Connectedness is essential for maintaining strong relationships and fostering collaboration in both personal and professional settings. Your ability to stay linked through digital and face-to-face interactions enhances communication and promotes shared understanding. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical tips for staying connected in an increasingly digital world.
Table of Comparison
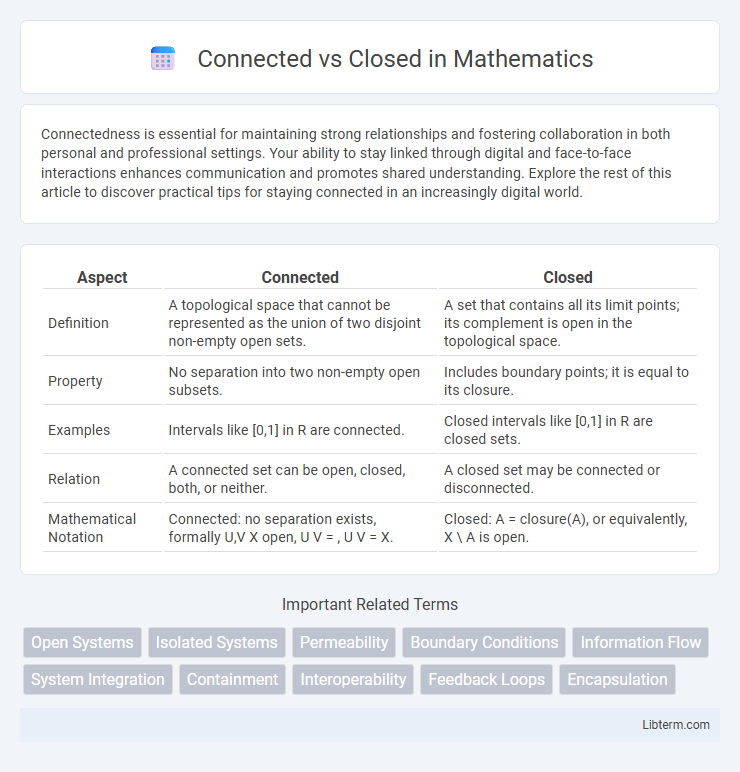
| Aspect | Connected | Closed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A topological space that cannot be represented as the union of two disjoint non-empty open sets. | A set that contains all its limit points; its complement is open in the topological space. |
| Property | No separation into two non-empty open subsets. | Includes boundary points; it is equal to its closure. |
| Examples | Intervals like [0,1] in R are connected. | Closed intervals like [0,1] in R are closed sets. |
| Relation | A connected set can be open, closed, both, or neither. | A closed set may be connected or disconnected. |
| Mathematical Notation | Connected: no separation exists, formally U,V X open, U V = , U V = X. | Closed: A = closure(A), or equivalently, X \ A is open. |
Introduction to Connected vs Closed
Connected systems enable seamless data exchange and interoperability across multiple devices and platforms, enhancing user experience and operational efficiency. Closed systems restrict access to their components, promoting security and control but limiting flexibility and integration capabilities. Understanding the difference helps businesses and developers choose the right architecture based on their goals for scalability, security, and connectivity.
Understanding Connected Systems
Connected systems facilitate real-time data exchange and collaboration across multiple devices and platforms, enabling seamless integration and enhanced user experiences. These systems rely on cloud computing, IoT technology, and APIs to provide continuous connectivity and scalable solutions. Understanding connected systems is essential for optimizing operational efficiency, improving decision-making, and driving digital transformation in various industries.
Defining Closed Systems
Closed systems are defined by their lack of interaction with external environments, maintaining internal processes without exchanging matter or energy. In a closed system, boundaries are rigid, preventing external influence and ensuring stability and predictability within the system's operations. This contrasts with connected systems, which dynamically interact and adapt through continuous external inputs and feedback loops.
Key Differences Between Connected and Closed
Connected systems enable seamless data exchange across multiple platforms, fostering collaboration and real-time updates, while closed systems operate in isolation with restricted data flow, enhancing security but limiting interoperability. Connected environments prioritize openness and integration, supporting APIs and third-party extensions, whereas closed environments emphasize control and proprietary standards. The key difference lies in accessibility and flexibility: connected models drive innovation through connectivity, whereas closed models offer stringent governance and protection.
Benefits of Connected Environments
Connected environments enable seamless data exchange between multiple devices and systems, enhancing operational efficiency and real-time decision-making. They support scalability and flexibility by integrating diverse technologies, driving innovation and improved user experiences. Increased connectivity fosters collaboration across departments, leading to optimized workflows and reduced downtime.
Advantages of Closed Systems
Closed systems offer enhanced security by limiting external access, reducing the risk of cyberattacks and unauthorized data breaches. They provide greater control over system components and configurations, ensuring stability and consistent performance in critical applications. These systems also simplify compliance with regulatory standards, as the controlled environment minimizes vulnerabilities and facilitates easier monitoring.
Common Use Cases for Each Approach
Connected systems are commonly used in retail environments where real-time inventory updates and seamless customer interactions are essential for enhancing user experience and operational efficiency. Closed systems find frequent application in security-sensitive industries like banking, where strict access control and data integrity are prioritized to prevent unauthorized access and ensure compliance. Both approaches are chosen based on specific operational needs, with connected systems favoring flexibility and integration, while closed systems emphasize control and protection.
Security Considerations: Connected vs Closed
Connected systems enable real-time data sharing and remote access, increasing exposure to cybersecurity threats like hacking and data breaches. Closed systems limit external connectivity, reducing vulnerabilities but potentially hindering timely updates and collaboration. Choosing between connected and closed architectures requires balancing accessibility with implementing robust security protocols such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular patching.
Future Trends in System Architecture
Future trends in system architecture emphasize a shift towards connected systems that enhance interoperability through open interfaces and cloud integration, enabling real-time data sharing across diverse platforms. Closed systems maintain strict security and control, favoring proprietary protocols and isolated environments to protect sensitive information. Emerging hybrid models aim to balance connectivity and security by incorporating edge computing and blockchain technologies to optimize performance and trustworthiness.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Choosing between a connected and closed system depends on your specific needs for flexibility and security. Connected systems offer seamless integration and data sharing, ideal for collaborative environments requiring real-time updates. Closed systems prioritize control and data protection, suitable for sensitive operations demanding strict access and minimal external interaction.
Connected Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com