Please provide the specific topic or subject you would like the semantic-optimized paragraph to focus on.
Table of Comparison
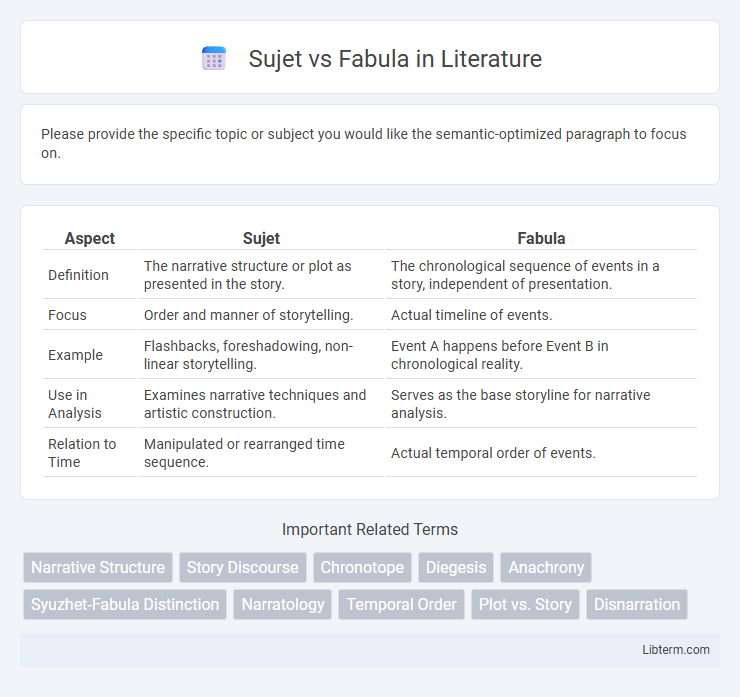
| Aspect | Sujet | Fabula |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The narrative structure or plot as presented in the story. | The chronological sequence of events in a story, independent of presentation. |
| Focus | Order and manner of storytelling. | Actual timeline of events. |
| Example | Flashbacks, foreshadowing, non-linear storytelling. | Event A happens before Event B in chronological reality. |
| Use in Analysis | Examines narrative techniques and artistic construction. | Serves as the base storyline for narrative analysis. |
| Relation to Time | Manipulated or rearranged time sequence. | Actual temporal order of events. |
Introduction to Sujet and Fabula
Sujet refers to the way a narrative is presented or structured, encompassing the sequence and arrangement of events as they appear in the story. Fabula represents the raw chronological timeline of events as they logically occur in the story's world, independent of narrative order. Understanding the distinction between sujet and fabula aids in analyzing narrative techniques and the manipulation of time in storytelling.
Definitions: What Are Sujet and Fabula?
Sujet and fabula are key concepts in narrative theory that distinguish between the structure of a story and its chronological events. Fabula refers to the raw, chronological sequence of events as they occur in the story world, representing the actual timeline. Sujet, on the other hand, is the narrative presentation or plot, which arranges events in a specific order to create thematic or emotional impact for the audience.
Historical Background of the Concepts
The concepts of Sujet and Fabula originated in Russian Formalist theory during the early 20th century, primarily developed by scholars like Viktor Shklovsky and Boris Tomashevsky. Fabula refers to the raw chronological sequence of events in a narrative, while Sujet denotes the structured, artistic presentation of those events within the story. This distinction laid the foundation for modern narratology, influencing subsequent theories on plot and narrative structure.
Key Differences Between Sujet and Fabula
Sujet refers to the structured presentation and order of events as they appear in a narrative, while fabula represents the chronological sequence of events in the story's timeline. The key difference lies in their narrative organization: fabula is the raw, linear storyline, whereas sujet is the manipulated arrangement crafted by the author to create suspense, thematic emphasis, or artistic effect. Understanding this distinction is crucial for analyzing narrative techniques and storytelling methods in literature and film.
The Role of Sujet in Narrative Structure
The sujet in narrative structure organizes events in a deliberate sequence, shaping the audience's perception and engagement with the story. Unlike fabula, which represents the raw chronological events, sujet manipulates time, perspective, and emphasis to create meaning and suspense. This structuring function of sujet is crucial for controlling narrative flow and thematic development in literature and film.
Exploring Fabula: The Underlying Story
Fabula represents the raw chronological sequence of events in a narrative, providing the foundational story without any artistic rearrangement. Exploring fabula reveals the underlying structure that guides the plot's coherence and causal relationships, essential for understanding narrative progression. This concept contrasts with sujet, which is the storytelling approach, emphasizing how events are presented rather than the story itself.
Practical Examples in Literature
Sujet refers to the narrative structure or the way events are presented in a story, while fabula is the chronological sequence of events as they logically occur. In Marcel Proust's "In Search of Lost Time," the fabula follows the narrator's life in temporal order, but the sujet employs flashbacks and non-linear storytelling to reveal memories and emotions. Similarly, in William Faulkner's "The Sound and the Fury," the fabula is the straightforward timeline of the Compson family's decline, whereas the sujet fragments the narrative through different perspectives and time shifts, creating a complex reading experience.
Importance of Sujet and Fabula in Storytelling
Sujet and fabula serve distinct but interrelated roles in storytelling, with fabula representing the raw chronological sequence of events and sujet shaping these events into a structured narrative. The importance of sujet lies in its ability to organize fabula elements, crafting suspense, thematic depth, and emotional impact that captivate audiences. Mastery of sujet enables storytellers to manipulate time, perspective, and information, thereby enriching narrative complexity and enhancing audience engagement.
Implications for Writers and Readers
Understanding the distinction between Sujet and Fabula is crucial for writers to craft compelling narratives by manipulating chronological order and presenting events non-linearly to enhance suspense or thematic depth. Readers engage more actively with the text when they recognize this narrative structure, as piecing together Fabula (the raw story events) from Sujet (the ordered presentation) enriches interpretation and emotional impact. Mastery of Sujet vs Fabula enables storytellers to innovate plot delivery while providing readers with a layered, immersive experience.
Conclusion: Mastering Narrative Through Sujet and Fabula
Mastering narrative structure involves understanding the distinction between sujet and fabula, where fabula represents the raw chronological events of a story and sujet refers to the organized presentation of these events. Effective storytelling depends on manipulating the sujet to enhance engagement, create suspense, or highlight themes without altering the fundamental fabula. This dynamic interplay allows writers to craft compelling narratives that resonate with audiences while maintaining coherence and depth.
Sujet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com