Objectivity is essential for unbiased analysis and clear decision-making, ensuring facts are evaluated without personal feelings influencing the outcome. Maintaining objectivity strengthens credibility and promotes fair judgment in any situation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how mastering objectivity can enhance your critical thinking skills.
Table of Comparison
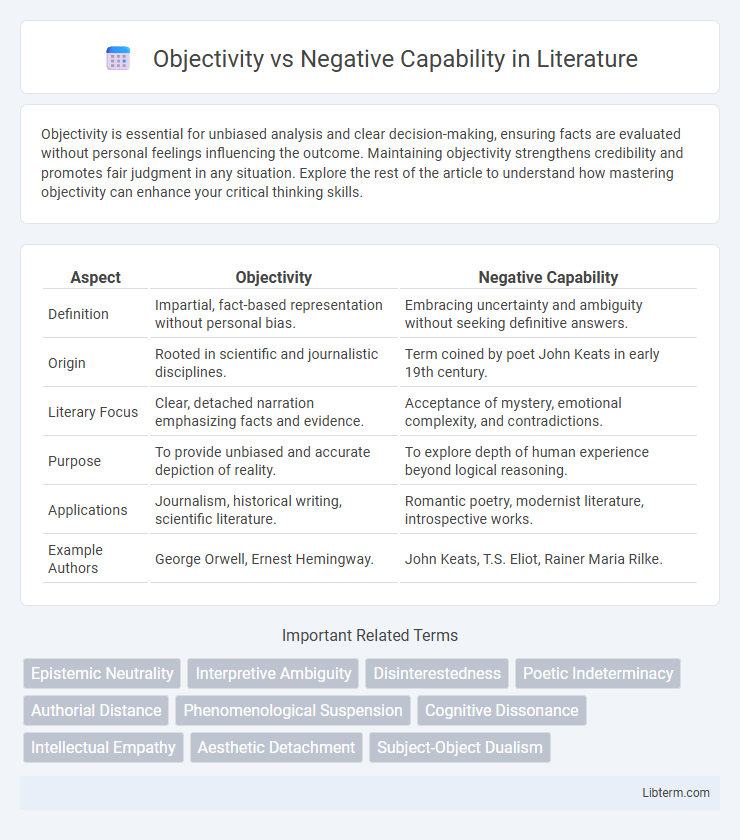
| Aspect | Objectivity | Negative Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Impartial, fact-based representation without personal bias. | Embracing uncertainty and ambiguity without seeking definitive answers. |
| Origin | Rooted in scientific and journalistic disciplines. | Term coined by poet John Keats in early 19th century. |
| Literary Focus | Clear, detached narration emphasizing facts and evidence. | Acceptance of mystery, emotional complexity, and contradictions. |
| Purpose | To provide unbiased and accurate depiction of reality. | To explore depth of human experience beyond logical reasoning. |
| Applications | Journalism, historical writing, scientific literature. | Romantic poetry, modernist literature, introspective works. |
| Example Authors | George Orwell, Ernest Hemingway. | John Keats, T.S. Eliot, Rainer Maria Rilke. |
Understanding Objectivity: A Brief Overview
Objectivity emphasizes impartiality and the pursuit of factual accuracy, minimizing personal biases to achieve a clear representation of reality. It relies on evidence-based analysis and observable data to form conclusions that are universally valid across different perspectives. Understanding objectivity involves recognizing the importance of neutrality in assessing information, which contrasts with the acceptance of ambiguity found in negative capability.
What Is Negative Capability?
Negative Capability, coined by poet John Keats, describes the ability to accept uncertainty, doubt, and ambiguity without the need for definitive answers. Unlike objectivity, which emphasizes impartiality and factual clarity, Negative Capability embraces the complexity of human experience and the unknown. This concept encourages openness to multiple perspectives and a tolerance for unresolved contradictions in creative and intellectual processes.
Historical Context: Origins of the Concepts
Objectivity emerged during the Enlightenment as a foundational principle in science and philosophy, emphasizing unbiased observation and measurable facts. Negative Capability, coined by poet John Keats in the early 19th century, originated as a concept valuing the acceptance of uncertainty and ambiguity in human experience. The historical context of these concepts reflects a transition from strict rationalism to the Romantic embrace of subjective nuance and emotional complexity.
Objectivity in Philosophy and Science
Objectivity in philosophy and science emphasizes unbiased observation and analysis, relying on empirical evidence to uncover truths independent of personal beliefs or emotions. It serves as a critical foundation for the scientific method, ensuring reproducibility and validity in experimental results. Philosophers and scientists strive to detach subjective influence to maintain clarity, precision, and neutrality in the pursuit of knowledge.
Negative Capability in Literature: Keats’ Vision
Negative Capability in literature emphasizes embracing uncertainty and ambiguity, allowing writers like John Keats to explore complex human emotions without the compulsion for logical resolution. Keats' vision champions intuitive perception over rigid objectivity, fostering a poetic depth that thrives on doubt and mystery. This approach enhances literary richness by valuing emotional truth and imaginative openness rather than factual certainty.
Comparing Perspectives: Objectivity vs Negative Capability
Objectivity emphasizes impartial observation and detachment to achieve factual accuracy, while Negative Capability values embracing uncertainty and ambiguity without forcing definitive conclusions. Objectivity relies on measurable evidence and reproducibility, contrasting with Negative Capability's acceptance of emotional and intuitive responses as valid forms of understanding. These differing approaches highlight the tension between analytical clarity and creative openness in interpreting complex realities.
The Role of Emotion and Ambiguity
Emotion shapes the balance between objectivity and negative capability by allowing individuals to embrace ambiguity without the need for definitive answers. This interplay enriches cognitive processes, fostering deeper understanding through emotional resonance rather than strict factual detachment. Ambiguity, embraced through negative capability, challenges rigid objectivity, promoting tolerance for uncertainty and nuanced interpretation.
Practical Applications in Critical Thinking
Objectivity in critical thinking emphasizes unbiased analysis and evidence-based conclusions, essential for making rational decisions in scientific research and legal evaluation. Negative capability encourages embracing uncertainty and ambiguity, fostering creativity and open-mindedness in problem-solving and complex ethical discussions. Practical application involves balancing objective data assessment with tolerance for unknowns to enhance decision-making accuracy and adaptability in dynamic environments.
Balancing Certainty and Uncertainty
Balancing certainty and uncertainty involves navigating the tension between objectivity, which seeks clear facts and measurable truths, and negative capability, the capacity to embrace ambiguity and unresolved questions. Objectivity demands firm evidence and logical analysis to form conclusions, while negative capability nurtures creativity and openness by accepting doubt as an inherent part of understanding. Mastering this balance enhances critical thinking and emotional intelligence, allowing individuals to make informed decisions while remaining adaptable to complexity and change.
Embracing Complexity: Lessons for Modern Discourse
Objectivity demands clear, measurable facts to ensure unbiased understanding, whereas Negative Capability embraces uncertainty and paradox without immediate resolution, valuing complexity and nuance in thought. Modern discourse benefits from integrating Negative Capability to foster open-mindedness amid ambiguous or conflicting information, enhancing empathy and critical reflection. Embracing this balance encourages deeper engagement with multifaceted issues beyond rigid objectivity, cultivating richer dialogue and more inclusive perspectives.
Objectivity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com