Forming a well-informed opinion requires understanding multiple perspectives and evaluating evidence critically. Your ability to articulate and defend your viewpoint strengthens communication and decision-making skills. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your insight into developing and expressing thoughtful opinions.
Table of Comparison
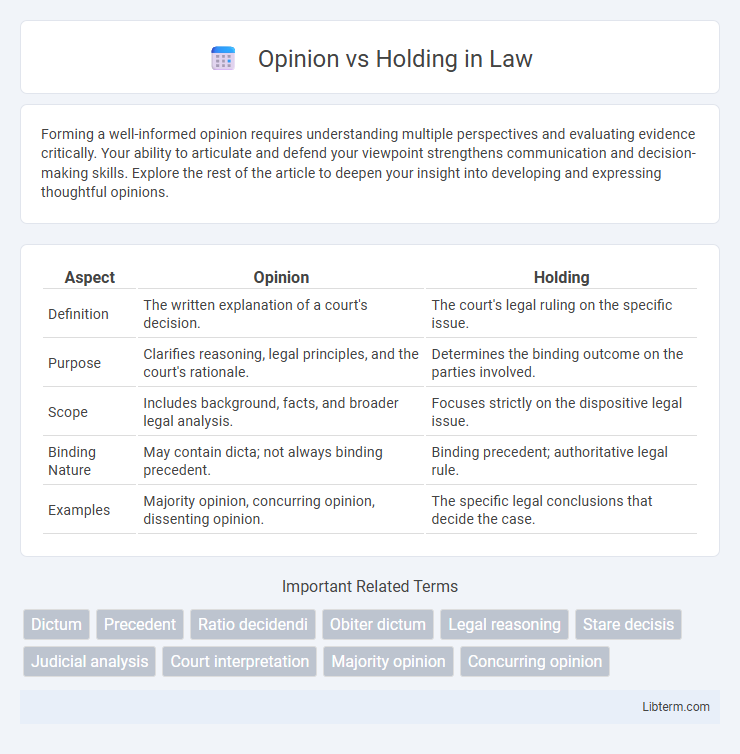
| Aspect | Opinion | Holding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The written explanation of a court's decision. | The court's legal ruling on the specific issue. |
| Purpose | Clarifies reasoning, legal principles, and the court's rationale. | Determines the binding outcome on the parties involved. |
| Scope | Includes background, facts, and broader legal analysis. | Focuses strictly on the dispositive legal issue. |
| Binding Nature | May contain dicta; not always binding precedent. | Binding precedent; authoritative legal rule. |
| Examples | Majority opinion, concurring opinion, dissenting opinion. | The specific legal conclusions that decide the case. |
Defining Opinion and Holding
An opinion is the written explanation issued by a judge or a panel of judges that outlines the reasoning behind the court's decision in a case. The holding is the legal principle or rule derived from the opinion that directly resolves the specific issue before the court. Distinguishing the holding from the broader opinion is essential for understanding binding precedent in case law.
Key Differences Between Opinion and Holding
Opinion and holding are fundamental components of judicial decisions with distinct roles and implications. The opinion encompasses the court's entire written explanation, including background, legal reasoning, and conclusions, providing the context and rationale behind the ruling. The holding, on the other hand, is the precise legal principle or rule derived from the opinion that directly resolves the issue before the court, serving as the binding precedent for future cases.
The Role of Opinion in Legal Decisions
The opinion in legal decisions provides the detailed reasoning and legal principles applied by the court to arrive at its judgment, offering guidance for future cases and clarifying how the law should be interpreted. It encompasses the court's analysis, interpretation of statutes, and application of precedent, distinguishing it from the holding, which is the binding legal rule derived from the opinion. The opinion plays a critical role in the development of case law by shaping judicial reasoning and influencing how similar cases are decided.
The Significance of a Holding
A holding is the court's definitive legal ruling resolving the issues in a case and establishing binding precedent for future cases. Unlike an opinion, which includes the rationale, background, and commentary, the holding is the essential rule derived directly from the judgment. The significance of a holding lies in its authoritative guidance for lower courts and litigants, shaping the interpretation and application of the law beyond the specific facts of the case.
How Courts Formulate Opinions
Courts formulate opinions by thoroughly analyzing facts, legal issues, and relevant precedents to articulate their reasoning behind a decision. The opinion includes the holding, which is the court's formal ruling on the specific legal question presented. The holding serves as the binding precedent, while other parts of the opinion may contain dicta, which are explanatory remarks not essential to the decision.
Precedential Value: Opinion vs Holding
A court's holding carries binding precedential value, establishing a legal rule that lower courts must follow in future cases, while an opinion includes the court's reasoning and commentary without necessarily being binding. The holding defines the core legal principle decided, whereas other statements in the opinion may be considered dicta and hold persuasive but non-binding authority. Understanding the distinction ensures accurate application of case law in legal analysis and decision-making.
Common Misconceptions Explained
Opinion refers to a judge's detailed explanation of the reasoning behind a court's decision, while holding is the legal principle or rule derived from that decision which serves as binding precedent. Common misconceptions often confuse opinions with dicta, mistakenly treating non-binding commentary as precedent, or misinterpret holdings as the entirety of the opinion rather than the specific legal rule. Clarifying these distinctions ensures accurate application of case law in legal research and argumentation.
Real-World Examples in Case Law
In case law, an opinion is the written explanation provided by a judge outlining the reasoning behind their decision, while the holding represents the court's actual ruling or legal principle established by the case. For example, in Brown v. Board of Education (1954), the opinion detailed the psychological and social implications of segregation, whereas the holding declared that state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students were unconstitutional. This distinction is critical for legal professionals as the holding sets precedent binding future courts, while the opinion offers interpretative guidance and context.
Why Distinguishing Matters in Legal Practice
Distinguishing between opinion and holding is crucial in legal practice because a holding establishes binding precedent, while an opinion includes broader commentary that is persuasive but not mandatory. Accurate identification of holdings ensures lawyers rely on authoritative rulings to develop case strategies and draft compelling arguments. Misinterpreting dicta as binding precedent can lead to flawed legal reasoning and jeopardize case outcomes.
Practical Tips for Law Students and Attorneys
Holding defines the court's legal decision essential for case precedent, while opinion explains the reasoning supporting that decision, offering interpretive insights. Law students and attorneys should pinpoint the holding to understand binding authority and analyze the opinion to grasp judicial rationale. Mastering this distinction enhances brief writing, legal analysis, and effective argumentation in practice.
Opinion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com