The constitution establishes the fundamental principles and framework of governance that shape a nation's legal and political system. It outlines the rights and duties of citizens, ensuring protection and order within society. Discover how understanding your constitution empowers you to engage more fully with your country's democratic processes.
Table of Comparison
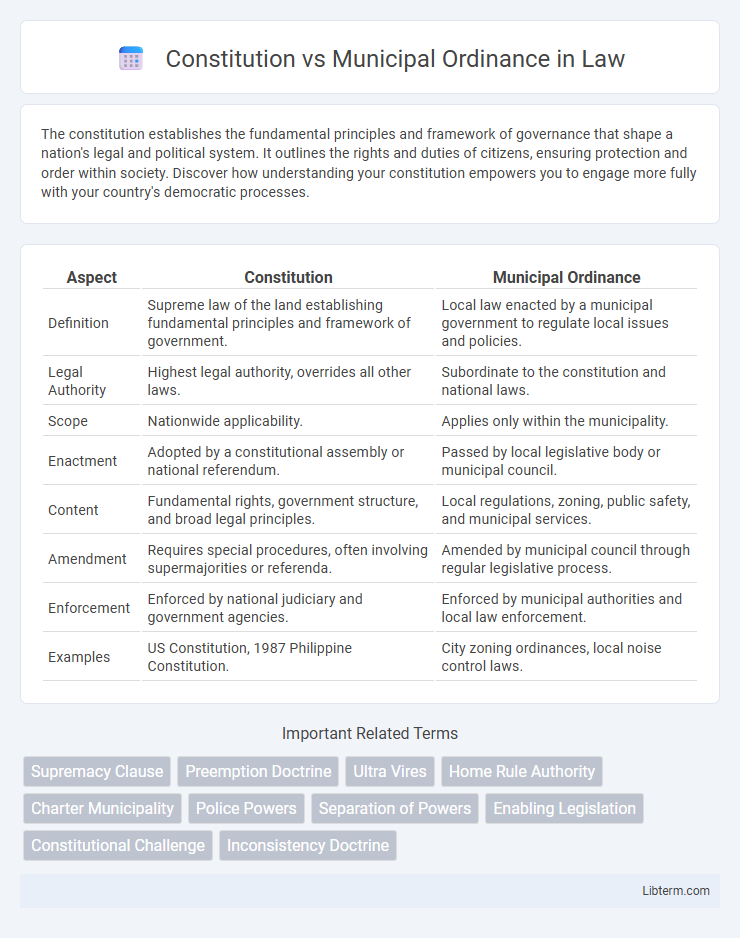
| Aspect | Constitution | Municipal Ordinance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supreme law of the land establishing fundamental principles and framework of government. | Local law enacted by a municipal government to regulate local issues and policies. |
| Legal Authority | Highest legal authority, overrides all other laws. | Subordinate to the constitution and national laws. |
| Scope | Nationwide applicability. | Applies only within the municipality. |
| Enactment | Adopted by a constitutional assembly or national referendum. | Passed by local legislative body or municipal council. |
| Content | Fundamental rights, government structure, and broad legal principles. | Local regulations, zoning, public safety, and municipal services. |
| Amendment | Requires special procedures, often involving supermajorities or referenda. | Amended by municipal council through regular legislative process. |
| Enforcement | Enforced by national judiciary and government agencies. | Enforced by municipal authorities and local law enforcement. |
| Examples | US Constitution, 1987 Philippine Constitution. | City zoning ordinances, local noise control laws. |
Introduction to Constitutions and Municipal Ordinances
Constitutions serve as the fundamental legal framework establishing the structure, powers, and limits of government, while municipal ordinances are local laws enacted by city or municipal authorities to address community-specific issues. Constitutions typically outline broad principles and rights applicable to the entire nation or state, whereas municipal ordinances focus on regulations tailored to local governance, such as zoning, public safety, and local services. Understanding the hierarchical nature of these laws is essential, as constitutions supersede municipal ordinances in cases of conflict.
Definition and Scope of Constitutions
Constitutions are the fundamental legal frameworks that establish the structure, powers, and functions of a government, defining the rights and duties of citizens within a sovereign state. They provide the supreme law that governs the creation and operation of all other laws, including municipal ordinances, ensuring consistency and adherence to national principles. Municipal ordinances, on the other hand, are local laws enacted by city or municipal governments, limited in scope to address specific community needs under the authority granted by the constitution or state law.
Definition and Scope of Municipal Ordinances
The Constitution serves as the supreme law that outlines the fundamental principles and framework of a government, while municipal ordinances are local laws enacted by city or municipal governments to address specific community needs. Municipal ordinances have a narrower scope, regulating issues such as zoning, public safety, health regulations, and local business licensing within the municipality's jurisdiction. These ordinances must align with both the Constitution and higher laws, ensuring they do not conflict with state or national legal provisions.
Legal Hierarchy: Constitution Over Ordinances
The Constitution stands as the supreme legal authority, overriding all municipal ordinances that conflict with its provisions. Municipal ordinances must adhere strictly to constitutional mandates, ensuring local laws do not infringe upon fundamental rights or exceed granted powers. In legal disputes, courts prioritize constitutional interpretation, invalidating ordinances that contradict constitutional principles.
Sources of Authority: National vs Local
The Constitution serves as the supreme source of authority at the national level, establishing fundamental laws and principles that govern the entire country. Municipal ordinances derive their authority from the Constitution but operate at the local government level to address community-specific needs and issues. While the Constitution provides overarching legal frameworks, municipal ordinances must conform to constitutional provisions and cannot override national laws.
Amendment and Enactment Processes
The Constitution undergoes a rigorous amendment process requiring supermajority approval by legislative bodies or ratification through a national referendum, reflecting its supreme legal status. Municipal ordinances are enacted by local government councils through simpler majority votes, allowing more rapid adaptation to community needs. Unlike constitutional amendments, municipal ordinance enactments do not require extensive public ratification or higher legislative scrutiny.
Areas of Regulation and Coverage
The Constitution establishes the fundamental framework and supreme law governing national policies, rights, and powers, setting broad mandates for government operation and civil liberties. Municipal ordinances regulate local matters within a specific city's or municipality's jurisdiction, addressing issues like zoning, local safety, health regulations, and community welfare. While the Constitution provides overarching legal principles applicable nationwide, municipal ordinances offer detailed rules tailored to local needs and governance.
Enforcement and Legal Consequences
The Constitution establishes the supreme law of the land, providing the foundational legal framework that courts strictly enforce to protect fundamental rights and govern state power. Municipal ordinances derive authority from the Constitution and state laws, applying localized rules with enforcement typically executed by local government agencies or law enforcement, with penalties including fines, community service, or misdemeanor charges. Violations of the Constitution often lead to judicial review and potential nullification of laws or actions, while breaches of municipal ordinances result in administrative or criminal sanctions specific to the locality's legal code.
Conflicts Between Constitution and Municipal Ordinances
Conflicts between the constitution and municipal ordinances arise when local laws contravene constitutional provisions, rendering such ordinances unconstitutional and legally unenforceable. Municipal ordinances must adhere to constitutional mandates, and any conflict favors the supremacy of the constitution as the highest law of the land. Judicial review serves as the mechanism through which courts invalidate municipal ordinances that violate constitutional rights or principles.
Practical Implications for Citizens and Local Governments
Constitutional provisions establish the fundamental legal framework protecting citizens' rights and defining government powers, while municipal ordinances address specific local issues such as zoning, public safety, and community services. Citizens benefit from constitutional guarantees that ensure equal protection and due process, whereas municipal ordinances provide tailored regulations that directly impact daily life within communities. Local governments rely on ordinances to enforce policies responsive to local needs, but must ensure these laws comply with constitutional standards to avoid legal challenges.
Constitution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com