Sole ownership grants you complete control and responsibility over your property or business, allowing for streamlined decision-making without the need for partners. This form of ownership simplifies management but also means you bear all risks and liabilities personally. Explore the advantages and challenges of sole ownership in the rest of the article to understand if it aligns with your goals.
Table of Comparison
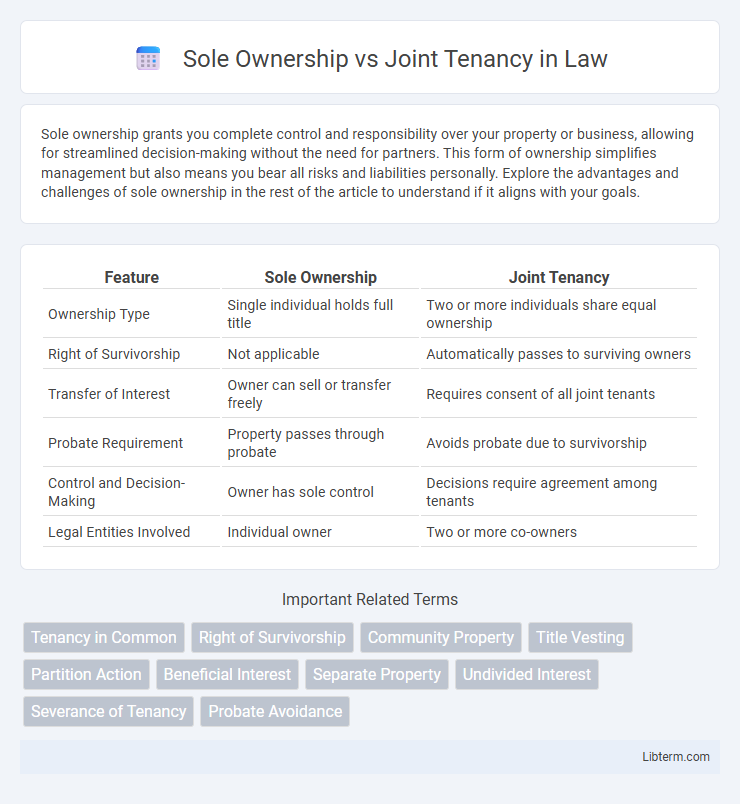
| Feature | Sole Ownership | Joint Tenancy |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership Type | Single individual holds full title | Two or more individuals share equal ownership |
| Right of Survivorship | Not applicable | Automatically passes to surviving owners |
| Transfer of Interest | Owner can sell or transfer freely | Requires consent of all joint tenants |
| Probate Requirement | Property passes through probate | Avoids probate due to survivorship |
| Control and Decision-Making | Owner has sole control | Decisions require agreement among tenants |
| Legal Entities Involved | Individual owner | Two or more co-owners |
Understanding Sole Ownership
Sole ownership grants one individual exclusive legal title to a property, providing complete control over its use, transfer, or sale without requiring consent from others. This form of ownership simplifies decision-making and minimizes potential disputes, making it ideal for individuals seeking full authority and responsibility over their assets. Unlike joint tenancy, sole ownership does not include rights of survivorship, so the property passes according to the owner's will or state inheritance laws upon death.
Defining Joint Tenancy
Joint tenancy is a form of property ownership where two or more individuals hold equal shares with rights of survivorship, meaning upon the death of one tenant, their interest automatically passes to the surviving tenants. This ownership structure requires the four unities of time, title, interest, and possession to be legally valid. Unlike sole ownership, joint tenancy prevents the deceased tenant's share from being inherited through a will, streamlining property succession among co-owners.
Key Differences Between Sole Ownership and Joint Tenancy
Sole ownership grants full control and responsibility of a property to one individual, allowing unrestricted rights to sell, lease, or transfer ownership without consent from others. Joint tenancy involves two or more owners sharing equal interests with survivorship rights, meaning upon an owner's death, their share automatically passes to the surviving tenants. The key differences include the legal transfer of ownership, the division of property shares, and the impact on estate planning, where sole ownership simplifies inheritance, whereas joint tenancy bypasses probate through automatic succession.
Legal Implications of Each Ownership Structure
Sole ownership grants an individual complete legal control over the property, enabling them to sell, mortgage, or bequeath the asset without requiring consent from others, but the property is subject to probate upon the owner's death. Joint tenancy includes the right of survivorship, meaning if one owner passes away, their interest automatically transfers to the surviving joint tenants, bypassing probate and simplifying the transfer process. Legal implications of joint tenancy also include potential vulnerability to creditors of any joint tenant, as their interest in the property can be seized to satisfy debts.
Rights and Responsibilities of Owners
Sole ownership grants one person full rights to possess, use, and transfer the property without needing consent from others, bearing all responsibilities including taxes, maintenance, and liabilities solely. Joint tenancy involves two or more owners sharing equal rights in possession and use, with each party responsible for their share of financial obligations and legal duties; survivorship rights ensure ownership automatically passes to remaining tenants upon death of one. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for managing property control, inheritance implications, and legal accountability effectively.
Impact on Property Transfer and Inheritance
Sole ownership allows a property to be transferred directly through a will, ensuring clear inheritance according to the owner's wishes, while joint tenancy includes the right of survivorship, automatically transferring ownership to surviving tenants without probate. Joint tenancy simplifies the inheritance process by bypassing courts, but limits individual control over the property transfer. Estate taxes and legal implications vary significantly between sole ownership and joint tenancy, affecting estate planning strategies.
Tax Considerations for Property Owners
Sole ownership enables property owners to report all income, deductions, and capital gains on their individual tax returns, simplifying tax filing but potentially increasing taxable income. Joint tenancy involves shared ownership where rental income, expenses, and capital gains must be allocated among co-owners based on their ownership interest, affecting each owner's tax liability. Understanding differences in estate tax implications and step-up basis rules is crucial, as joint tenancy may provide automatic rights of survivorship and favorable tax treatment upon the death of a co-owner.
Advantages of Sole Ownership
Sole ownership provides complete control over property decisions without requiring consent from others, simplifying transactions and management. It ensures that the owner has exclusive rights to income, benefits, and liabilities arising from the property. Sole ownership also enables straightforward transfer or sale, protecting an individual's assets in cases of divorce or business dissolution.
Benefits of Joint Tenancy
Joint tenancy offers key benefits such as the right of survivorship, allowing property to automatically pass to surviving co-owners without probate delays or costs. It promotes shared financial responsibility among tenants, which can ease mortgage payments and maintenance expenses. This ownership structure also simplifies estate management by avoiding complex probate procedures that sole ownership often requires.
Choosing the Best Ownership Structure for Your Needs
Sole ownership provides complete control and decision-making power over property, ideal for individuals seeking full autonomy without sharing responsibilities or liabilities. Joint tenancy offers equal ownership among partners, featuring the right of survivorship, which ensures the property passes directly to co-owners upon death, beneficial for couples or close associates. Assessing factors like control preferences, estate planning goals, liability concerns, and relationship dynamics helps determine the best ownership structure tailored to your needs.
Sole Ownership Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com