically inherit a deceased tenant's share. Fixed Term Tenancy specifies a lease agreement for a set period, granting the tenant exclusive possession during that time while obligating the landlord to provide accommodation for the agreed duration. Unlike Joint Tenancy, Fixed Term Tenancy does not imply shared ownership or automatic transfer upon death, focusing instead on time-bound occupancy and contractual obligations.
Legal Definitions and Frameworks
Joint Tenancy is a form of property ownership where two or more individuals hold equal shares with rights of survivorship, governed by property laws that emphasize unity of possession, interest, title, and time. Fixed Term Tenancy refers to a leasehold agreement for a specified period, defined by landlord-tenant laws that outline contract duration, renewal terms, and termination conditions. Legal frameworks for Joint Tenancy protect co-owners' rights upon death, while Fixed Term Tenancy regulations prioritize tenant protections and lease enforcement within the specified term.
Rights and Responsibilities of Tenants
Joint tenancy tenants share equal rights and responsibilities, including the right of survivorship, where the interest automatically passes to the surviving tenants upon death. Fixed term tenancy tenants have a defined lease period with specific obligations, such as timely rent payment and property maintenance, enforceable only during the lease term. Both tenancy types require tenants to uphold property care, but joint tenants have mutual co-ownership rights, while fixed term tenants hold leasehold interests limited to the contract duration.
Landlord Obligations Under Each Tenancy Type
Landlords under joint tenancy must maintain a single lease agreement covering all tenants, ensuring shared responsibility for rent and property upkeep among co-tenants. Fixed term tenancy requires landlords to honor agreed-upon lease durations while fulfilling obligations such as property maintenance, timely repairs, and adherence to notice periods for termination. Compliance with local housing laws and clear communication of tenant rights remain essential under both tenancy types to avoid disputes and ensure tenant satisfaction.
Ending or Terminating the Tenancy
Joint Tenancy ends when one tenant serves notice or breaches the lease terms, resulting in termination for all parties involved according to the lease agreement and local tenancy laws. Fixed Term Tenancy automatically terminates at the end of the specified lease period, unless both landlord and tenant agree to renew or extend the contract. Early termination of Fixed Term Tenancy may involve penalties or require mutual consent, defined by the lease terms and jurisdictional regulations.
Rent Payments and Financial Liabilities
In Joint Tenancy, all tenants share equal responsibility for rent payments, making each individual fully liable for the entire amount if others default. Fixed Term Tenancy establishes a set rental period with agreed-upon payments, where the tenant signing the contract is primarily accountable for fulfilling the rent obligations. Financial liabilities in Joint Tenancy extend to shared debts and obligations related to the property, whereas in Fixed Term Tenancy, liabilities are confined to the contractual term and amount specified in the lease agreement.
Pros and Cons of Joint Tenancy
Joint tenancy offers equal ownership rights, allowing each tenant to have undivided interest and survivorship rights, meaning the property automatically passes to the surviving tenants without probate. However, joint tenancy can complicate decision-making since all parties must agree on property use or sale, and one tenant's financial troubles or actions can impact the entire ownership. Unlike fixed term tenancy, joint tenancy lacks fixed lease duration, which provides flexibility but also less certainty for the parties involved.
Pros and Cons of Fixed Term Tenancy
Fixed Term Tenancy offers tenants security with a guaranteed lease duration, ensuring stable housing and predictable rent payments. However, it limits flexibility as tenants must commit to the entire lease period, potentially incurring penalties for early termination. Landlords benefit from consistent income during the term but may face challenges if market rates rise or tenant needs change.
Choosing the Right Tenancy Option
Choosing between joint tenancy and fixed term tenancy depends on the tenants' long-term goals and legal considerations. Joint tenancy offers co-ownership with survivorship rights, suitable for those seeking shared ownership and automatic transfer of the lease upon a tenant's death. Fixed term tenancy provides a clear, time-bound lease agreement, ideal for tenants requiring stability and defined rental periods without shared ownership complexities.
Joint Tenancy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com