Ellipsis is a powerful linguistic tool that allows speakers and writers to omit parts of a sentence while retaining meaning, enhancing clarity and conciseness in communication. This device is commonly used in dialogue, quotations, and informal writing to indicate hesitation, trailing off, or omitted text. Explore the full article to understand how ellipsis can refine your writing and interpretative skills.
Table of Comparison
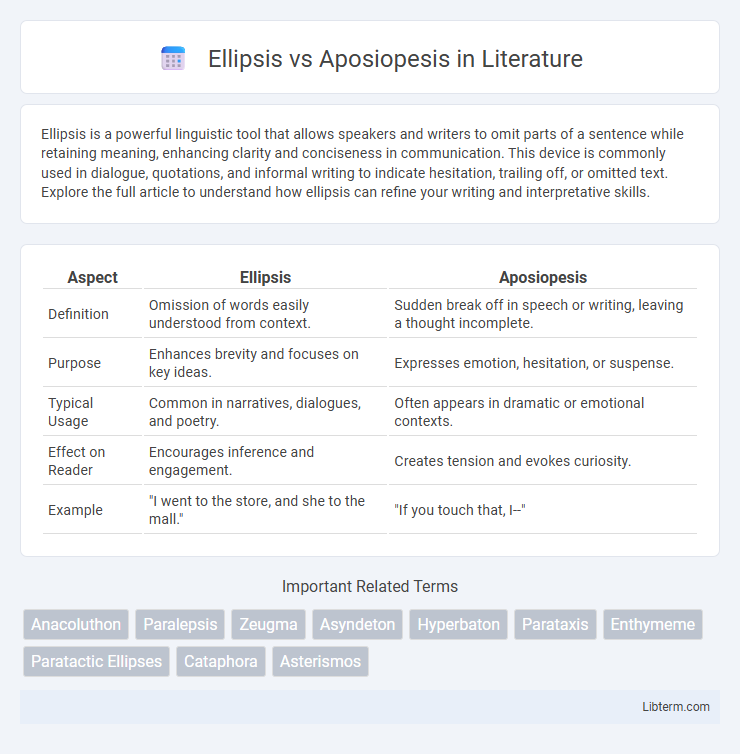
| Aspect | Ellipsis | Aposiopesis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Omission of words easily understood from context. | Sudden break off in speech or writing, leaving a thought incomplete. |
| Purpose | Enhances brevity and focuses on key ideas. | Expresses emotion, hesitation, or suspense. |
| Typical Usage | Common in narratives, dialogues, and poetry. | Often appears in dramatic or emotional contexts. |
| Effect on Reader | Encourages inference and engagement. | Creates tension and evokes curiosity. |
| Example | "I went to the store, and she to the mall." | "If you touch that, I--" |
Understanding Ellipsis: Definition and Usage
Ellipsis is a grammatical phenomenon where one or more words are omitted from a sentence because they are implied by the context, enhancing brevity and cohesion in communication. It typically occurs in conversational language, literature, and everyday speech to avoid redundancy while maintaining clarity, such as in the sentence "She can play the guitar, and he can [play the guitar] too." Understanding ellipsis involves recognizing its function in streamlining sentences without losing essential meaning, which distinguishes it from aposiopesis that intentionally leaves a sentence incomplete for dramatic effect.
What is Aposiopesis? Exploring Its Meaning
Aposiopesis is a rhetorical device where a sentence is deliberately broken off and left unfinished, creating a dramatic effect by implying more than what is explicitly stated. This technique often conveys strong emotion, hesitation, or unwillingness to continue, engaging the audience's imagination to complete the thought. Unlike ellipsis, which omits words for brevity, aposiopesis relies on the intentional interruption of speech to emphasize tension or suspense.
Key Differences Between Ellipsis and Aposiopesis
Ellipsis involves the deliberate omission of words that are implied by context, allowing readers to fill in the gaps, whereas aposiopesis is a sudden break or interruption in speech, leaving a thought incomplete due to emotion or hesitation. Ellipsis enhances brevity and efficiency by removing redundant elements, while aposiopesis conveys dramatic tension or uncertainty through unfinished statements. Key differences lie in ellipsis serving clarity and economy in language, contrasted with aposiopesis expressing psychological or rhetorical effects by breaking the flow of expression.
Grammatical Functions of Ellipsis in Sentences
Ellipsis in grammar involves the omission of one or more words that are understood from the context, serving to avoid redundancy and enhance sentence fluency. It functions grammatically by allowing sentence elements such as subjects, verbs, or objects to be left out when they are inferable, as in responses like "I can" instead of "I can do it." In contrast, aposiopesis involves an intentional interruption or sudden breaking off of speech, often marked by an ellipsis, to convey emotion or suspense rather than grammatical brevity.
The Rhetorical Power of Aposiopesis
Aposiopesis intensifies rhetorical impact by deliberately breaking off speech, creating suspense and inviting the audience to infer the unsaid, whereas ellipsis simply omits redundant words for conciseness. This strategic silence leverages the listener's imagination, enhancing emotional engagement and emphasizing strong feelings like anger or fear. By leaving thoughts incomplete, aposiopesis generates dramatic tension and amplifies persuasive power in literary and spoken discourse.
Common Contexts for Using Ellipsis
Ellipsis frequently appears in everyday conversations to omit redundant information, enhancing fluency and brevity. In literary contexts, ellipsis creates suspense or indicates a trailing off of thought, often replacing omitted words in dialogue or narrative. Unlike aposiopesis, which implies an intentional break due to emotion or hesitation, ellipsis mainly serves to streamline communication while maintaining coherence.
Situational Appropriateness of Aposiopesis
Aposiopesis is situationally appropriate when a speaker intentionally breaks off mid-sentence to convey strong emotions such as fear, anger, or hesitation, leaving the thought incomplete for dramatic effect. Unlike ellipsis, which is a general omission of words for conciseness or style, aposiopesis relies on context and emotional intensity to engage the audience's imagination through what remains unsaid. This rhetorical device is effective in dialogue or narrative moments that demand suspense, emotional depth, or a portrayal of overwhelming feelings.
Visual Representation: Ellipsis vs. Aposiopesis
Ellipsis is visually represented by three evenly spaced dots (...) indicating the omission of words or trailing off of thought, creating an intentional pause or gap in text. Aposiopesis is depicted by an abrupt dash (--) or incomplete sentence, signifying a sudden interruption or an unfinished statement driven by emotion or hesitation. Both punctuation marks serve distinct rhetorical and visual functions in conveying meaning, with ellipsis emphasizing omission and aposiopesis highlighting dramatic silence.
Impact on Tone and Reader Interpretation
Ellipsis creates a subtle pause by omitting words, often softening tone and encouraging reader inference, which fosters engagement and deeper thought. Aposiopesis sharply breaks off mid-sentence, conveying intense emotion or hesitation, thereby heightening dramatic tension and inviting readers to imagine unspoken implications. Both devices shape reader interpretation by emphasizing what is left unsaid, but ellipsis tends to suggest continuity, while aposiopesis emphasizes abrupt emotional interruption.
Practical Examples: Ellipsis and Aposiopesis in Literature
Ellipsis in literature involves the omission of words that are implied by context, such as in the sentence "She can sing, and he can too," where "sing" is omitted after "he can." Aposiopesis occurs when a sentence is deliberately broken off, as in Shakespeare's "Julius Caesar": "Et tu, Brute?--Then fall, Caesar!" where the speaker stops abruptly to convey emotional intensity. These rhetorical devices enhance dialogue realism by mimicking natural speech patterns and emphasizing unspoken thoughts or emotions.
Ellipsis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com