A license grants you legal permission to use, distribute, or modify intellectual property under specific terms and conditions. Understanding the scope and restrictions of your license is crucial to avoid infringement and ensure compliance. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to choose the right license for your needs and protect your rights effectively.
Table of Comparison
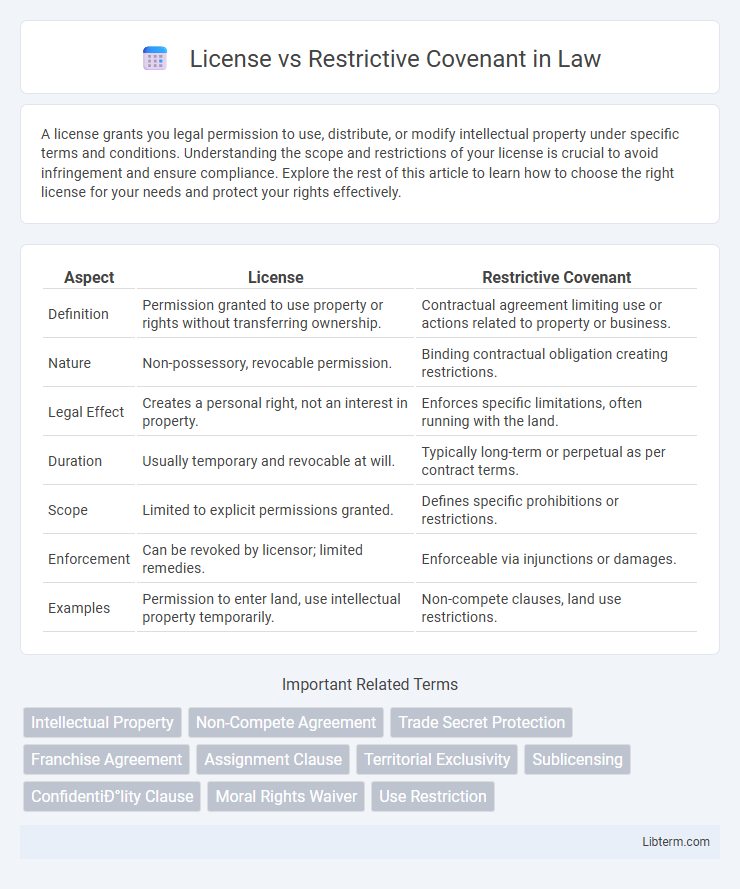
| Aspect | License | Restrictive Covenant |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permission granted to use property or rights without transferring ownership. | Contractual agreement limiting use or actions related to property or business. |
| Nature | Non-possessory, revocable permission. | Binding contractual obligation creating restrictions. |
| Legal Effect | Creates a personal right, not an interest in property. | Enforces specific limitations, often running with the land. |
| Duration | Usually temporary and revocable at will. | Typically long-term or perpetual as per contract terms. |
| Scope | Limited to explicit permissions granted. | Defines specific prohibitions or restrictions. |
| Enforcement | Can be revoked by licensor; limited remedies. | Enforceable via injunctions or damages. |
| Examples | Permission to enter land, use intellectual property temporarily. | Non-compete clauses, land use restrictions. |
Introduction: Understanding Licenses and Restrictive Covenants
Licenses grant permission to use property without transferring ownership, often temporary and revocable, while restrictive covenants impose limitations on property use to protect value or maintain neighborhood standards. Licenses are typically informal agreements, whereas restrictive covenants are legally binding and recorded in property deeds. Understanding these distinctions is essential for property owners and users to ensure compliance and protect interests.
Definitions: License vs Restrictive Covenant
A license grants permission for specific use of land or property without transferring ownership, allowing temporary or revocable rights to the licensee. A restrictive covenant is a contractual obligation imposed in a deed that limits the use or development of land to protect certain interests or maintain property values. Licenses are generally personal and non-transferable, whereas restrictive covenants run with the land and bind successive owners.
Key Legal Distinctions
A license grants permission to use property without transferring any interest, while a restrictive covenant imposes legally binding limitations on property use or development. Licenses are generally revocable and non-assignable, lacking the enforceable obligations that restrictive covenants create for current and future property owners. Restrictive covenants run with the land, ensuring encumbrances persist beyond ownership changes, whereas licenses typically terminate upon the grantor's decision or property transfer.
Purposes and Applications
A license grants permission for specific use of property or intellectual rights without transferring ownership, commonly applied in software distribution and real estate access. Restrictive covenants impose limitations on property usage to preserve value or community standards, frequently used in residential developments and commercial leases. Both serve distinct purposes: licenses enable controlled access, while restrictive covenants enforce long-term behavioral or usage restrictions.
Rights Granted and Limitations Imposed
A license grants permission to use property or intellectual property without transferring ownership, typically offering limited rights that can be revoked at any time. Restrictive covenants impose specific limitations or obligations on the use of land or property, running with the land and binding future owners to those restrictions. While licenses allow certain uses within defined parameters, restrictive covenants enforce ongoing constraints to restrict actions such as building alterations or land use changes.
Impact on Property Ownership
A license grants permission to use property without transferring any estate or interest, allowing the owner to retain full ownership rights, whereas a restrictive covenant imposes binding obligations or restrictions on the property's use, directly affecting the owner's rights and potentially decreasing the property's value or usability. Restrictive covenants run with the land, binding future owners and creating long-term encumbrances, while licenses are typically revocable and do not bind successors. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for property owners when assessing legal control, property value, and future development options.
Enforceability and Legal Remedies
Licenses generally grant permission to use property without transferring ownership and are often non-exclusive and revocable, making their enforceability limited compared to restrictive covenants, which impose binding obligations on property use and run with the land. Enforceability of restrictive covenants is stronger due to their ability to bind successors and the availability of equitable remedies such as injunctions to prevent breach. Legal remedies for license violations typically involve damages, while restrictive covenant breaches allow for specific performance or injunctions, providing more robust protection for property interests.
Common Use Cases in Real Estate and Business
Licenses in real estate and business commonly grant temporary, revocable permissions to use property or intellectual property without conveying ownership, often used for events, signage, or software access. Restrictive covenants impose binding obligations on property owners or business parties, such as limiting land use in real estate developments or enforcing non-compete agreements in business contracts. These tools serve distinct purposes: licenses provide flexible, short-term permissions, while restrictive covenants ensure long-term control over property use or competitive behavior.
Comparative Advantages and Disadvantages
Licenses offer greater flexibility and ease of termination, making them ideal for short-term or non-exclusive rights, whereas restrictive covenants provide stronger, enforceable protections limiting specific actions or competition but can be harder to modify or revoke. Licensing agreements generally involve fewer legal restrictions and lower enforcement costs but lack the binding power to prevent misuse, while restrictive covenants impose significant limitations on parties, enhancing control and security at the expense of flexibility. Choosing between a license and a restrictive covenant depends on the need for adaptability versus the necessity of stringent protection in commercial or employment contexts.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Legal Instrument
Selecting between a license and a restrictive covenant depends on the desired legal effect and enforceability; licenses grant permission to use property without creating an interest, while restrictive covenants impose binding obligations limiting land use. Property owners should opt for licenses when flexible, revocable rights are needed and choose restrictive covenants to ensure long-term control and enforceable restrictions. Legal advice is crucial to navigate jurisdictional variations and draft instruments that align with specific property goals and regulatory frameworks.
License Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com