A Maintenance Covenant outlines the obligations of property owners to keep a building or infrastructure in good condition, ensuring safety and functionality over time. These agreements protect investments by specifying repair responsibilities and upkeep standards. Discover how understanding your Maintenance Covenant can help you manage property maintenance effectively by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
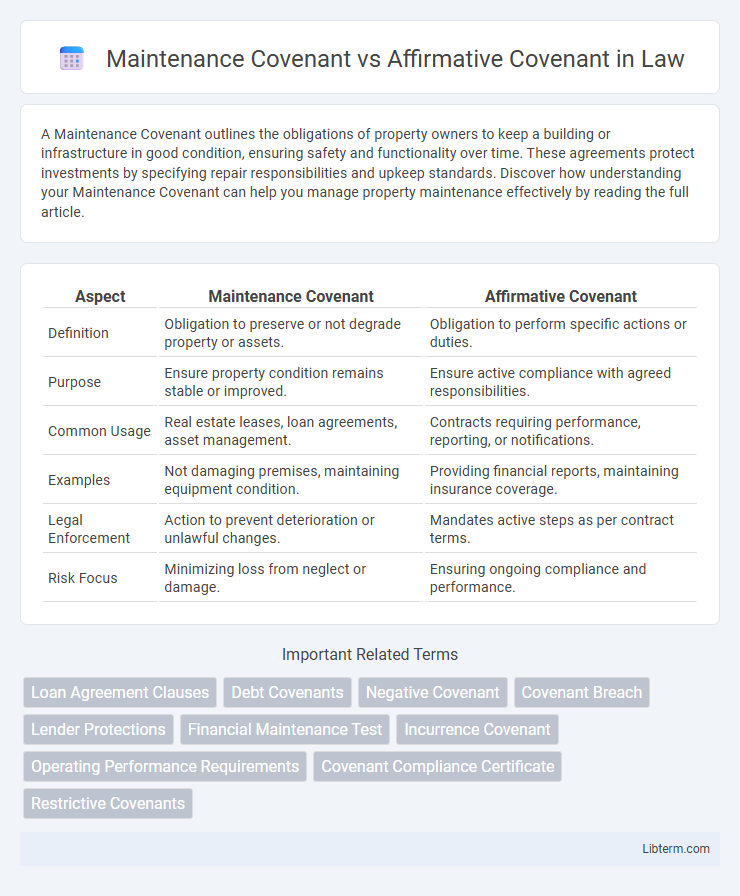
| Aspect | Maintenance Covenant | Affirmative Covenant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Obligation to preserve or not degrade property or assets. | Obligation to perform specific actions or duties. |
| Purpose | Ensure property condition remains stable or improved. | Ensure active compliance with agreed responsibilities. |
| Common Usage | Real estate leases, loan agreements, asset management. | Contracts requiring performance, reporting, or notifications. |
| Examples | Not damaging premises, maintaining equipment condition. | Providing financial reports, maintaining insurance coverage. |
| Legal Enforcement | Action to prevent deterioration or unlawful changes. | Mandates active steps as per contract terms. |
| Risk Focus | Minimizing loss from neglect or damage. | Ensuring ongoing compliance and performance. |
Introduction to Maintenance and Affirmative Covenants
Maintenance covenants require the borrower to uphold certain operational standards, such as maintaining insurance and preserving assets, ensuring the property's value and functionality over time. Affirmative covenants mandate specific actions that the borrower must perform, including timely financial reporting and regulatory compliance, to support transparent communication and risk management. Both types of covenants are critical in loan agreements to protect the lender's interests and ensure the ongoing viability of the financed asset.
Defining Maintenance Covenant
A Maintenance Covenant requires a borrower or lessee to uphold specific ongoing obligations, such as preserving property condition or meeting financial ratios, to maintain the value and operational status of the asset or agreement. In contrast, an Affirmative Covenant mandates positive actions or behaviors that must be performed, like submitting reports or paying taxes. Understanding the Maintenance Covenant is crucial for ensuring continuous compliance and protecting stakeholder interests throughout the contract term.
Understanding Affirmative Covenant
An Affirmative Covenant is a contractual obligation requiring a party to perform specific actions, such as maintaining property, paying taxes, or adhering to regulations, ensuring ongoing compliance with agreed terms. Unlike a Maintenance Covenant, which often focuses on preserving physical condition or operational standards, Affirmative Covenants encompass broader duties that promote the overall purpose and functionality of an agreement. Understanding Affirmative Covenants involves recognizing their role in enforcing proactive responsibilities that support long-term contractual goals and mitigate risks.
Key Differences Between Maintenance and Affirmative Covenants
Maintenance covenants require the borrower to preserve the condition of assets or operations, such as keeping equipment functional or maintaining insurance coverage, to protect the lender's collateral value. Affirmative covenants mandate specific actions or behaviors the borrower must undertake, like timely financial reporting, payment of taxes, or compliance with laws, ensuring ongoing operational and financial transparency. The key difference lies in maintenance covenants focusing on preserving current conditions, while affirmative covenants impose active obligations to fulfill certain duties.
Legal Implications of Maintenance Covenants
Maintenance covenants impose ongoing obligations on a party to preserve and maintain property or assets, ensuring compliance with specific standards to avoid breaches that could lead to legal disputes or damages claims. The legal implications of maintenance covenants include enforceability through remedial actions or penalties if the obligated party fails to uphold the required maintenance duties. Unlike affirmative covenants that mandate positive actions, maintenance covenants specifically focus on preserving existing conditions, making adherence critical to prevent contract violations and potential liability.
Legal Impact of Affirmative Covenants
Affirmative covenants legally require a party to perform specific actions, such as maintaining insurance or adhering to environmental regulations, ensuring ongoing compliance and operational standards. These obligations create enforceable duties that can lead to legal consequences like penalties or default if breached, directly impacting contractual relationships. Unlike maintenance covenants, which focus on preserving asset conditions, affirmative covenants impose proactive responsibilities crucial for risk management and investor protection.
Common Examples in Real Estate and Finance
Maintenance covenants in real estate commonly require property owners to keep buildings in good repair and comply with safety regulations, ensuring asset value preservation. Affirmative covenants in finance often mandate borrowers to provide financial statements, maintain insurance, and pay taxes on collateral, supporting lender protection. Both covenant types play critical roles in managing risk and ensuring ongoing compliance in lending and property agreements.
Benefits of Maintenance vs Affirmative Covenants
Maintenance covenants ensure a borrower upholds specific financial ratios and operational standards to maintain creditworthiness, providing lenders with ongoing risk control and early warning signals of financial distress. Affirmative covenants require borrowers to take certain positive actions, such as timely financial reporting or maintaining insurance, which safeguard lender interests by promoting transparency and operational diligence. The primary benefit of maintenance covenants lies in continuous financial monitoring, while affirmative covenants enhance trust through mandated proactive borrower compliance.
Risks and Challenges Associated with Each Covenant
Maintenance covenants impose ongoing obligations to preserve assets or financial ratios, creating risks of increased operational costs and potential breaches during economic downturns or unexpected expenses. Affirmative covenants require specific actions such as timely reporting and compliance measures, presenting challenges in maintaining consistent administrative oversight and regulatory adherence. Failure to meet maintenance covenants often triggers immediate loan default, while lapses in affirmative covenants typically lead to remedial steps but can escalate if unresolved, impacting borrower-creditor relationships and financial stability.
Choosing the Right Covenant for Your Agreement
Choosing the right covenant for your agreement depends on the specific obligations and restrictions you want to enforce. Maintenance covenants require the borrower to uphold certain financial ratios or operational standards throughout the loan term, ensuring ongoing compliance and financial health. Affirmative covenants mandate specific actions the borrower must take, such as providing regular financial reports or maintaining insurance, promoting transparency and risk management in the lending relationship.
Maintenance Covenant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com