Data forms the foundation of informed decision-making and drives innovation across industries by enabling pattern recognition and predictive analysis. Proper data management and analysis unlock valuable insights that enhance operational efficiency and competitive advantage. Discover how leveraging your data can transform business outcomes by reading the full article.
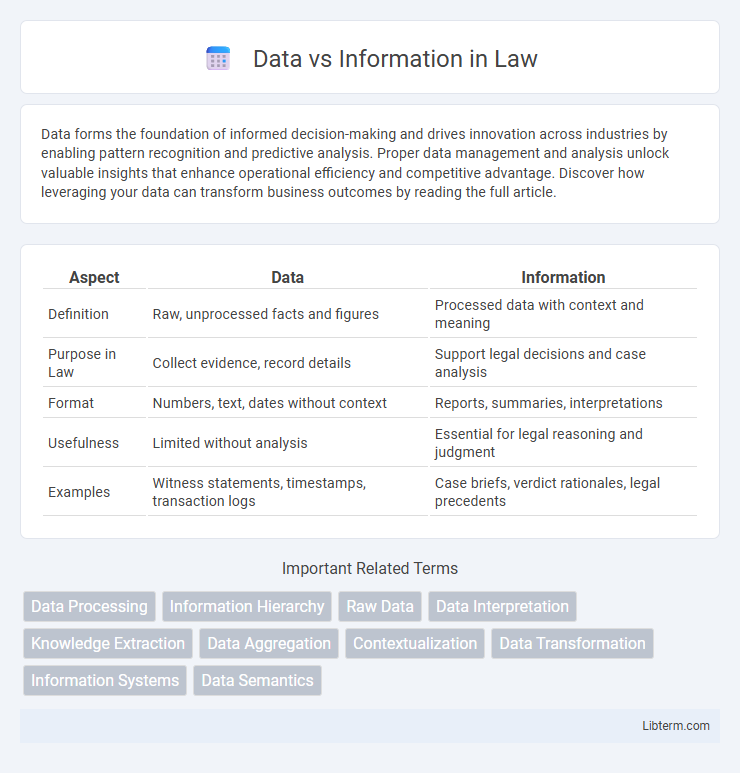
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Data | Information |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw, unprocessed facts and figures | Processed data with context and meaning |
| Purpose in Law | Collect evidence, record details | Support legal decisions and case analysis |
| Format | Numbers, text, dates without context | Reports, summaries, interpretations |
| Usefulness | Limited without analysis | Essential for legal reasoning and judgment |
| Examples | Witness statements, timestamps, transaction logs | Case briefs, verdict rationales, legal precedents |
Understanding Data: Definition and Characteristics
Data consists of raw, unprocessed facts and figures collected from various sources, lacking context or meaning on its own. It is characterized by its quantitative or qualitative nature, variability, and potential for storage in databases or spreadsheets. Transforming data into information requires interpretation, organization, and analysis to provide relevance and insight for decision-making.
What is Information? Key Features Explained
Information is organized and processed data that provides meaning and context, enabling decision-making and understanding. Key features include accuracy, relevance, timeliness, and completeness, which ensure the information is useful and reliable. It transforms raw data into valuable insights by highlighting patterns, relationships, and trends essential for strategic planning.
The Relationship Between Data and Information
Data consists of raw, unprocessed facts and figures that lack context, while information emerges when data is analyzed, organized, and interpreted to reveal meaningful patterns and insights. The transformation of data into information depends on the application of processes such as analysis, synthesis, and contextualization, enabling decision-making and knowledge creation. Effective data management and processing techniques enhance the accuracy and relevance of information derived from data inputs.
Data vs Information: Key Differences
Data consists of raw, unprocessed facts and figures without context, such as numbers, symbols, or observations. Information emerges when data is organized, processed, and interpreted to reveal meaning, patterns, or insights relevant to decision-making. The key difference lies in data being the input and information the meaningful output derived from analyzing data.
Real-World Examples: Data and Information in Action
Raw sales figures collected from an e-commerce platform represent data, while the analysis revealing a 20% increase in sales during a holiday season exemplifies information. Temperature readings taken hourly by weather stations are data; forecasting a storm based on these patterns transforms the data into actionable information. Social media likes and shares count as data, but identifying trending topics and user sentiment through these metrics becomes valuable information for marketers.
The Process: How Data Becomes Information
Data transforms into information through a systematic process of collection, organization, and analysis, where raw facts are filtered and contextualized to reveal meaningful patterns. Effective data processing involves cleaning, categorizing, and interpreting datasets using algorithms and statistical methods, enabling accurate decision-making. The quality and relevance of the processed data directly impact the value of the generated information, supporting strategic insights and operational efficiency.
Importance of Data Organization and Interpretation
Effective data organization and interpretation transform raw data into meaningful information, enabling accurate decision-making and strategic planning. Structured data categorization enhances retrieval efficiency and supports trend analysis, while insightful interpretation reveals patterns and correlations crucial for business intelligence. Proper handling of data ensures clarity, reduces errors, and maximizes its value in driving informed actions.
Data Quality vs Information Accuracy
Data quality refers to the condition of raw data, emphasizing completeness, consistency, and reliability, while information accuracy measures the correctness and truthfulness of processed data when interpreted for decision-making. High data quality ensures that datasets are error-free and relevant, directly impacting the level of information accuracy achieved during analysis. Maintaining strong data quality standards reduces the risk of inaccurate information, improving overall decision validity and organizational outcomes.
The Role of Technology in Data and Information Management
Technology enhances data and information management by enabling efficient data collection, storage, and processing through advanced databases and cloud computing platforms. It facilitates the transformation of raw data into actionable information via artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, improving decision-making accuracy. Robust cybersecurity measures integrated into technology protect the integrity and confidentiality of both data and information across digital ecosystems.
Choosing the Right: When to Use Data vs Information
Choosing between data and information depends on the context and purpose: use raw data when conducting detailed analysis, as it contains unprocessed facts necessary for generating insights. Opt for information when making decisions or communicating findings, since information is processed, structured, and meaningful, facilitating understanding and action. Organizations maximize efficiency by leveraging data for research and transforming it into information for strategic planning and operational use.
Data Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com