Elision is the omission of a sound or syllable when speaking, commonly used to make speech faster and more natural. This linguistic phenomenon often occurs in contractions, informal speech, and poetry to maintain rhythm or ease of pronunciation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how elision shapes language and impacts communication.
Table of Comparison
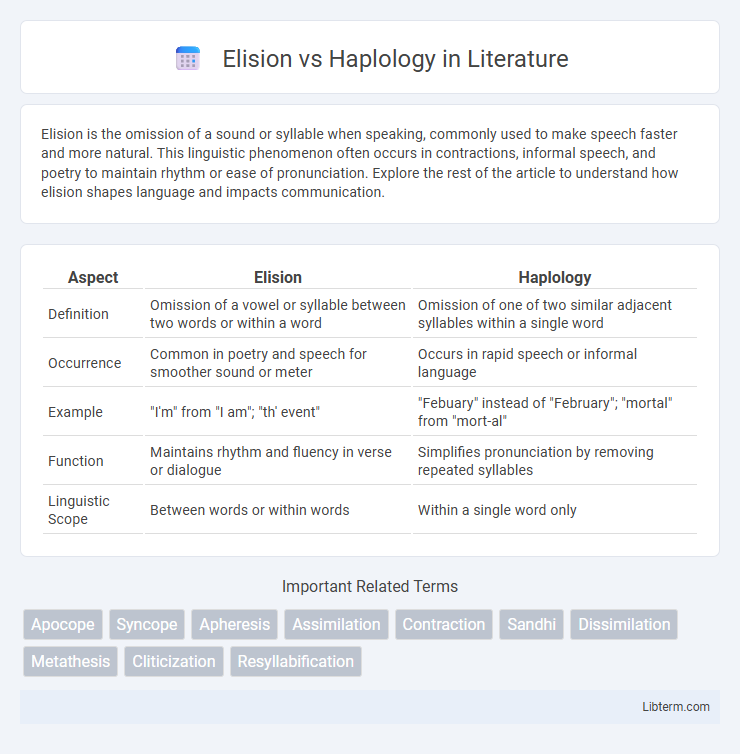
| Aspect | Elision | Haplology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Omission of a vowel or syllable between two words or within a word | Omission of one of two similar adjacent syllables within a single word |
| Occurrence | Common in poetry and speech for smoother sound or meter | Occurs in rapid speech or informal language |
| Example | "I'm" from "I am"; "th' event" | "Febuary" instead of "February"; "mortal" from "mort-al" |
| Function | Maintains rhythm and fluency in verse or dialogue | Simplifies pronunciation by removing repeated syllables |
| Linguistic Scope | Between words or within words | Within a single word only |
Introduction to Elision and Haplology
Elision is a phonological process where one or more sounds are omitted from a word or phrase to facilitate smoother and quicker pronunciation, commonly observed in casual speech and poetry. Haplology specifically involves the omission of one syllable when two similar syllables occur consecutively, often to avoid repetition and simplify articulation. Both elision and haplology contribute significantly to the natural rhythm and efficiency of spoken language by streamlining complex sound patterns.
Defining Elision: Meaning and Examples
Elision is the phonological process where a sound or syllable is omitted from a word or phrase to facilitate smoother and faster speech, often occurring in everyday conversation. Common examples include the omission of the /t/ or /d/ sounds in contractions like "don't" pronounced as /doUnt/ without the clear /t/ sound, or in rapid speech where "camera" is pronounced as /'kaemr@/. This process enhances fluency and naturalness in spoken language by reducing the complexity of pronunciation without altering the meaning.
Understanding Haplology: Concept and Usage
Haplology is a phonological phenomenon where a sequence of similar or identical syllables is shortened by omitting one syllable, often to simplify pronunciation in natural speech, such as "probably" pronounced as "probly." This differs from elision, which involves the omission of sounds between words or within words to facilitate smoother transitions, like dropping the 't' in "next day." Understanding haplology is crucial for linguists studying language evolution and speech patterns, as it reveals natural tendencies in language economy and sound simplification.
Key Differences Between Elision and Haplology
Elision involves the omission of one or more sounds or syllables in a word or phrase to facilitate smoother pronunciation, especially in rapid speech, such as dropping the vowel in "camera" pronounced as "camra." Haplology refers to the linguistic phenomenon where a repeated similar syllable is omitted within a word, like "library" often pronounced as "libry," focusing on the simplification of repetitive sounds. The key difference lies in elision omitting sounds for phonetic convenience across or within words, whereas haplology specifically targets the removal of repeated syllables within a single word to reduce redundancy.
Linguistic Contexts: When Does Elision Occur?
Elision occurs primarily in fast, casual speech where speakers omit vowels or consonants to enhance fluency, such as in contractions like "I'm" instead of "I am." It frequently appears in connected speech, particularly between words, to reduce effort in articulation while maintaining intelligibility. In contrast to haplology, which simplifies repetitive sounds within a single word, elision operates across word boundaries and is heavily influenced by phonetic environment and speech tempo.
Common Scenarios for Haplology in Language
Haplology commonly occurs in language when two identical or similar syllables appear consecutively, leading speakers to omit one for ease of pronunciation, as seen in words like "library" pronounced as "libry." It frequently appears in rapid speech, compound words, and casual conversation where phonetic efficiency is favored. This linguistic phenomenon helps streamline communication by reducing redundant sounds without losing meaning.
Elision in English and Other Languages
Elision in English involves the omission of sounds or syllables for smoother pronunciation, such as in "next day" pronounced as "nex day." Other languages like French frequently use elision, commonly dropping vowels in connected speech, for example, "je aime" becoming "j'aime." Elision contrasts with haplology, which is the elimination of a repeated syllable within a word, not between words.
Haplology Across Different Linguistic Systems
Haplology, the phonological phenomenon where a repeated syllable is omitted for ease of pronunciation, appears across diverse linguistic systems including English, Spanish, and Japanese. In English, haplology is evident in informal speech forms such as "probly" from "probably," while in Spanish, it manifests in contractions like "pa'l" from "para el." Japanese exhibits haplology in rapid speech, simplifying repeated morae to enhance fluency and naturalness.
Impacts of Elision and Haplology on Pronunciation
Elision simplifies pronunciation by omitting sounds or syllables within words, leading to smoother and faster speech patterns, crucial in natural conversational fluency. Haplology, the omission of one of two similar adjacent syllables, reduces redundancy and streamlines phonetic flow, affecting word clarity and recognition. Both processes influence syllable structure and rhythm, shaping regional accents and impacting linguistic comprehension in spoken language.
Conclusion: Importance in Phonological Studies
Elision and haplology are crucial phonological processes that simplify speech by reducing syllable complexity and enhancing fluency. Understanding these phenomena aids linguists in analyzing language evolution, speech patterns, and phonetic variations across dialects. Their study provides valuable insights into natural language optimization and informs both theoretical phonology and applied linguistics.
Elision Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com