Quo warranto is a legal proceeding used to challenge an individual's right to hold a public office or exercise authority. This writ ensures that officials or corporations do not exceed their powers or claim positions unlawfully. Discover how quo warranto protects your rights and maintains governmental accountability by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
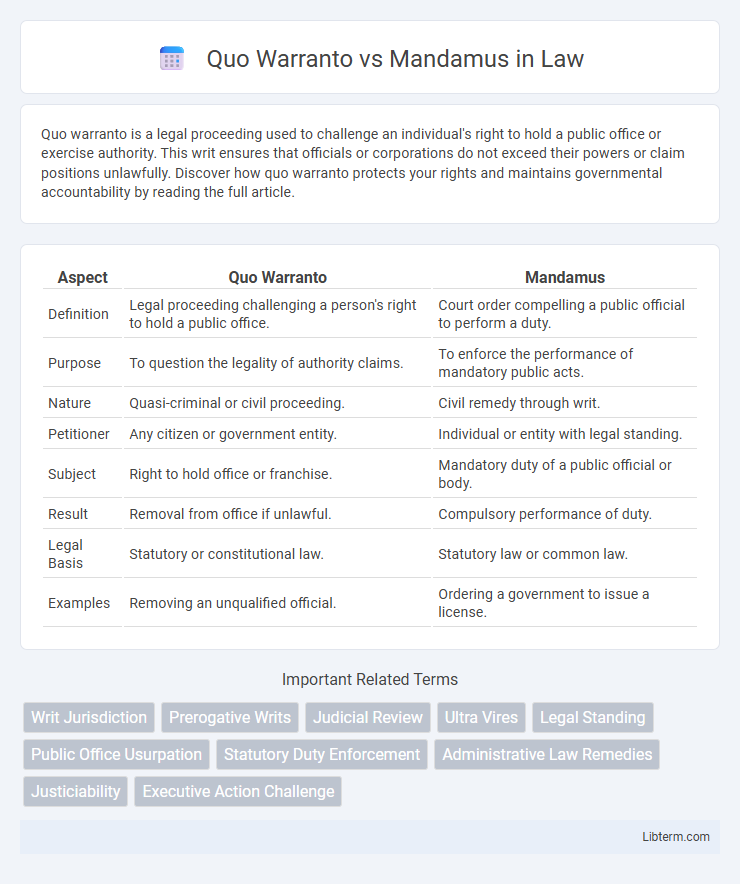
| Aspect | Quo Warranto | Mandamus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal proceeding challenging a person's right to hold a public office. | Court order compelling a public official to perform a duty. |
| Purpose | To question the legality of authority claims. | To enforce the performance of mandatory public acts. |
| Nature | Quasi-criminal or civil proceeding. | Civil remedy through writ. |
| Petitioner | Any citizen or government entity. | Individual or entity with legal standing. |
| Subject | Right to hold office or franchise. | Mandatory duty of a public official or body. |
| Result | Removal from office if unlawful. | Compulsory performance of duty. |
| Legal Basis | Statutory or constitutional law. | Statutory law or common law. |
| Examples | Removing an unqualified official. | Ordering a government to issue a license. |
Introduction to Quo Warranto and Mandamus
Quo Warranto is a legal proceeding used to challenge an individual's right to hold a public office or governmental authority, questioning the legitimacy of their power. Mandamus is a writ issued by a court to compel a public official or government entity to perform a mandatory duty that they are legally obligated to complete. Both writs serve as important judicial tools to ensure accountability and lawful exercise of official duties within administrative and constitutional law.
Definition of Quo Warranto
Quo Warranto is a legal writ used to challenge an individual's right to hold a public office or exercise a franchise, questioning the authority by which they occupy the position. It serves as a control mechanism to prevent unauthorized or unlawful claim over public offices. Mandamus, on the other hand, is a judicial order compelling a public official or entity to perform a mandatory duty that they are obligated to execute by law.
Definition of Mandamus
Mandamus is a judicial writ issued by a higher court directing a lower court, government official, or public authority to perform a mandatory duty that they are legally obligated to complete. It serves as a remedy to compel the fulfillment of public or statutory duties that have been neglected or refused. Unlike quo warranto, which challenges a person's right to hold a public office, mandamus focuses on enforcing the performance of official duties.
Legal Foundations of Quo Warranto
Quo Warranto is a legal proceeding used to challenge an individual's right to hold a public office or exercise a franchise, grounded in common law principles that protect public authority from unauthorized usurpation. The foundation of Quo Warranto lies in the requirement that any person occupying a public office must prove their legal entitlement or authority, ensuring accountability and adherence to statutory or constitutional qualifications. This remedy enforces the rule of law by preventing illegitimate possession of public offices, distinguishing it from Mandamus, which compels a public official to perform a duty they are legally obligated to execute.
Legal Basis of Mandamus
Mandamus is a judicial remedy compelling a government official or entity to perform a mandatory duty under the law, primarily grounded in statutory provisions and constitutional mandates. The legal basis for Mandamus typically resides in constitutional articles such as Article 224 of the Indian Constitution or equivalent provisions in other jurisdictions, ensuring public authorities do not neglect their mandatory obligations. Unlike Quo Warranto, which challenges an individual's right to hold public office, Mandamus enforces performance of legal duties entrusted to public officials.
Key Differences Between Quo Warranto and Mandamus
Quo Warranto challenges the legality of a person's claim to a public office, questioning their authority to hold the position, while Mandamus compels a public official or authority to perform a mandatory duty they are legally obligated to execute. Quo Warranto seeks to oust an individual unlawfully holding office, whereas Mandamus enforces the fulfillment of a duty without addressing the legitimacy of officeholder status. In terms of scope, Quo Warranto pertains exclusively to public office claims, and Mandamus applies broadly to public duties and administrative functions.
Grounds for Filing Quo Warranto
The grounds for filing Quo Warranto include unlawful usurpation, intrusions, or unlawful claim to a public office or franchise by a person not entitled to hold such position. This writ challenges the legality of an individual's claim to office, typically when the person lacks legal qualifications or acquired the position through fraud or illegality. It serves as a remedy to protect public interest by ensuring that only qualified individuals hold public offices.
Conditions for Issuing Mandamus
Mandamus is issued when a public official or lower court fails to perform a mandatory duty imposed by law, and there is no other adequate remedy available. The petitioner must demonstrate a clear legal right to the performance of the duty, along with a corresponding duty on the part of the respondent to act. Unlike quo warranto, which challenges the authority of a person holding a public office, mandamus compels the fulfillment of an existing obligation.
Significant Case Laws on Quo Warranto and Mandamus
The landmark case of *In re: Presidential Election Petition* (2017) significantly expanded the scope of Quo Warranto by allowing challenges to the qualifications of elected officials beyond their term's start. In *Ashok Kumar Pandey v. Union of India* (1985), the Supreme Court affirmed that Mandamus is an extraordinary remedy compelling public officials to perform their duties, reinforcing its role in enforcing constitutional obligations. These precedents highlight Quo Warranto as a tool for questioning authority legitimacy, while Mandamus ensures administrative accountability and public duty fulfillment.
Practical Implications and Current Relevance
Quo Warranto challenges the legal authority of a person or entity holding a public office, serving as a vital tool to prevent usurpation and ensure proper governance. Mandamus compels a government official or agency to perform a mandatory duty, reinforcing accountability in public administration. Both remedies are essential in judicial review, with Quo Warranto addressing unlawful office occupancy while Mandamus enforces the execution of official responsibilities, maintaining the integrity of public service today.
Quo Warranto Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com