Corporate laws govern the formation, operation, and dissolution of corporations, ensuring legal compliance and protection for shareholders and stakeholders. These regulations cover aspects such as corporate governance, fiduciary duties, mergers and acquisitions, and dispute resolution. Explore the article to understand how corporate laws can impact your business decisions and corporate strategy.
Table of Comparison
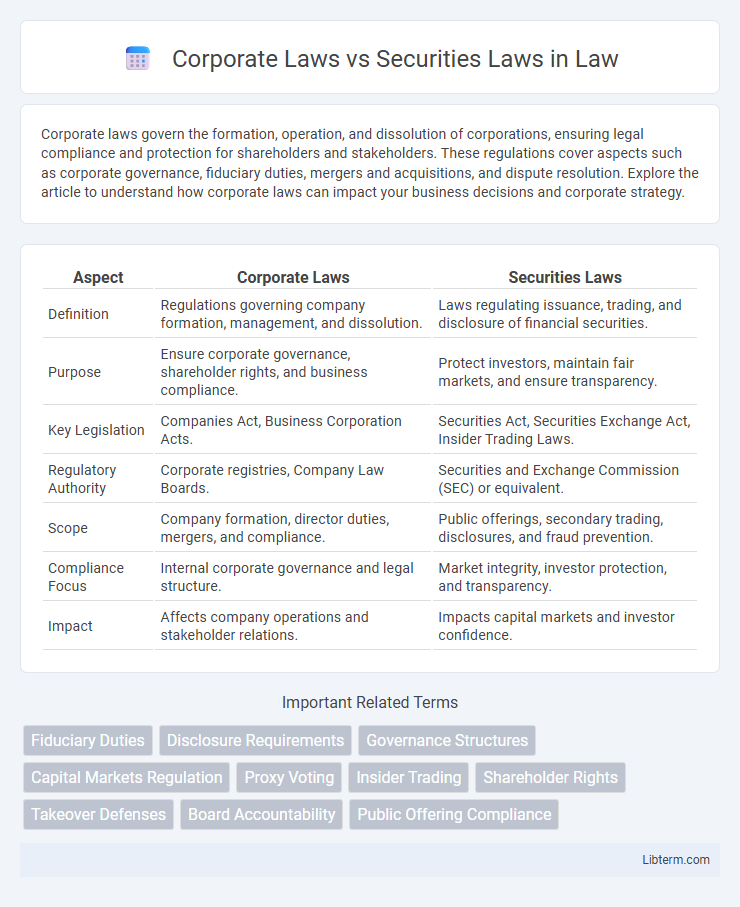
| Aspect | Corporate Laws | Securities Laws |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regulations governing company formation, management, and dissolution. | Laws regulating issuance, trading, and disclosure of financial securities. |
| Purpose | Ensure corporate governance, shareholder rights, and business compliance. | Protect investors, maintain fair markets, and ensure transparency. |
| Key Legislation | Companies Act, Business Corporation Acts. | Securities Act, Securities Exchange Act, Insider Trading Laws. |
| Regulatory Authority | Corporate registries, Company Law Boards. | Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or equivalent. |
| Scope | Company formation, director duties, mergers, and compliance. | Public offerings, secondary trading, disclosures, and fraud prevention. |
| Compliance Focus | Internal corporate governance and legal structure. | Market integrity, investor protection, and transparency. |
| Impact | Affects company operations and stakeholder relations. | Impacts capital markets and investor confidence. |
Introduction to Corporate Laws and Securities Laws
Corporate laws govern the formation, operation, and dissolution of corporations, focusing on the rights and duties of shareholders, directors, and officers to ensure lawful business conduct. Securities laws regulate the issuance, trading, and disclosure of financial instruments like stocks and bonds, aiming to protect investors and maintain market integrity. Both sets of laws interact to create a comprehensive legal framework that supports transparent corporate governance and efficient capital markets.
Defining Corporate Laws: Scope and Purpose
Corporate laws govern the formation, operation, and dissolution of companies, outlining the rights and duties of shareholders, directors, and officers to ensure proper management and accountability. These laws regulate corporate governance frameworks, mergers and acquisitions, fiduciary duties, and compliance with statutory reporting requirements to protect stakeholders' interests. The primary purpose of corporate laws is to create a legal structure that facilitates business activities while minimizing conflicts and promoting transparency.
What Are Securities Laws? An Overview
Securities laws regulate the issuance, trading, and disclosure of financial instruments like stocks and bonds to protect investors and ensure market integrity. These laws require companies to provide accurate information through prospectuses and periodic filings with regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Enforcement mechanisms include registration requirements, anti-fraud provisions, and penalties for insider trading or market manipulation.
Key Differences Between Corporate and Securities Laws
Corporate laws primarily regulate the formation, governance, and dissolution of companies, establishing fiduciary duties, shareholder rights, and internal management protocols. Securities laws focus on the issuance, trading, and disclosure requirements of financial instruments to protect investors and maintain market integrity. The key difference lies in corporate laws governing organizational structure and control, while securities laws emphasize transparency and fairness in capital markets.
Regulatory Authorities: Comparing Governance Structures
Corporate laws are primarily governed by state agencies such as the Secretary of State and state corporate commissions, which oversee company formation, compliance, and internal governance. Securities laws fall under the jurisdiction of federal regulatory bodies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), responsible for market regulation, investor protection, and enforcement related to securities trading. The governance structures differ in scope, with corporate law focusing on organizational and operational rules within states, while securities law provides a broader, federal-level framework ensuring transparency and fairness in capital markets.
Corporate Laws: Impact on Business Structures
Corporate laws govern the formation, governance, and dissolution of business entities, directly influencing corporate structures such as corporations, partnerships, and limited liability companies (LLCs). These laws establish the legal framework for shareholder rights, board responsibilities, and compliance requirements, shaping how businesses organize internal operations and capital management. By defining fiduciary duties and organizational hierarchy, corporate laws ensure transparency and accountability within business structures.
Securities Laws: Protecting Investors and Markets
Securities laws play a critical role in protecting investors by ensuring transparency, fairness, and integrity within financial markets. These laws regulate the issuance, trading, and disclosure of securities, preventing fraud and insider trading through enforcement by agencies like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Effective securities regulation fosters investor confidence, supports capital formation, and promotes efficient market functioning globally.
Compliance Requirements: Corporate vs. Securities Laws
Corporate laws primarily mandate compliance with governance structures, fiduciary duties, and disclosure obligations to shareholders, ensuring transparency and accountability within the organization. Securities laws focus on regulating the issuance, trading, and registration of securities, requiring strict adherence to reporting standards and anti-fraud provisions to protect investors and maintain market integrity. Both frameworks emphasize disclosure but differ in scope, with corporate law centered on internal management and securities law targeting public investment activities.
Legal Challenges and Common Overlaps
Corporate laws regulate the formation, governance, and dissolution of corporations, ensuring compliance with fiduciary duties and shareholder rights, while securities laws focus on the issuance, trading, and disclosure of financial instruments to protect investors and maintain market integrity. Legal challenges often arise from overlapping jurisdictions, such as insider trading, proxy battles, and disclosure obligations, where both corporate governance and securities regulations apply simultaneously. Navigating these overlaps requires careful legal analysis to avoid conflicts between corporate responsibilities and securities compliance, particularly in mergers, acquisitions, and public offerings.
Conclusion: Navigating Corporate and Securities Law Frameworks
Navigating corporate and securities law frameworks requires a clear understanding of their distinct regulatory scopes: corporate laws govern the formation, governance, and fiduciary duties of companies, while securities laws regulate the issuance, trading, and disclosure requirements of financial instruments. Effective compliance involves coordinating legal strategies to address both the structural governance of corporations and the transparency and investor protection mandates of securities markets. Mastery of this dual regulatory landscape ensures robust corporate governance and mitigates risks associated with securities fraud and regulatory enforcement.
Corporate Laws Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com