Eye witness accounts offer crucial, firsthand perspectives that can significantly impact the outcome of legal cases or historical events. Understanding the reliability and potential biases of these testimonies is essential for making informed judgments. Explore the rest of the article to learn how eye witness evidence shapes truth and justice in various contexts.
Table of Comparison
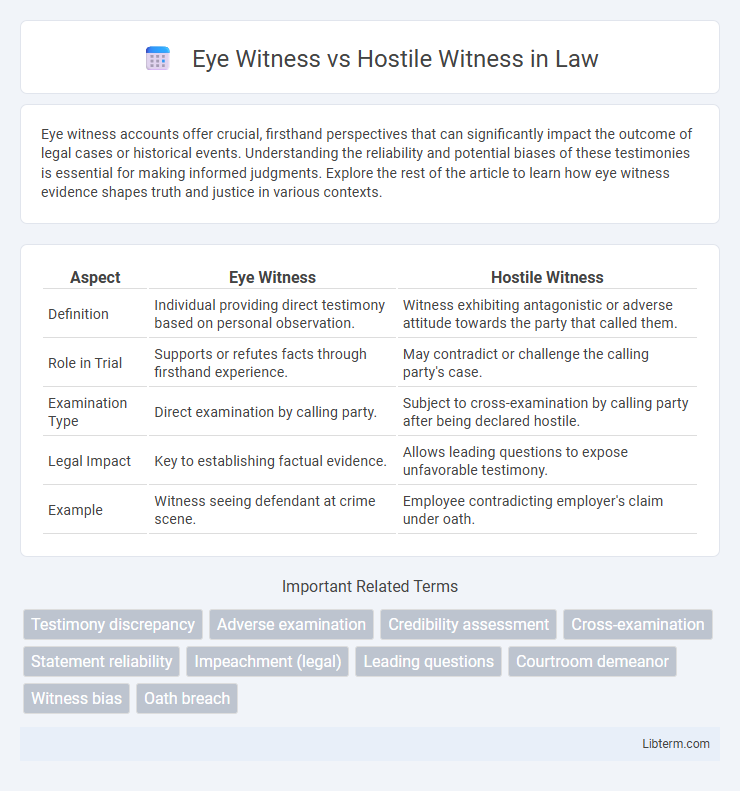
| Aspect | Eye Witness | Hostile Witness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual providing direct testimony based on personal observation. | Witness exhibiting antagonistic or adverse attitude towards the party that called them. |
| Role in Trial | Supports or refutes facts through firsthand experience. | May contradict or challenge the calling party's case. |
| Examination Type | Direct examination by calling party. | Subject to cross-examination by calling party after being declared hostile. |
| Legal Impact | Key to establishing factual evidence. | Allows leading questions to expose unfavorable testimony. |
| Example | Witness seeing defendant at crime scene. | Employee contradicting employer's claim under oath. |
Definition of Eye Witness and Hostile Witness
An eye witness is a person who directly observes an event, typically a crime or incident, and provides a firsthand account based on their sensory experience. A hostile witness is a witness whose testimony is adverse to the party that called them, often showing antagonism or unwillingness to cooperate during legal proceedings. Understanding the difference between these witness types is crucial for legal strategy and witness examination in court cases.
Key Differences Between Eye Witness and Hostile Witness
An eyewitness provides a firsthand account of an event or crime, offering direct observations relevant to the case, while a hostile witness is one who shows antagonism or unwillingness to cooperate during testimony, often contradicting their prior statements. Eyewitnesses are typically considered credible sources of information, whereas hostile witnesses may be challenged or impeached by opposing counsel due to their adversarial stance. The key difference lies in the witness's attitude and reliability, influencing how their testimony is received and weighted in court proceedings.
Legal Importance of Eye Witness Testimony
Eye witness testimony holds critical legal importance as it provides direct, firsthand accounts of events, often influencing the outcome of criminal and civil cases. In contrast, a hostile witness is one who shows antagonism or unwillingness to cooperate during testimony, potentially undermining the credibility of their statements. Courts heavily rely on the reliability and consistency of eye witness evidence to establish facts and support verdicts, making their accounts pivotal in the judicial process.
Role and Impact of Hostile Witness in Court
A hostile witness is a person called to testify who demonstrates opposition or unwillingness to cooperate with the party that called them, often contradicting expected testimony. Their role permits counsel to treat them as adversarial, allowing leading questions to challenge their statements effectively. The impact of a hostile witness in court can significantly influence a case by undermining credibility, introducing unexpected evidence, and providing the opposing side with opportunities to counter the original party's arguments.
Admissibility of Witness Testimonies
Eye witness testimonies are generally considered highly admissible in court due to their direct observation of the event, often providing crucial details that establish facts. Hostile witness testimonies, while admissible, require the examining party to demonstrate the witness's antagonistic stance, allowing for leading questions and potentially limiting the credibility of their statements. Courts evaluate the reliability and consistency of both types, but eye witness accounts tend to carry more weight in establishing factual accuracy unless challenged by evidence of bias or inconsistency.
Challenges Associated with Hostile Witnesses
Hostile witnesses pose significant challenges in legal proceedings due to their adversarial stance, often exhibiting reluctance or refusal to provide truthful or complete testimony. Their inconsistent statements and potential bias complicate fact-finding, requiring attorneys to employ strategic questioning and motions to overcome direct examination limitations. Effective handling demands thorough preparation and a nuanced understanding of witness credibility to mitigate the impact on case outcomes.
Cross-Examination Techniques for Hostile Witnesses
Cross-examination techniques for hostile witnesses involve aggressive questioning to challenge credibility and extract truthful information despite resistance. Lawyers use leading questions, controlled narratives, and impeachment methods to expose inconsistencies or bias that weaken the hostile witness's testimony. Strategic repetition and evidence confrontation help break down fabricated or evasive answers, turning a hostile witness's statements to the examiner's advantage.
Reliability and Credibility of Eye Witness Accounts
Eye witness accounts often provide crucial testimony but vary significantly in reliability due to factors such as stress, lighting, and memory distortion. Hostile witnesses, typically hostile to the party who called them, may offer less credible statements since their testimony can be biased or evasive. Evaluating eye witness reliability involves scrutinizing consistency, detail, and corroboration with physical evidence, while hostile witness credibility requires assessing motives and cross-examination effectiveness.
Protection and Rights of Witnesses in Legal Proceedings
Eye witnesses provide direct testimony about events or actions they personally observed, requiring legal protections to ensure their accurate and fearless participation, including confidentiality measures and protection from intimidation. Hostile witnesses, identified when their testimony opposes the calling party's interest, still retain rights such as protection from coercion and the right to counsel, ensuring their testimony is obtained fairly and without duress. Legal frameworks mandate safeguarding both types of witnesses to uphold judicial integrity, balancing witness security with the rights to a fair trial.
Implications for Justice: Eye Witness vs Hostile Witness
Eye witnesses provide firsthand accounts, often strengthening prosecutorial cases by offering direct observations of the event, which can significantly impact verdict accuracy. Hostile witnesses, who may display antagonism or reluctance, create challenges in extracting credible testimony, potentially leading to doubts about case reliability and fairness. The contrasting nature of these testimonies influences judicial outcomes by affecting jury perception, evidentiary weight, and the overall pursuit of justice.
Eye Witness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com