Retained counsel offers you dedicated legal representation through a formal agreement, ensuring prioritized attention to your case and ongoing legal support. This arrangement provides consistent access to expert advice, tailored strategies, and proactive management of your legal matters. Explore the article to understand how retained counsel can safeguard your interests and streamline your legal needs.
Table of Comparison
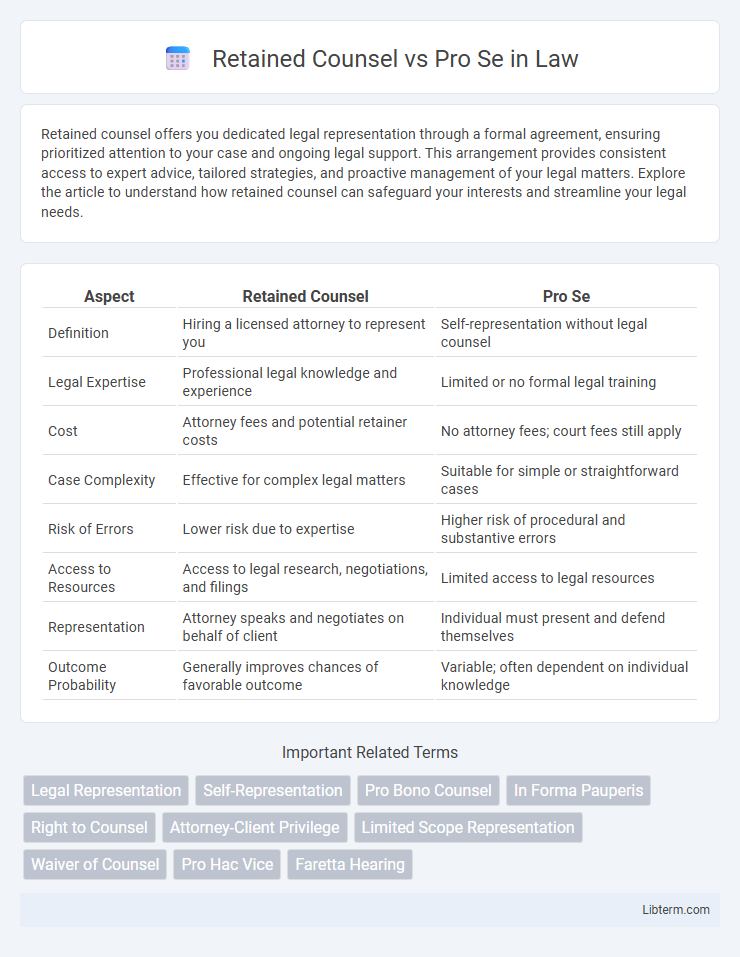
| Aspect | Retained Counsel | Pro Se |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring a licensed attorney to represent you | Self-representation without legal counsel |
| Legal Expertise | Professional legal knowledge and experience | Limited or no formal legal training |
| Cost | Attorney fees and potential retainer costs | No attorney fees; court fees still apply |
| Case Complexity | Effective for complex legal matters | Suitable for simple or straightforward cases |
| Risk of Errors | Lower risk due to expertise | Higher risk of procedural and substantive errors |
| Access to Resources | Access to legal research, negotiations, and filings | Limited access to legal resources |
| Representation | Attorney speaks and negotiates on behalf of client | Individual must present and defend themselves |
| Outcome Probability | Generally improves chances of favorable outcome | Variable; often dependent on individual knowledge |
Introduction to Retained Counsel and Pro Se Representation
Retained counsel refers to an attorney hired and paid by a client to provide continuous legal services and representation in a case. Pro se representation occurs when an individual chooses to represent themselves in court without the assistance of a lawyer. Understanding the differences in expertise, legal procedure knowledge, and case strategy is crucial when deciding between retained counsel and pro se options.
Defining Retained Counsel
Retained counsel refers to an attorney who is formally engaged and compensated by a client to provide ongoing legal representation and advice throughout a case. This legal professional offers expertise, negotiates on behalf of the client, and ensures procedural compliance, significantly enhancing the client's ability to navigate complex legal systems. Unlike pro se litigants who represent themselves, retained counsel brings specialized knowledge and strategic advocacy to achieve favorable outcomes.
Understanding Pro Se Representation
Pro Se representation means a party represents themselves in legal proceedings without hiring retained counsel, often leading to challenges in navigating complex legal rules and procedures. Courts generally expect pro se litigants to follow the same rules as attorneys, which can result in disadvantages due to lack of legal expertise. Understanding the limitations and potential risks of Pro Se representation is crucial before deciding to proceed without professional legal assistance.
Key Differences Between Retained Counsel and Pro Se
Retained counsel involves hiring a licensed attorney who provides expert legal representation, ensuring thorough case analysis, strategic planning, and professional negotiation on behalf of clients, while pro se litigants represent themselves without legal counsel, which can limit their understanding of complex legal procedures and reduce their chances of favorable outcomes. Retained attorneys have knowledge of court rules, evidence law, and procedural intricacies, which enhances case management and advocacy compared to self-representation that may lead to procedural errors and missed deadlines. Costs are a significant differentiator; retained counsel requires paying legal fees, which can be substantial, whereas pro se representation eliminates these costs but increases the risk of ineffective legal arguments and inadequate defense.
Advantages of Hiring Retained Counsel
Hiring retained counsel offers significant advantages, including expert knowledge of legal procedures and the ability to develop a tailored strategy specific to the case's nuances. Experienced attorneys ensure thorough representation, reducing the risk of costly mistakes and increasing the likelihood of favorable outcomes. Retained counsel also provides access to resources such as expert witnesses and comprehensive legal research, which enhance the overall effectiveness of the defense or prosecution.
Challenges Faced by Pro Se Litigants
Pro se litigants face significant challenges including limited knowledge of legal procedures, difficulty in understanding complex statutes, and restricted access to legal resources compared to retained counsel. Navigating court rules without professional guidance often results in procedural errors, delayed case progress, and unfavorable outcomes. These obstacles underscore the critical advantage retained counsel provides in ensuring proper case handling and advocacy.
Cost Considerations: Retained Counsel vs Pro Se
Retained counsel often involves significant upfront costs, including retainer fees, hourly rates, and additional expenses for expert witnesses or court filings, which can range from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars depending on case complexity. Pro se representation eliminates attorney fees but may incur indirect costs such as lost time for legal research, potential procedural mistakes, and higher risks of unfavorable outcomes that could result in financial penalties or extended litigation. Evaluating cost considerations requires balancing the immediate financial outlay for professional legal services against the potential long-term expenses and risks of self-representation.
Impact on Case Outcomes
Retained counsel significantly improves case outcomes by leveraging specialized legal knowledge, strategic case management, and effective negotiation skills, often resulting in favorable settlements or verdicts. Pro se litigants face challenges due to limited legal expertise, increasing risks of procedural errors and lower success rates in complex cases. Studies show defendants with retained counsel achieve higher conviction reversal rates and better plea bargains compared to self-represented individuals.
When to Choose Retained Counsel over Pro Se
Choosing retained counsel over proceeding pro se is crucial when facing complex legal issues that require expert knowledge and experience, such as criminal defense, family law disputes, or significant civil litigation. Retained counsel provides tailored legal strategies, ensures proper procedural compliance, and offers negotiation skills that a self-represented litigant typically lacks. Cases involving substantial financial stakes, potential incarceration, or intricate evidentiary matters especially benefit from professional legal representation.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Legal Matter
Choosing between retained counsel and proceeding pro se depends on the complexity of the legal matter, potential risks, and personal comfort with legal procedures. Retained counsel brings expertise, experience, and a strategic approach that can significantly impact case outcomes, especially in complex litigation or high-stakes situations. Pro se representation may save costs but often lacks the professional guidance necessary to navigate legal nuances, making it crucial to weigh the importance of legal expertise against budget constraints when deciding the best path.
Retained Counsel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com