Transitional provisions ensure a smooth shift from old regulations to new ones by defining how current cases and obligations should be handled during the changeover. They clarify the application period and any exceptions to maintain legal certainty and fairness. Explore the article to understand how these provisions might impact your rights and obligations.
Table of Comparison
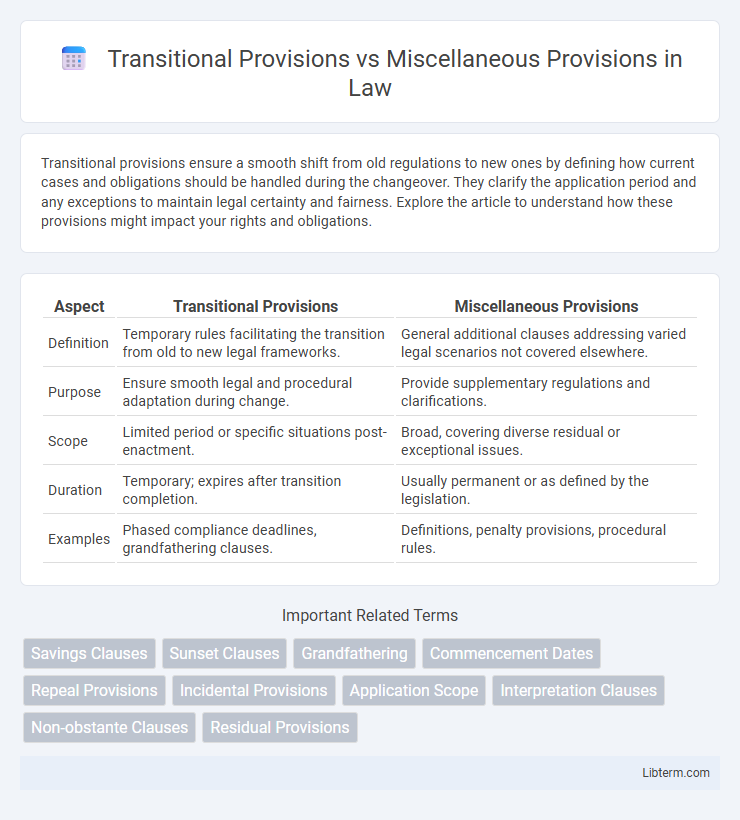
| Aspect | Transitional Provisions | Miscellaneous Provisions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary rules facilitating the transition from old to new legal frameworks. | General additional clauses addressing varied legal scenarios not covered elsewhere. |
| Purpose | Ensure smooth legal and procedural adaptation during change. | Provide supplementary regulations and clarifications. |
| Scope | Limited period or specific situations post-enactment. | Broad, covering diverse residual or exceptional issues. |
| Duration | Temporary; expires after transition completion. | Usually permanent or as defined by the legislation. |
| Examples | Phased compliance deadlines, grandfathering clauses. | Definitions, penalty provisions, procedural rules. |
Introduction to Transitional and Miscellaneous Provisions
Transitional Provisions facilitate a smooth changeover from old regulations or systems to new ones by addressing temporary conditions and exceptions during the implementation phase. Miscellaneous Provisions encompass various supplementary clauses that do not fit into other sections, covering diverse regulatory details, procedural aspects, and specific exceptions. Together, they ensure legal clarity and operational continuity during regulatory updates or legislative reforms.
Defining Transitional Provisions
Transitional provisions are legal clauses that facilitate the smooth implementation of new laws or regulations by addressing the status of existing rights, obligations, or procedures during the changeover period. They ensure continuity and prevent legal gaps by specifying how previous rules apply temporarily while the new framework takes effect. Miscellaneous provisions, by contrast, cover various supplementary rules that do not fit into primary categories but support the comprehensive application of the legislation.
Defining Miscellaneous Provisions
Miscellaneous provisions encompass diverse legal clauses addressing various administrative, procedural, or interpretative matters that do not fit within the primary categories of legislation. These provisions ensure comprehensive coverage by including exemptions, repeals, or savings, facilitating the effective implementation of laws. Unlike transitional provisions, which specifically manage the shift from old to new legal frameworks, miscellaneous provisions cover a broader range of supplementary legal details.
Legal Significance of Transitional Provisions
Transitional provisions hold significant legal importance as they ensure smooth implementation of new laws by providing clear guidelines on handling ongoing cases and existing rights affected by legislative changes. These provisions prevent legal uncertainty and conflicts by explicitly defining how previous laws will be phased out or integrated with the new regulatory framework. Miscellaneous provisions, in contrast, typically address varied administrative or procedural details that do not directly affect the core transition and continuity of legal norms.
Practical Role of Miscellaneous Provisions
Miscellaneous Provisions serve as flexible clauses in legal documents, addressing various practical details that do not fit neatly into other sections, such as administrative procedures, amendments, or procedural clarifications. They ensure comprehensive coverage by encompassing ancillary but essential elements necessary for effective implementation and enforcement. Unlike Transitional Provisions, which specifically govern the shift from old to new regulations, Miscellaneous Provisions support ongoing administrative efficiency and legal coherence throughout the lifecycle of the legislation.
Key Differences Between Transitional and Miscellaneous Provisions
Transitional provisions primarily address the implementation phase of new laws or regulations, detailing how existing situations or contracts should be treated during the changeover period. Miscellaneous provisions cover a broader range of general rules, including procedural matters, enforcement, and ancillary issues that do not fit into specific categories of the legislation. Key differences lie in their purpose, with transitional provisions facilitating legal continuity and adaptation, while miscellaneous provisions consolidate various supplementary elements to ensure the law operates effectively.
Common Examples in Legislation
Transitional provisions in legislation address the application of new laws to past actions or ongoing situations, such as phasing out old regulations or protecting vested rights during a statutory change. Common examples include clauses allowing ongoing contracts to continue under previous laws or setting deadlines for compliance with new standards. Miscellaneous provisions typically cover diverse legal elements like definitions, enforcement mechanisms, penalty structures, and procedural rules that do not fit neatly into the main body of the legislation.
Drafting Considerations for Transitional and Miscellaneous Provisions
Drafting transitional provisions requires precise language to ensure smooth implementation of new laws or regulations, addressing the continuity of rights, obligations, and procedures from the old framework to the new. Miscellaneous provisions should be carefully crafted to cover diverse procedural and administrative details, avoiding ambiguity while consolidating supplementary rules that support the main statutory framework. Attention to clarity, consistency, and legal compatibility is essential to prevent conflicts and ensure coherence between transitional and miscellaneous provisions.
Impact on Stakeholders and Legal Compliance
Transitional provisions provide a structured timeline for stakeholders to adapt to new legal frameworks, minimizing disruption and ensuring smoother compliance during changes in regulations. Miscellaneous provisions address various supplementary legal requirements and clarifications, impacting stakeholders by covering gaps or unforeseen circumstances to maintain comprehensive legal compliance. Both provisions play a critical role in safeguarding stakeholder interests and ensuring continuous adherence to evolving laws and regulations.
Conclusion: Best Practices and Recommendations
Transitional provisions ensure a smooth shift by clearly outlining deadlines, responsibilities, and exceptions during regulatory or procedural changes, minimizing confusion and legal risks. Miscellaneous provisions address various other regulatory aspects, supporting the document's overall coherence but often lack the structured clarity of transitional clauses. Best practices emphasize drafting detailed transitional provisions with explicit timelines and exceptions, while miscellaneous provisions should be concise and relevant to avoid ambiguity and enhance legal compliance.
Transitional Provisions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com