Colloquialism refers to the use of informal language and expressions that are common in everyday speech but may not be suitable for formal writing. These phrases often reflect regional dialects or cultural nuances, making communication feel more natural and relatable. Explore the rest of this article to understand how colloquialisms impact language and enhance your communication skills.
Table of Comparison
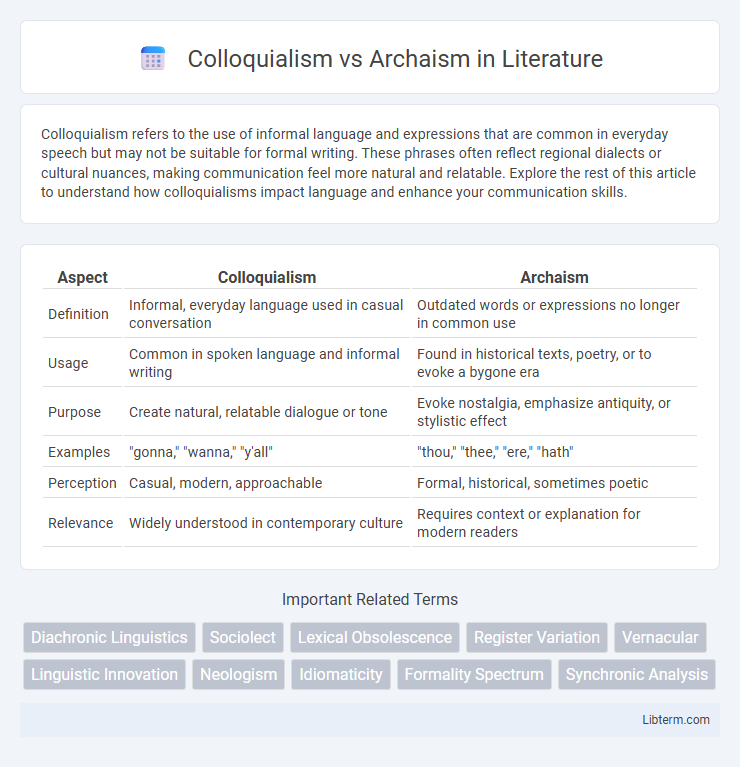
| Aspect | Colloquialism | Archaism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal, everyday language used in casual conversation | Outdated words or expressions no longer in common use |
| Usage | Common in spoken language and informal writing | Found in historical texts, poetry, or to evoke a bygone era |
| Purpose | Create natural, relatable dialogue or tone | Evoke nostalgia, emphasize antiquity, or stylistic effect |
| Examples | "gonna," "wanna," "y'all" | "thou," "thee," "ere," "hath" |
| Perception | Casual, modern, approachable | Formal, historical, sometimes poetic |
| Relevance | Widely understood in contemporary culture | Requires context or explanation for modern readers |
Understanding Colloquialism: Definition and Features
Colloquialism refers to informal language used in everyday conversation, characterized by casual expressions, slang, and regional dialects that are easily understood by native speakers. It contrasts with archaism, which involves words or phrases that have fallen out of common usage and are considered outdated or obsolete. Understanding colloquialism is essential for grasping contemporary speech patterns and cultural nuances within a language.
What Is Archaism? Key Characteristics
Archaism refers to the use of words, phrases, or expressions that were common in the past but have fallen out of everyday use in contemporary language. Key characteristics of archaisms include their historical origin, limited modern usage primarily in literary or formal contexts, and their role in evoking a sense of antiquity or tradition. Unlike colloquialisms, which reflect informal, everyday speech, archaisms often carry a nostalgic or classical tone that highlights historical linguistic features.
Historical Origins: How Colloquialisms and Archaisms Emerge
Colloquialisms emerge from everyday speech within specific communities, evolving through informal usage and social interaction over time. Archaisms originate from historical language forms that fall out of common use but persist in literature, legal documents, or ceremonial contexts. Both reflect linguistic shifts influenced by cultural, social, and technological changes in society.
Usage in Modern Language: Colloquialism vs Archaism
Colloquialisms dominate modern spoken language, reflecting everyday speech patterns and informal communication, often evolving rapidly with cultural trends. Archaisms, by contrast, appear sporadically in literary or historical contexts, serving to evoke a sense of antiquity or formality rather than facilitate regular conversation. The prevalence of colloquialisms in digital communication platforms emphasizes their role in modern linguistic expression, while archaisms remain largely confined to specialized or artistic usage.
Effects on Tone and Style
Colloquialism infuses writing with a casual, conversational tone, making the style more relatable and accessible to contemporary audiences. Archaism introduces a formal, historical, or poetic tone, lending a sense of tradition or gravity to the text. Choosing between colloquialism and archaism significantly influences the reader's perception, shaping whether the tone feels modern and lively or timeless and solemn.
Colloquialism in Everyday Conversation
Colloquialism refers to informal language used in everyday conversation, characterized by casual expressions and slang that vary by region and social group. It enhances natural communication and reflects cultural identity while evolving over time to include new phrases and idioms. In contrast, archaism involves outdated words and phrases that have largely fallen out of daily use, serving primarily literary or historical purposes.
Archaism in Literature and Formal Writing
Archaism in literature and formal writing serves to evoke a sense of tradition, historical authenticity, or elevated style by intentionally using words, phrases, or grammatical forms that have fallen out of everyday use. This technique enriches texts by connecting contemporary audiences with past eras, enhancing the thematic depth and atmosphere, especially in poetry, historical novels, and legal documents. Archaisms contrast with colloquialisms, which reflect informal, regional, or contemporary speech, making the former crucial for achieving solemnity and timelessness in literary and formal contexts.
Social and Cultural Impacts
Colloquialisms reflect contemporary social dynamics and cultural identities, fostering relatability and informal communication across communities. Archaisms, often confined to literature or formal contexts, preserve historical language forms that connect societies to their cultural heritage and collective memory. The social impact of colloquialisms encourages linguistic evolution and inclusivity, while archaisms reinforce cultural continuity and traditional values.
Common Examples of Colloquialisms and Archaisms
Colloquialisms such as "gonna," "wanna," and "y'all" are widely used in everyday conversation to create an informal, relatable tone. Archaisms like "thou," "thy," and "forsake" are rarely used in modern language but often appear in historical texts and classical literature to convey an old-fashioned or formal atmosphere. Understanding the differences between these linguistic forms helps in analyzing language style and evolution in English communication.
When and Why to Use Colloquialism or Archaism
Colloquialisms are best used in informal communication to create a conversational tone and connect with the audience on a personal level, often reflecting contemporary speech patterns. Archaisms serve to evoke a historical atmosphere or add a poetic and formal flavor to writing, typically employed in literature or speeches to convey tradition and timelessness. Choosing between them depends on the desired effect: colloquialisms enhance relatability and immediacy, while archaisms lend weight and a sense of antiquity.
Colloquialism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com