A joint will is a single testamentary document signed by two individuals, typically spouses, outlining how their combined estates will be distributed upon both their deaths. This type of will is designed to simplify estate planning and ensure that assets pass directly to the surviving partner or designated beneficiaries without multiple separate wills. Explore the rest of the article to understand the benefits, drawbacks, and legal considerations of joint wills for your estate planning needs.
Table of Comparison
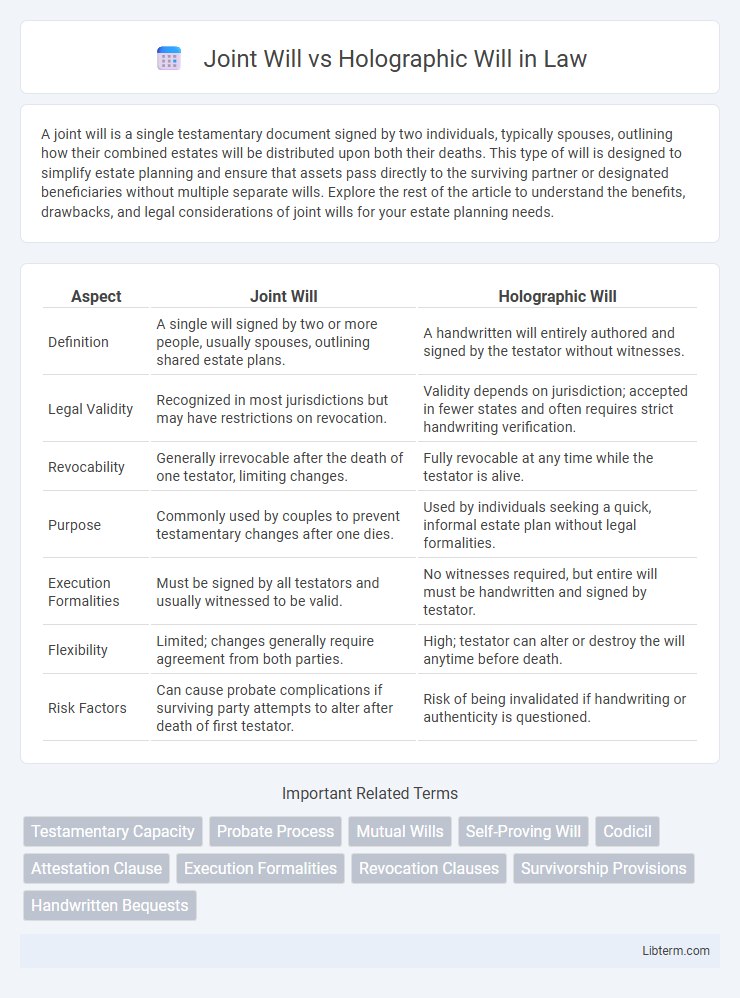
| Aspect | Joint Will | Holographic Will |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A single will signed by two or more people, usually spouses, outlining shared estate plans. | A handwritten will entirely authored and signed by the testator without witnesses. |
| Legal Validity | Recognized in most jurisdictions but may have restrictions on revocation. | Validity depends on jurisdiction; accepted in fewer states and often requires strict handwriting verification. |
| Revocability | Generally irrevocable after the death of one testator, limiting changes. | Fully revocable at any time while the testator is alive. |
| Purpose | Commonly used by couples to prevent testamentary changes after one dies. | Used by individuals seeking a quick, informal estate plan without legal formalities. |
| Execution Formalities | Must be signed by all testators and usually witnessed to be valid. | No witnesses required, but entire will must be handwritten and signed by testator. |
| Flexibility | Limited; changes generally require agreement from both parties. | High; testator can alter or destroy the will anytime before death. |
| Risk Factors | Can cause probate complications if surviving party attempts to alter after death of first testator. | Risk of being invalidated if handwriting or authenticity is questioned. |
Understanding Joint Wills: An Overview
Joint wills are a single legal document created and signed by two individuals, usually spouses, to outline the distribution of their combined estate after both pass away. Unlike holographic wills, which are handwritten and authored by a single person, joint wills cannot be easily altered once one party dies, ensuring a fixed plan for asset distribution. This binding nature makes joint wills a strategic choice for couples seeking mutual and irrevocable estate planning arrangements.
What Is a Holographic Will?
A holographic will is a handwritten and signed document created entirely by the testator without witnesses, recognized as valid in many jurisdictions if it meets specific legal requirements. Unlike joint wills, which are typically prepared by two individuals together and often designed to be irrevocable after one party's death, holographic wills offer greater flexibility and simplicity for individuals drafting their own testament. This type of will allows for personal, informal estate planning but requires careful adherence to local laws to ensure its enforceability.
Key Differences Between Joint Wills and Holographic Wills
Joint wills are a single document created and signed by two parties, typically spouses, expressing mutual testamentary intentions, while holographic wills are handwritten and signed solely by one individual without witnesses. Joint wills often include binding agreements preventing changes after one party's death, whereas holographic wills allow the testator to modify or revoke at any time before death. The enforceability of joint wills is generally stricter due to contractual elements, contrasting with the flexible nature and informal requirements of holographic wills recognized in certain jurisdictions.
Legal Validity and Requirements
Joint wills, typically created by spouses, are legally binding documents that combine two individuals' testamentary intentions into a single will, often requiring formal execution through witnesses and notaries to meet state-specific legal validity standards. Holographic wills, handwritten and signed by the testator without witnesses, have varying acceptance depending on jurisdiction, with some states recognizing their validity if the handwriting and signature can be authenticated. Understanding each type's execution requirements and probate acceptance is essential for ensuring that estate plans are legally enforceable and reflective of the testators' intentions.
Pros and Cons of Joint Wills
Joint wills simplify estate planning for couples by combining assets into a single document, ensuring mutual agreement on property distribution after both parties pass. However, joint wills lack flexibility since they generally cannot be changed once one testator dies, potentially causing complications if circumstances evolve. They may also limit each individual's ability to manage separate estates, making them less suitable for diverse or independently managed assets.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Holographic Wills
Holographic wills offer the benefit of easy and quick drafting without the need for witnesses, making them ideal in emergencies or for those uncomfortable with formal legal procedures. However, their drawbacks include potential disputes over authenticity, as handwritten wills are often challenged in court, and they may not comply with statutory requirements in certain jurisdictions. Joint wills, while less flexible due to their mutual agreement nature, provide clear, legally binding instructions for asset distribution after both parties' deaths.
Situations Best Suited for Joint Wills
Joint wills are best suited for married couples or partners seeking a unified estate plan that ensures mutual assets are distributed according to a pre-agreed arrangement after both have passed away. This type of will is especially beneficial when the testators desire to prevent changes after the first party's death, providing certainty and finality in the distribution of the estate. Situations involving shared property, business ownership, or blended families often rely on joint wills to avoid disputes and simplify the probate process.
When to Consider a Holographic Will
A holographic will is ideal when a handwritten, simple, and quickly created document is needed, especially in urgent situations without access to legal assistance. It is often considered by individuals who want to clearly outline their wishes without formal witnesses or notarization, which is crucial during unexpected circumstances. This type of will holds particular value when flexibility and immediacy are required, in contrast to the more structured and jointly executed formalities of a joint will.
Challenges and Risks in Both Will Types
Joint wills pose challenges such as limited flexibility since they cannot be altered after one testator's death, potentially causing conflicts if circumstances change. Holographic wills, being handwritten and often lacking formal witnesses, risk rejection due to questions on authenticity or failure to meet legal requirements. Both will types carry risks including disputes over interpretation, potential claims by disinherited heirs, and increased probate complexities.
Choosing the Right Will for Your Estate Plan
Choosing the right will for your estate plan depends on your specific circumstances, with joint wills offering a single, combined document used commonly by spouses to ensure mutual asset distribution after both pass away. Holographic wills, handwritten and signed by the testator, provide a flexible and personal approach but may face challenges in legal validation depending on jurisdiction. Understanding state laws, the complexity of your assets, and your long-term intentions is crucial for selecting between a joint will and a holographic will to effectively protect your estate and beneficiaries.
Joint Will Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com