Surrender is a powerful act of letting go, allowing you to release control and embrace acceptance in challenging situations. It fosters inner peace and opens the door to personal growth by shifting your perspective. Discover how surrender can transform your life by exploring the insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
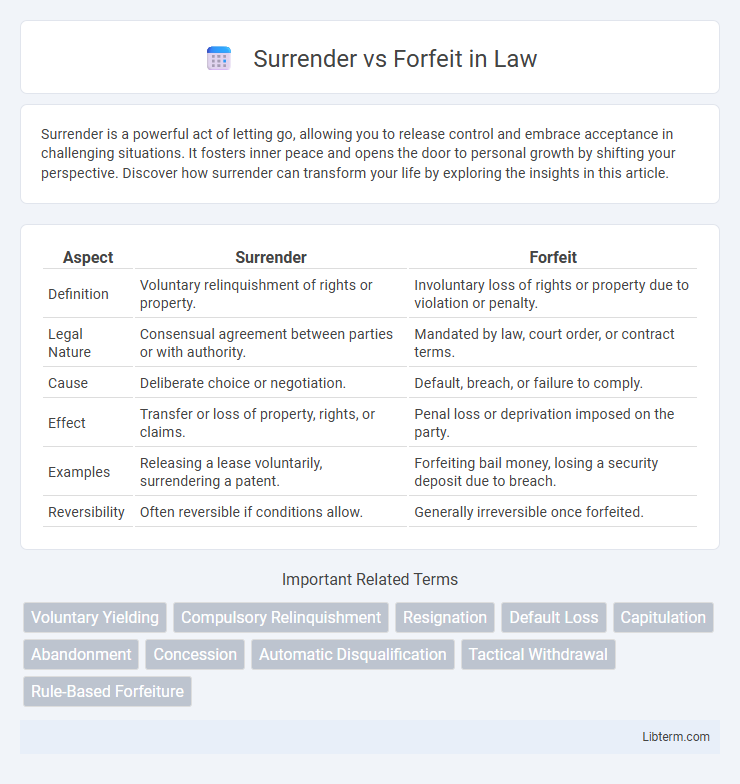
| Aspect | Surrender | Forfeit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary relinquishment of rights or property. | Involuntary loss of rights or property due to violation or penalty. |
| Legal Nature | Consensual agreement between parties or with authority. | Mandated by law, court order, or contract terms. |
| Cause | Deliberate choice or negotiation. | Default, breach, or failure to comply. |
| Effect | Transfer or loss of property, rights, or claims. | Penal loss or deprivation imposed on the party. |
| Examples | Releasing a lease voluntarily, surrendering a patent. | Forfeiting bail money, losing a security deposit due to breach. |
| Reversibility | Often reversible if conditions allow. | Generally irreversible once forfeited. |
Understanding Surrender: Definition and Context
Surrender refers to the voluntary act of giving up control or possession of something, often in the context of conflict, where a party ceases resistance and submits to the authority or demands of another. It typically involves a conscious decision to accept defeat or yield, frequently seen in military, legal, or competitive situations. Understanding surrender requires recognizing its basis in choice and negotiation, contrasting with forfeit, which implies losing rights or possession due to penalty or failure.
Forfeit Explained: What Does It Mean?
Forfeit means to lose or give up something as a penalty for wrongdoing, failure, or neglect, often enforced by rules or legal authority. In sports, a team may forfeit a game by refusing to play or not meeting requirements, resulting in an automatic loss. Unlike surrender, which implies a voluntary yielding, forfeit involves consequences imposed due to violations or infractions.
Key Differences Between Surrender and Forfeit
Surrender involves voluntarily yielding control or giving up resistance, often in a conflict or competition, while forfeit refers to losing something as a penalty or consequence for failing to meet an obligation or rule. Surrender is typically an active decision made under pressure, whereas forfeit is usually imposed automatically due to an infraction or failure. Legal and gaming contexts frequently differentiate these terms based on intent and conditions leading to the loss or yielding of rights, possessions, or status.
Legal Implications of Surrender vs Forfeit
Surrender involves voluntarily giving up rights or property, often recognized within legal contracts and property law, resulting in clear transfer of ownership or cessation of claims. Forfeit legally implies losing rights or property due to failure to meet obligations or as a penalty for wrongdoing, frequently enforced through court orders or statutory regulations. Understanding the distinction is crucial in legal contexts, as surrender is typically consensual and negotiated, whereas forfeiture is involuntary and imposed as a sanction.
Surrender in Gaming and Sports Scenarios
Surrender in gaming and sports refers to a deliberate decision to concede defeat before the conclusion of a match or competition, often to avoid unnecessary losses or injuries. In video games, surrender typically occurs when players recognize the futility of continuing, triggering a vote among teammates to end the game early. In sports, surrender can manifest as a team or individual ceasing to compete, which may result in a default loss without the penalties often associated with forfeiture.
Forfeiture: Common Causes and Consequences
Forfeiture occurs when an individual or entity loses property or rights due to legal violations such as fraud, breach of contract, or failure to meet regulatory requirements. Common causes include non-payment of debts, violation of loan terms, and involvement in criminal activity, leading to the automatic loss of assets without compensation. Consequences of forfeiture often involve permanent deprivation of property, damage to credit ratings, and potential legal penalties, significantly impacting financial stability and business operations.
Psychological Impact: Surrendering vs Forfeiting
Surrendering often involves a conscious psychological decision to yield control, which can lead to feelings of relief or empowerment by accepting reality and reducing internal conflict. Forfeiting, by contrast, frequently implies a loss or abandonment without active consent, potentially causing increased frustration, regret, or diminished self-esteem. Understanding the nuanced emotional consequences of surrender versus forfeit helps clarify personal responses to loss and control in challenging situations.
Strategic Considerations: When to Surrender or Forfeit
Surrender often involves a tactical decision to preserve resources or lives when continued resistance yields no strategic advantage, while forfeiture generally implies conceding a position or asset due to inability to maintain control or meet obligations. Strategic considerations include evaluating the long-term implications on morale, resource conservation, and potential for negotiation or regrouping after surrender, contrasted with forfeiture's impact on immediate operational capabilities and reputation. Leaders weigh factors such as enemy strength, logistical support, political consequences, and mission objectives to determine the optimal moment for surrender or forfeiture.
Real-World Examples of Surrender and Forfeit
Surrender often involves a formal or strategic yielding, such as a military force handing over weapons at the end of a battle, exemplified by Germany's surrender in World War II. Forfeit typically refers to losing a right or claim due to a breach of rules or failure to meet obligations, like a tennis player forfeiting a match after a rule violation. In sports and legal contexts, surrender implies voluntary compliance, whereas forfeit denotes a penalty or consequence for non-compliance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Course of Action
Surrender involves willingly giving up control or possession, often to avoid further conflict or harm, while forfeiture implies losing rights or property as a penalty or consequence. Choosing the right course depends on evaluating potential outcomes: surrender may preserve safety and allow negotiation, whereas forfeiture typically results in irreversible loss. Understanding legal and situational contexts ensures informed decisions that minimize negative impact and protect interests effectively.
Surrender Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com