Onomatopoeia brings words to life by imitating natural sounds, making your descriptions vivid and engaging. It enhances storytelling and poetry by creating immersive auditory experiences that resonate with readers. Discover how mastering onomatopoeia can transform your writing in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
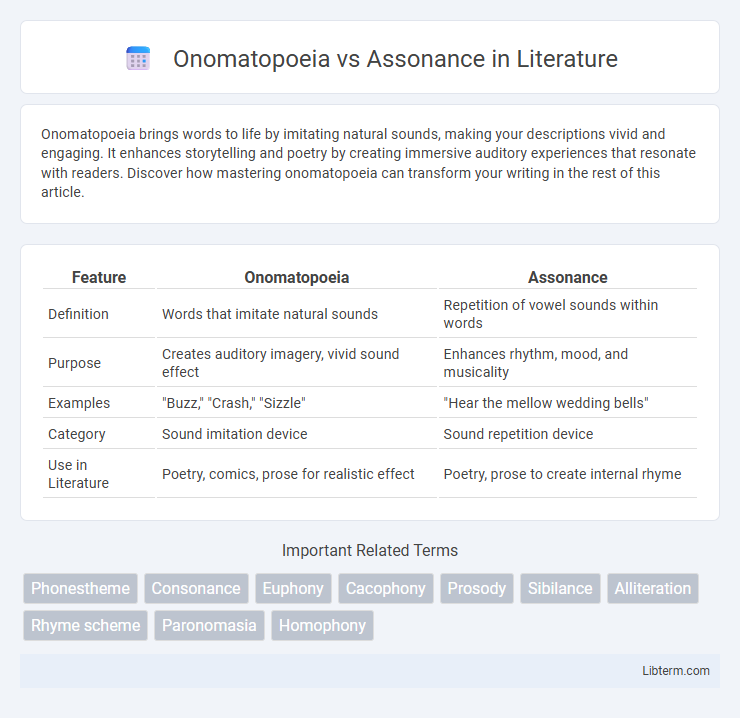
| Feature | Onomatopoeia | Assonance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Words that imitate natural sounds | Repetition of vowel sounds within words |
| Purpose | Creates auditory imagery, vivid sound effect | Enhances rhythm, mood, and musicality |
| Examples | "Buzz," "Crash," "Sizzle" | "Hear the mellow wedding bells" |
| Category | Sound imitation device | Sound repetition device |
| Use in Literature | Poetry, comics, prose for realistic effect | Poetry, prose to create internal rhyme |
Understanding Onomatopoeia: Definition and Examples
Onomatopoeia refers to words that phonetically imitate or resemble the sound they describe, such as "buzz," "clang," and "sizzle," enhancing sensory experience in writing. Examples include animal sounds like "meow" and environmental noises like "crash," which create vivid imagery by directly linking sound and meaning. This literary device differs from assonance, which focuses on vowel sound repetition, by emphasizing sound imitation to evoke auditory effects.
Exploring Assonance: Meaning and Illustration
Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words, creating internal rhyming that enhances the musicality and mood of a text. Unlike onomatopoeia, which mimics natural sounds with words like "buzz" or "clang," assonance relies on vowel harmony, as seen in phrases like "the early bird catches the worm." By emphasizing vowel sounds, assonance contributes to the rhythm and emotional impact of poetry and prose, enriching the reader's sensory experience.
Key Differences Between Onomatopoeia and Assonance
Onomatopoeia refers to words that phonetically imitate or resemble the sound they describe, such as "buzz" or "clang," enhancing auditory imagery in writing. Assonance involves the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words, like the "ee" sound in "fleet" and "free," contributing to the musical quality and rhythm of a line. The key difference lies in onomatopoeia's direct sound imitation versus assonance's focus on vowel sound repetition for poetic effect.
The Role of Sound Devices in Language
Sound devices like onomatopoeia and assonance play crucial roles in enhancing the sensory experience of language by mimicking natural sounds and emphasizing vowel sounds, respectively. Onomatopoeia directly replicates real-world noises, such as "buzz" or "clang," engaging listeners by creating vivid auditory imagery. Assonance, by repeating vowel sounds within words, improves the musicality and rhythm of poetry and prose, aiding memorability and emotional impact.
Onomatopoeia in Literature and Everyday Speech
Onomatopoeia in literature enhances sensory experience by imitating natural sounds, making descriptions vivid and engaging for readers. It appears frequently in poetry and prose, such as words like "buzz," "clang," or "sizzle," which evoke auditory imagery directly connected to their meanings. In everyday speech, onomatopoeic words facilitate expressive communication by mimicking real-world noises, enriching conversations with immediacy and emotional impact.
The Power of Assonance in Poetry and Prose
Assonance, the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words, enhances rhythm and mood in poetry and prose by creating internal echoes that resonate emotionally with readers. Unlike onomatopoeia, which imitates natural sounds directly, assonance subtly shapes tone and melody, enriching imagery and reinforcing themes. Writers strategically employ assonance to draw attention to key phrases, evoke atmosphere, and deepen the sensory experience of their narratives.
Enhancing Writing: When to Use Onomatopoeia or Assonance
Onomatopoeia enhances writing by creating vivid sensory experiences through words that mimic sounds, making scenes more immersive for readers. Assonance, the repetition of vowel sounds, enriches the musical quality of prose or poetry, emphasizing mood and rhythm without direct auditory imitation. Use onomatopoeia to evoke specific sounds and make descriptions more dynamic, while assonance suits subtle emotional or atmospheric effects that enhance lyrical flow.
Common Mistakes: Confusing Onomatopoeia with Assonance
Confusing onomatopoeia with assonance occurs frequently because both involve sound, yet onomatopoeia mimics natural sounds like "buzz" or "clang," while assonance repeats vowel sounds within words. Many mistakenly identify repeated vowel sounds as onomatopoeia, overlooking that assonance creates rhythm rather than imitating noise. Recognizing the distinct role of sonic imitation in onomatopoeia versus vowel repetition in assonance clarifies their unique contributions to literary style.
Famous Works Featuring Onomatopoeia and Assonance
Famous works featuring onomatopoeia include Edgar Allan Poe's "The Bells," where sounds like "tinkle," "clang," and "clangor" mimic the ringing of bells, enhancing the poem's auditory imagery. Assonance is notably present in Walt Whitman's "Song of Myself," utilizing repeated vowel sounds to create musicality and rhythm, such as the elongated "o" sound in phrases like "I loafe and invite my soul." Both literary devices enrich the sensory experience of poetry by emphasizing sound patterns that evoke emotion and imagery.
Creative Exercises to Master Onomatopoeia and Assonance
Creative exercises to master onomatopoeia involve mimicking natural sounds through words like "buzz," "clang," or "sizzle," encouraging writers to evoke vivid auditory imagery. For assonance, focused activities such as crafting sentences or poems that emphasize repeated vowel sounds, like "the light of the fire is a sight to inspire," enhance phonetic rhythm and musicality in writing. Combining both techniques within storytelling or poetry allows for immersive sensory experiences, sharpening a writer's ability to engage readers through sound-focused language.
Onomatopoeia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com