Independence is the foundation of personal freedom, enabling you to make decisions and live life on your own terms. Cultivating independence strengthens self-confidence and empowers you to overcome challenges without relying on others. Discover how embracing independence can transform your life by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
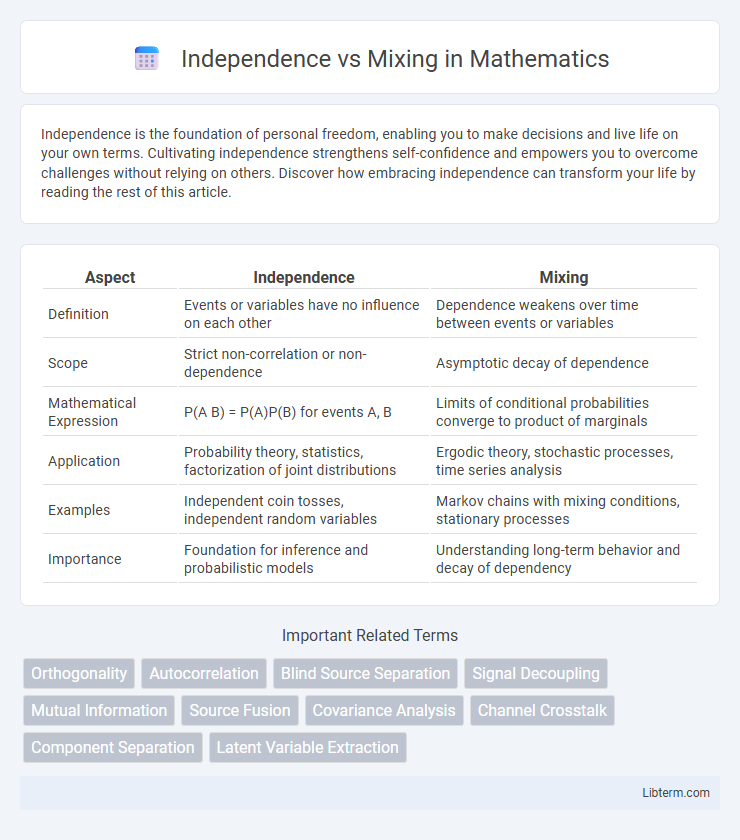
| Aspect | Independence | Mixing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Events or variables have no influence on each other | Dependence weakens over time between events or variables |
| Scope | Strict non-correlation or non-dependence | Asymptotic decay of dependence |
| Mathematical Expression | P(A B) = P(A)P(B) for events A, B | Limits of conditional probabilities converge to product of marginals |
| Application | Probability theory, statistics, factorization of joint distributions | Ergodic theory, stochastic processes, time series analysis |
| Examples | Independent coin tosses, independent random variables | Markov chains with mixing conditions, stationary processes |
| Importance | Foundation for inference and probabilistic models | Understanding long-term behavior and decay of dependency |
Understanding Independence and Mixing
Independence in probability theory refers to the condition where the occurrence of one event does not affect the probability of another event, mathematically expressed as P(A B) = P(A)P(B). Mixing, a stronger property, indicates that the dependence between events or random variables diminishes over time or space, ensuring asymptotic statistical independence despite initial dependence. Understanding these concepts is crucial in fields like ergodic theory and stochastic processes, where independence simplifies analysis, while mixing provides insights into long-term behavior and convergence.
Historical Perspectives on Independence vs Mixing
Historical perspectives on independence versus mixing reveal complex debates surrounding cultural identity and social cohesion, particularly during colonial and post-colonial periods. Movements for national independence often emphasized preserving distinct ethnic or cultural identities while opposing mixing, which was sometimes viewed as diluting sovereignty or heritage. Conversely, some historical narratives highlight how mixing, through migration and trade, fostered cultural innovation and hybrid identities that challenged rigid notions of independence.
The Psychological Impact of Independence
The psychological impact of independence fosters a strong sense of self-efficacy, autonomy, and emotional resilience. Independence supports personal growth by encouraging decision-making skills and self-reliance, which enhances mental well-being and reduces anxiety. In contrast, excessive mixing or dependence can dilute individuality and hinder the development of intrinsic motivation and confidence.
Social Dynamics of Mixing in Communities
Social dynamics of mixing in communities influence trust, cooperation, and the exchange of ideas across diverse groups. Independence fosters unique identities and autonomy, yet mixing promotes social cohesion and collective problem-solving by bridging cultural and social divides. Effective community development balances individual independence with inclusive interaction to enhance social capital and resilience.
Benefits of Embracing Independence
Embracing independence fosters critical thinking and self-reliance, enabling individuals to make informed decisions without undue influence from external factors. It enhances personal growth by encouraging autonomy and responsibility, which contribute to stronger problem-solving skills. Independence also promotes authentic creativity, allowing unique perspectives to flourish free from conformity constraints.
Advantages of Mixing and Collaboration
Mixing and collaboration enhance creativity by blending diverse skills and perspectives, leading to innovative solutions and richer content. Collaborative environments enable efficient problem-solving through shared expertise, which increases productivity and accelerates project completion. The synergy created by mixing talents fosters learning opportunities and builds stronger networks, promoting continuous growth and success.
Challenges of Maintaining Independence
Maintaining independence presents challenges such as resource constraints, potential isolation from collaborative opportunities, and difficulties in scaling operations effectively. Organizations often struggle to balance autonomy with the need for external partnerships and market competitiveness. Ensuring consistent quality and innovation without external support requires robust internal processes and strong leadership commitment.
Common Barriers to Successful Mixing
Common barriers to successful mixing in audio production include phase cancellation, frequency masking, and poor balance between instrument levels. Inadequate separation of sound sources often leads to muddiness and lack of clarity, while improper equalization can cause overlapping frequencies that diminish overall mix quality. Addressing these issues through strategic panning, dynamic processing, and careful frequency management ensures a cleaner, more cohesive mix.
Balancing Independence with Social Integration
Balancing independence with social integration involves fostering individual autonomy while maintaining meaningful connections within a community. Encouraging self-reliance supports personal growth and decision-making, whereas social integration enhances emotional well-being and collaborative opportunities. Effective strategies integrate personalized support systems that promote both independent functioning and active participation in social environments.
Choosing the Right Approach: Independence or Mixing?
Choosing between independence and mixing depends on the specific use case and data relationships; independence assumes variables do not influence each other, ideal for simpler models or when reducing computational complexity. Mixing approaches combine independent and dependent factors to capture interactions, enhancing predictive accuracy in complex datasets with intertwined variables. Evaluating model goals, data structure, and performance requirements guides the selection of the optimal approach for statistical modeling or machine learning tasks.
Independence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com