A lessee is an individual or entity who rents or leases property from a lessor for a specified period under agreed terms. Understanding your rights and responsibilities as a lessee ensures proper management of lease agreements and protects your interests during tenancy. Dive deeper into the article to learn everything you need to know about being a lessee.
Table of Comparison
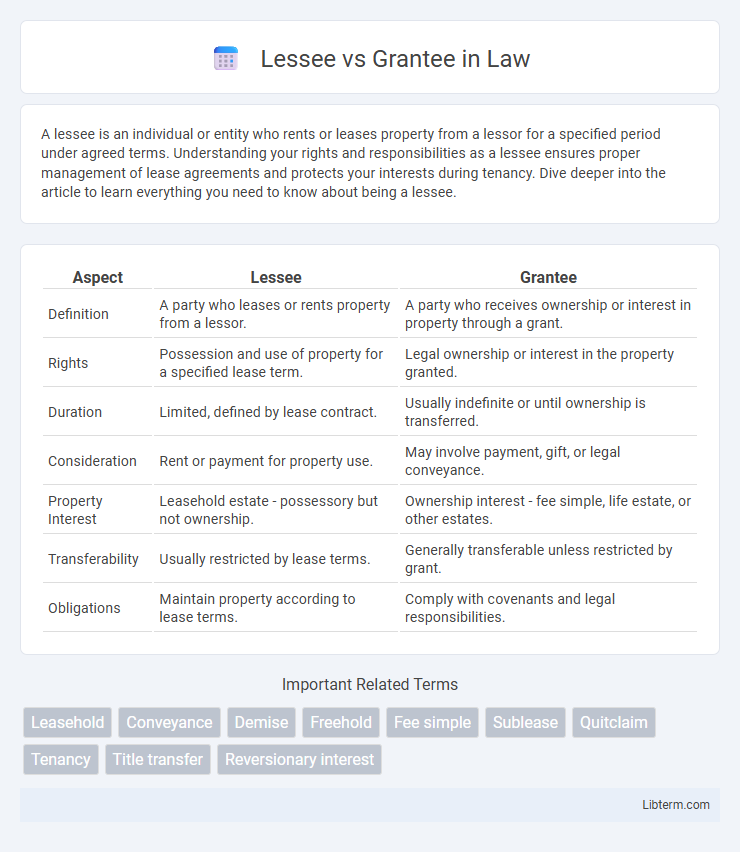
| Aspect | Lessee | Grantee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A party who leases or rents property from a lessor. | A party who receives ownership or interest in property through a grant. |
| Rights | Possession and use of property for a specified lease term. | Legal ownership or interest in the property granted. |
| Duration | Limited, defined by lease contract. | Usually indefinite or until ownership is transferred. |
| Consideration | Rent or payment for property use. | May involve payment, gift, or legal conveyance. |
| Property Interest | Leasehold estate - possessory but not ownership. | Ownership interest - fee simple, life estate, or other estates. |
| Transferability | Usually restricted by lease terms. | Generally transferable unless restricted by grant. |
| Obligations | Maintain property according to lease terms. | Comply with covenants and legal responsibilities. |
Understanding the Terms: Lessee and Grantee
A lessee is an individual or entity that obtains the right to use and occupy property through a lease agreement, typically for a specified period while paying rent to the lessor. A grantee, on the other hand, is the recipient of ownership interest or title to property conveyed through a deed or grant. Understanding the distinctions between lessee and grantee is crucial in property law, as the lessee holds possessory rights without ownership, whereas the grantee acquires legal ownership rights.
Legal Definitions of Lessee and Grantee
A lessee is an individual or entity granted the right to use and occupy real property under a lease agreement, typically for a specified period and rent payment, without ownership transfer. A grantee is the recipient of ownership rights in real property through a deed or conveyance, obtaining full title or interest from the grantor. Legal distinctions hinge on the lessee's possession rights limited by lease terms versus the grantee's ownership rights subject to deed conditions.
Key Differences Between Lessee and Grantee
A lessee holds a leasehold interest, granting them temporary possession and use of a property under a lease agreement, whereas a grantee receives ownership rights through a deed transfer, making them the legal owner. The lessee's rights are limited by the lease terms and duration, while the grantee typically acquires full title and control over the property. Lessees have rights protected by landlord-tenant law, but grantees are subject to real property laws related to ownership and conveyance.
Rights and Obligations of a Lessee
A lessee holds the right to possess and use leased property for a specified term while bearing the obligation to pay rent and maintain the property in good condition. Unlike a grantee, who acquires ownership rights, a lessee's interests are limited to lease terms without transferring title. Lessees must comply with lease agreements, ensuring proper use and timely payments to avoid breaches or eviction.
Rights and Obligations of a Grantee
A grantee holds title to real property, granting them the right to possess, use, and transfer the property according to the deed's terms, unlike a lessee who only obtains a temporary right to use. The grantee is obligated to comply with deed restrictions, pay property taxes, and maintain the property's condition as specified in the deed or local laws. Ownership responsibilities and rights of the grantee include securing clear title and defending against any claims or easements that may affect the property.
Types of Agreements Involving Lessees vs Grantees
Lessee agreements primarily involve lease contracts where the lessee obtains temporary possession and use of property, typically real estate or equipment, under specified terms and rent payments. Grantee agreements encompass deeds and transfer documents where the grantee receives ownership rights or title to property or assets from the grantor, usually without recurring payments. Understanding the distinction in agreement types is essential to determine rights, obligations, and duration for lessees versus grantees in property transactions.
Duration and Termination: Lessee vs Grantee
The duration of a lessee's interest is typically temporary, defined by a lease agreement specifying exact start and end dates, with termination occurring upon lease expiration or breach of contract. In contrast, a grantee receives a more permanent interest, often owning the property outright or for a defined estate, with termination only through sale, transfer, or legal forfeiture. Lessee rights are limited and revert to the lessor after termination, while grantee rights usually continue indefinitely until the holder decides to convey or relinquish ownership.
Transferability of Interests: Lessee and Grantee
A lessee holds a leasehold interest that is typically transferable through assignment or subleasing but remains subject to the landlord's consent and lease terms. A grantee receives a full estate or interest in property through a deed, granting greater transferability and control, often without requiring additional approvals. Transferability of a lessee's interest is more limited compared to a grantee's more comprehensive property rights.
Common Legal Issues and Disputes
Lessee and grantee often face common legal issues such as unclear property boundaries, disputes over possession rights, and conflicting lease or deed terms. Conflicts may arise from ambiguous language in lease agreements or deeds, leading to disagreements over the extent of property rights or obligations. Resolving these disputes frequently involves interpreting contract provisions, reviewing property titles, and adhering to state-specific real estate laws.
Choosing Between a Lease and a Grant: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a lessee and a grantee involves evaluating the duration and type of property rights desired; a lease grants temporary possession and use, while a grant confers permanent ownership or interest. Factors such as control over the property, legal responsibilities, and the intended length of use influence whether a lease agreement or a deed of grant is appropriate. Financial implications, including rent payments versus one-time transfer costs, also play a crucial role in deciding the optimal arrangement.
Lessee Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com