Decentralization distributes authority and decision-making power away from a central authority, fostering increased efficiency, transparency, and innovation. It empowers individuals and organizations to take ownership of processes, enhancing responsiveness and reducing bottlenecks. Discover how decentralization can transform your operations and why it matters in today's evolving landscape by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
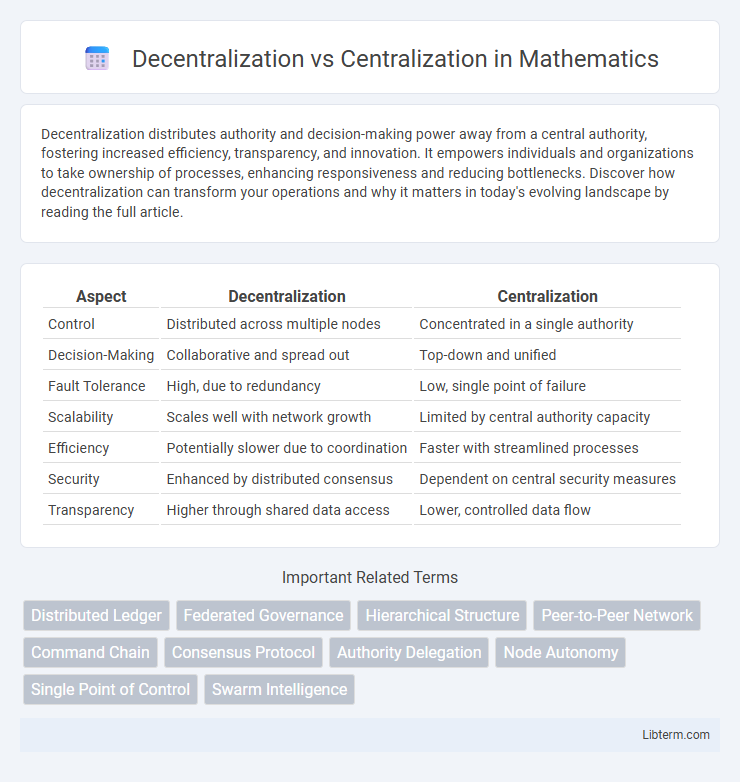
| Aspect | Decentralization | Centralization |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Distributed across multiple nodes | Concentrated in a single authority |
| Decision-Making | Collaborative and spread out | Top-down and unified |
| Fault Tolerance | High, due to redundancy | Low, single point of failure |
| Scalability | Scales well with network growth | Limited by central authority capacity |
| Efficiency | Potentially slower due to coordination | Faster with streamlined processes |
| Security | Enhanced by distributed consensus | Dependent on central security measures |
| Transparency | Higher through shared data access | Lower, controlled data flow |
Understanding Decentralization and Centralization
Decentralization distributes decision-making authority across multiple levels, enhancing flexibility and local responsiveness, while centralization consolidates power within a central authority to ensure uniformity and streamlined control. Understanding decentralization involves recognizing its role in empowering lower organizational tiers to adapt and innovate, whereas centralization emphasizes standardized processes and cohesive strategic direction. Both structures impact organizational efficiency, communication flow, and control mechanisms depending on the context and goals.
Key Differences Between Decentralized and Centralized Systems
Decentralized systems distribute decision-making authority across multiple nodes or locations, enhancing resilience, scalability, and local autonomy, while centralized systems concentrate control within a single authority, allowing for streamlined management and faster decision execution. Key differences include the level of control, where centralized systems rely on a central point that can become a bottleneck or single point of failure, contrasted with decentralized architectures that promote transparency and fault tolerance by avoiding single points of control. Security models also differ, with centralized systems often easier to protect against external threats but vulnerable to insider risks, whereas decentralized systems leverage consensus mechanisms and distributed ledgers to improve robustness against attacks.
Historical Evolution of Organizational Structures
Organizational structures have evolved from highly centralized models during the Industrial Revolution to more decentralized forms in the digital age, reflecting shifts in technology and management philosophy. Early centralization emphasized hierarchical control and efficiency in large manufacturing enterprises, while modern decentralization promotes agility, innovation, and employee empowerment. This historical evolution aligns with the increasing complexity of global markets and the need for rapid decision-making at multiple organizational levels.
Benefits of Centralization
Centralization streamlines decision-making processes by consolidating authority, which enhances organizational efficiency and consistency. It enables stronger control over resources, ensuring alignment with strategic goals and reducing duplication of efforts. Centralized systems facilitate faster implementation of policies and uniformity across departments, improving overall coordination and accountability.
Advantages of Decentralization
Decentralization enhances organizational flexibility by distributing decision-making authority closer to operational levels, leading to faster responses and increased innovation. It promotes employee empowerment and accountability, fostering a more motivated workforce and improving problem-solving efficiency. Furthermore, decentralization reduces the risks associated with single points of failure, ensuring greater resilience and adaptability in dynamic business environments.
Challenges of Centralized Approaches
Centralized approaches face significant challenges including single points of failure, vulnerability to cyberattacks, and limited scalability. These systems often lead to bottlenecks in decision-making and data processing, hindering operational efficiency. Concentrating control increases risks of data breaches and censorship, compromising system reliability and trustworthiness.
Potential Risks of Decentralized Models
Decentralized models face potential risks such as security vulnerabilities due to multiple access points, leading to increased exposure to cyberattacks and data breaches. The lack of a unified control system can result in inconsistent decision-making and slower response times during critical incidents. Additionally, governance challenges arise from dispersed authority, complicating coordination and accountability across diverse stakeholders.
Decentralization vs Centralization in Technology
Decentralization in technology distributes control across multiple nodes, enhancing security, resilience, and transparency, as seen in blockchain networks and peer-to-peer systems. Centralization consolidates authority in a single entity or server, enabling faster decision-making and simplified management but increasing vulnerability to single points of failure. The balance between decentralization and centralization impacts scalability, data privacy, and system robustness in modern digital infrastructures.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Decentralization in blockchain technology is exemplified by Bitcoin, where transaction validation is distributed across a global network of miners, ensuring security and resistance to censorship. In contrast, centralization is visible in traditional banking systems like JPMorgan Chase, where a single authority controls transaction verification and data management, enabling efficiency but creating single points of failure. Case studies in organizations such as Walmart demonstrate hybrid models, using blockchain for decentralized supply chain transparency while maintaining centralized control over proprietary data.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Organization
Choosing the right structure for your organization depends on factors like size, industry, and decision-making speed requirements. Decentralization empowers individual departments or teams with authority, enhancing flexibility and innovation, while centralization consolidates decision-making to ensure uniformity and efficient resource management. Evaluating organizational goals and operational complexity helps determine whether a decentralized approach with delegated responsibilities or a centralized model focused on control better supports growth and performance.
Decentralization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com