Absurdism explores the conflict between humans' search for meaning and the universe's inherent lack of it, highlighting the tension between our desire for purpose and the chaotic nature of existence. This philosophy challenges you to confront uncertainty and embrace the absurd without relying on conventional beliefs or false hope. Dive into the rest of the article to uncover how absurdism shapes our understanding of life and influences modern thought.
Table of Comparison
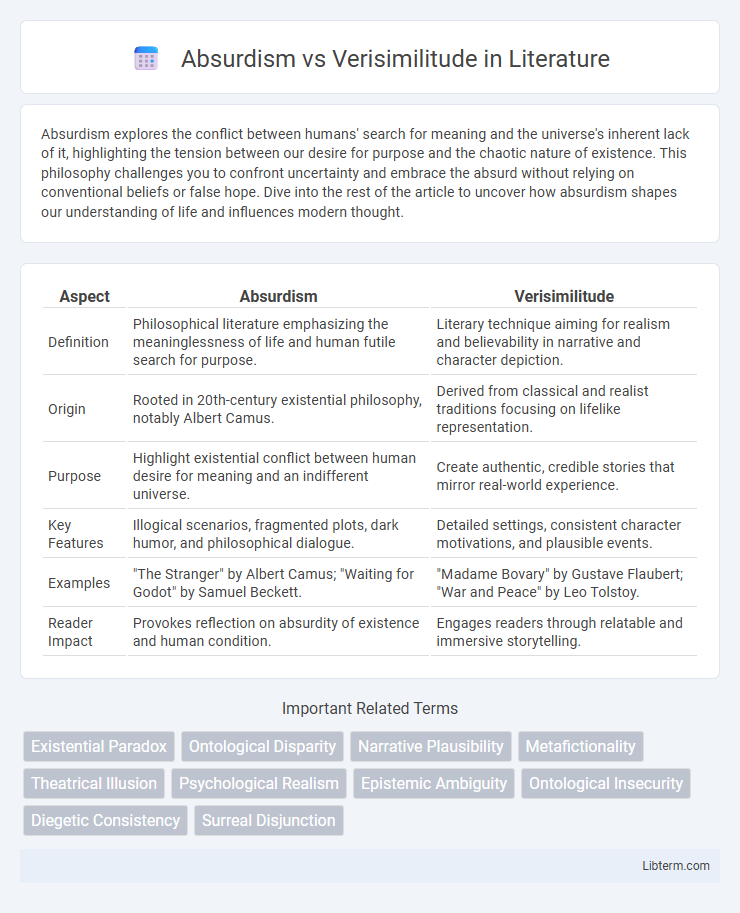
| Aspect | Absurdism | Verisimilitude |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical literature emphasizing the meaninglessness of life and human futile search for purpose. | Literary technique aiming for realism and believability in narrative and character depiction. |
| Origin | Rooted in 20th-century existential philosophy, notably Albert Camus. | Derived from classical and realist traditions focusing on lifelike representation. |
| Purpose | Highlight existential conflict between human desire for meaning and an indifferent universe. | Create authentic, credible stories that mirror real-world experience. |
| Key Features | Illogical scenarios, fragmented plots, dark humor, and philosophical dialogue. | Detailed settings, consistent character motivations, and plausible events. |
| Examples | "The Stranger" by Albert Camus; "Waiting for Godot" by Samuel Beckett. | "Madame Bovary" by Gustave Flaubert; "War and Peace" by Leo Tolstoy. |
| Reader Impact | Provokes reflection on absurdity of existence and human condition. | Engages readers through relatable and immersive storytelling. |
Defining Absurdism: Philosophy and Artistic Expression
Absurdism explores the inherent conflict between humans' search for meaning and the universe's indifferent silence, emphasizing themes of existential uncertainty and irrationality. Artistic expression in Absurdism utilizes illogical scenarios, fragmented narratives, and paradoxes to reflect life's inherent meaninglessness and provoke existential reflection. This philosophy challenges traditional notions of coherence and purpose found in verisimilitude, which strives for realistic representation and truthful resemblance to life.
Understanding Verisimilitude: The Pursuit of Realism
Verisimilitude in literature and art emphasizes the accurate representation of reality by creating believable characters, settings, and events that resonate with the audience's experience. This pursuit of realism aims to establish a coherent and consistent narrative world, fostering emotional engagement and suspension of disbelief. In contrast to Absurdism, which highlights the irrational and chaotic nature of existence, verisimilitude seeks to mirror the logical structures and plausible outcomes of real life.
Origins and Historical Context of Absurdism
Absurdism emerged in the mid-20th century, primarily influenced by the existential philosophy of Albert Camus and the post-World War II disillusionment with traditional values and meaning. Rooted in the historical context of the chaotic aftermath of war and rapid societal changes, Absurdism emphasizes the conflict between humans' search for purpose and the universe's inherent meaninglessness. This contrasts with Verisimilitude, which prioritizes lifelike realism and plausibility in literature and art, reflecting classical and Enlightenment ideals of order and reason.
The Roots of Verisimilitude in Literary Tradition
Verisimilitude in literary tradition traces back to ancient Greek and Roman texts where adherence to believable events and character motivations was essential for audience engagement. This principle emphasizes the importance of realistic representation within fiction, contrasting sharply with the thematic ambiguity and irrationality found in Absurdism. Rooted in Aristotelian poetics, verisimilitude sustains narrative coherence by mirroring plausible human experiences and societal norms.
Absurdism in Literature, Theatre, and Film
Absurdism in literature, theatre, and film explores the inherent meaninglessness of life through illogical plots, fragmented dialogue, and existential themes, challenging traditional narrative structures that emphasize verisimilitude or realistic representation. Works like Samuel Beckett's *Waiting for Godot* and Albert Camus' essays exemplify how absurdist art confronts human isolation and the absurd condition with dark humor and paradox. This genre disrupts conventional expectations by prioritizing existential inquiry over plausible storytelling, contrasting sharply with verisimilitude's focus on lifelike detail and coherence.
Techniques and Tools for Achieving Verisimilitude
Verisimilitude in literature relies on detailed characterization, realistic dialogue, and setting authenticity to create a believable narrative world. Techniques such as consistent internal logic, accurate historical or cultural references, and sensory-rich descriptions enhance the reader's suspension of disbelief. Tools including thorough research, precise language, and narrative cohesion ensure the story convincingly mirrors real life, contrasting the intentional irrationality found in Absurdism.
Central Themes: Meaninglessness vs. Believability
Absurdism explores the inherent meaninglessness of life and the human struggle to find purpose in an indifferent universe, highlighting themes of existential confusion and the clash between human desire for significance and life's inherent randomness. Verisimilitude emphasizes the importance of believability and logical coherence in storytelling, ensuring narratives reflect plausible realities that audiences can relate to emotionally and intellectually. Central themes contrast Absurdism's focus on existential chaos with Verisimilitude's commitment to realistic representation and narrative authenticity.
Major Figures: Absurdist and Realist Creators
Major figures in Absurdism include Albert Camus and Samuel Beckett, who explore existential themes through illogical, surreal narratives that emphasize the meaninglessness of life. In contrast, Realist creators like Gustave Flaubert and Henrik Ibsen focus on verisimilitude by portraying everyday life with detailed, authentic characters and situations reflecting societal truths. These distinct approaches highlight the tension between depicting life's absurdity versus striving for objective reality in literature and theater.
Audience Experience and Interpretation
Absurdism deliberately challenges audience expectations by presenting irrational scenarios that defy logical interpretation, prompting viewers to confront the meaninglessness of existence. Verisimilitude emphasizes a lifelike representation, allowing audiences to immerse themselves in familiar realities and derive coherent, relatable interpretations. The contrast between these approaches shapes the audience experience by either fostering existential reflection through ambiguity or encouraging empathy through believable narratives.
Modern Relevance: Clash and Synthesis in Contemporary Art
Absurdism challenges conventional reality by embracing irrationality and existential uncertainty, while verisimilitude strives for lifelike accuracy and believable representation in contemporary art. This clash manifests in artworks that juxtapose surreal, illogical elements with realistic details, creating a tension that reflects modern societal complexities and fragmented identities. The synthesis of these approaches fosters innovative expressions that question objective truth, highlighting the fluid boundaries between reality and perception in today's cultural landscape.
Absurdism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com