False imprisonment occurs when someone intentionally restricts another person's freedom of movement without legal justification. This unlawful restraint can happen through physical barriers, threats, or other forms of coercion. Understand the key elements and legal consequences of false imprisonment to protect Your rights and learn more in the full article.
Table of Comparison
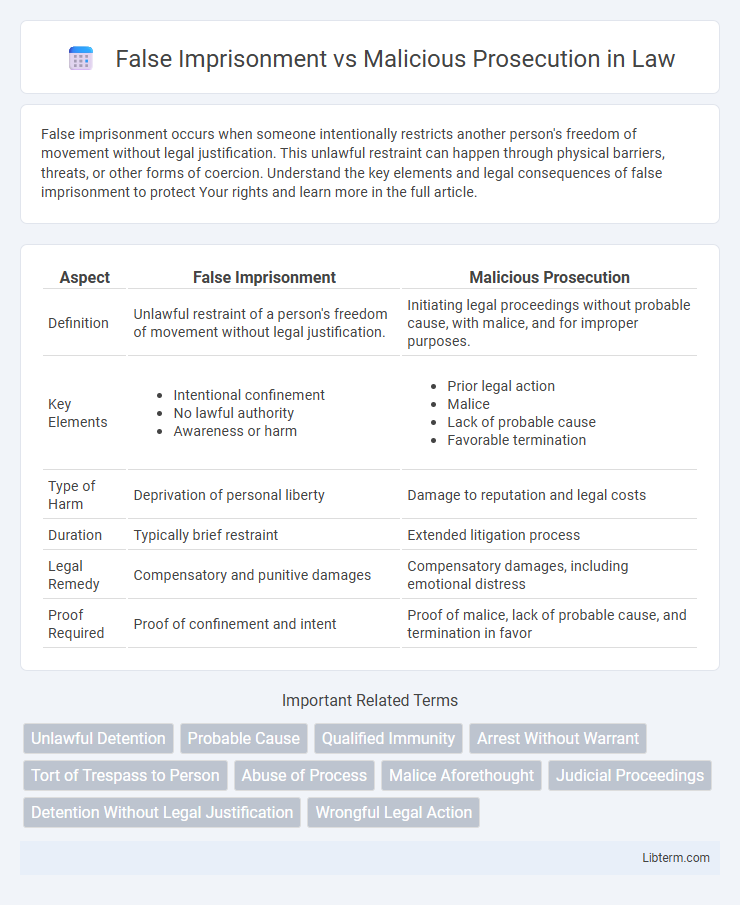
| Aspect | False Imprisonment | Malicious Prosecution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unlawful restraint of a person's freedom of movement without legal justification. | Initiating legal proceedings without probable cause, with malice, and for improper purposes. |
| Key Elements |
|
|
| Type of Harm | Deprivation of personal liberty | Damage to reputation and legal costs |
| Duration | Typically brief restraint | Extended litigation process |
| Legal Remedy | Compensatory and punitive damages | Compensatory damages, including emotional distress |
| Proof Required | Proof of confinement and intent | Proof of malice, lack of probable cause, and termination in favor |
Understanding False Imprisonment: Definition and Elements
False imprisonment involves the unlawful restraint of an individual's freedom of movement without legal authority or consent. Key elements include intentional confinement, lack of valid justification, and awareness of the confinement by the victim. Unlike malicious prosecution, false imprisonment centers on the physical restriction rather than initiating baseless legal action.
What Constitutes Malicious Prosecution? Key Legal Criteria
Malicious prosecution occurs when a legal action is initiated without probable cause, driven by malice rather than legitimate grounds, resulting in damage to the defendant. Key legal criteria include the termination of the prior proceeding in favor of the accused, absence of probable cause, improper purpose, and demonstrable harm caused by the prosecution. Courts require clear evidence that the original lawsuit or criminal charge was baseless and filed with wrongful intent to prove malicious prosecution.
Major Differences Between False Imprisonment and Malicious Prosecution
False imprisonment involves the unlawful restraint or confinement of a person without consent or legal authority, emphasizing the deprivation of physical liberty. Malicious prosecution targets the wrongful initiation or continuation of legal proceedings without probable cause, focusing on the abuse of judicial process rather than physical detention. Key distinctions include the nature of the harm--physical confinement versus legal harassment--and the requirement of a favorable termination of the prior case in malicious prosecution claims, which is absent in false imprisonment.
Legal Rights of Victims Under Each Tort
Victims of false imprisonment have the legal right to seek compensation for unlawful restraint or confinement without consent, emphasizing the protection of personal liberty. In cases of malicious prosecution, victims are entitled to damages for wrongful initiation of legal action conducted with malice and without probable cause, safeguarding their reputation and integrity. Both torts require proving specific elements, but false imprisonment centers on physical restraint, while malicious prosecution focuses on misuse of judicial processes.
Burden of Proof: Comparing Requirements for Each Claim
False imprisonment requires the plaintiff to prove unlawful restraint or confinement without legal justification, emphasizing the defendant's intent and absence of consent. Malicious prosecution demands showing the defendant initiated a legal action with malice and without probable cause, along with a favorable termination for the plaintiff. The burden of proof differs as false imprisonment centers on immediate physical restraint, while malicious prosecution focuses on wrongful initiation and conduct in judicial proceedings.
Common Defenses in False Imprisonment and Malicious Prosecution Cases
Common defenses in false imprisonment cases include consent, lawful authority, and probable cause, where the defendant argues that the detention was legally justified. In malicious prosecution cases, defenses often focus on lack of malice, probable cause for initiating the original proceedings, and the absence of a favorable termination for the plaintiff. Both claims require careful analysis of the intent and legality of the detention or prosecution actions to determine liability.
Real-Life Case Examples Highlighting Key Distinctions
False imprisonment involves unlawfully restraining a person's freedom of movement without legal authority, as seen in *People v. Lopez* (2018), where a store clerk detained a suspected shoplifter without probable cause. Malicious prosecution, exemplified by *Smith v. Jones* (2015), arises when legal action is initiated against someone without reasonable grounds and with malice, resulting in damages to the defendant. These cases highlight that false imprisonment centers on unlawful detention, while malicious prosecution addresses wrongful legal actions initiated with improper intent.
Remedies and Damages: What Victims Can Recover
Victims of false imprisonment can recover compensatory damages for loss of liberty, emotional distress, and physical harm, along with punitive damages if the conduct was egregiously wrongful. In malicious prosecution cases, remedies often include compensatory damages for reputational harm, legal expenses, emotional distress, and sometimes punitive damages to deter malicious intent. Both torts allow plaintiffs to seek restitution for attorney fees and lost income resulting from the wrongful actions.
Statute of Limitations: Filing Timelines for Each Claim
The statute of limitations for false imprisonment typically ranges from one to three years, varying by jurisdiction, and begins at the time the individual is unlawfully restrained. Malicious prosecution claims generally have a statute of limitations between one and two years, starting from the termination of the prior legal proceeding in favor of the plaintiff. Understanding these filing timelines is crucial to preserving the right to sue in each respective tort claim.
Choosing the Right Legal Action: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right legal action between false imprisonment and malicious prosecution hinges on the specific elements of each claim, where false imprisonment involves unlawful restraint without legal justification, while malicious prosecution requires proving initiation of a legal proceeding with malice and lack of probable cause. Key factors include the nature of the restraint, the presence of a legal process, and evidence of intent or malice by the defendant. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in selecting an effective legal strategy tailored to the facts of the case.
False Imprisonment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com