Irregular patterns often defy conventional rules, making them challenging to predict or categorize. Understanding these anomalies can improve your ability to manage unexpected situations effectively. Explore the rest of the article to uncover practical strategies for dealing with irregularities.
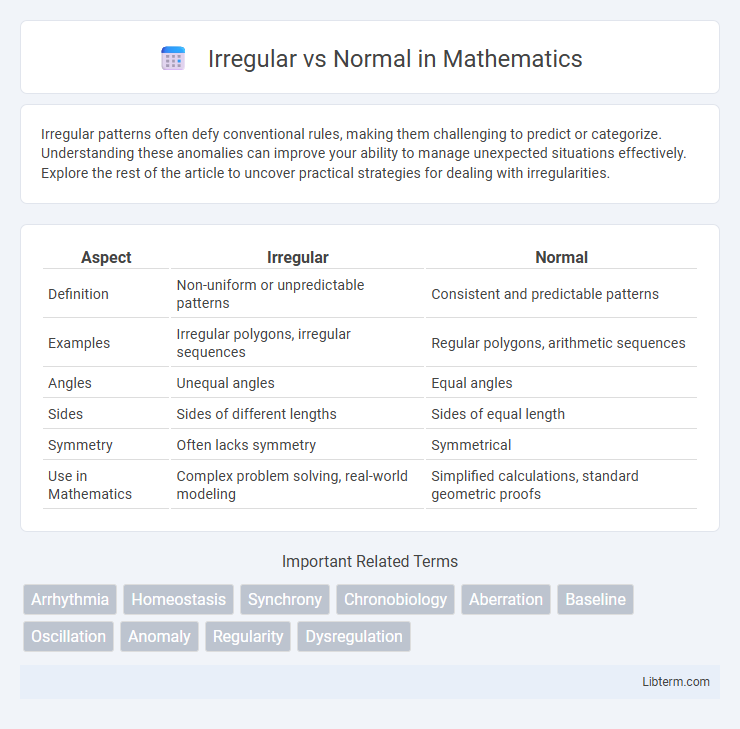
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Irregular | Normal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-uniform or unpredictable patterns | Consistent and predictable patterns |
| Examples | Irregular polygons, irregular sequences | Regular polygons, arithmetic sequences |
| Angles | Unequal angles | Equal angles |
| Sides | Sides of different lengths | Sides of equal length |
| Symmetry | Often lacks symmetry | Symmetrical |
| Use in Mathematics | Complex problem solving, real-world modeling | Simplified calculations, standard geometric proofs |
Understanding Irregular vs Normal: Key Definitions
Irregular refers to patterns or occurrences that deviate from established rules, such as irregular verbs in language that do not follow standard conjugation patterns, while normal denotes conformity to common or expected rules. Understanding irregular versus normal involves recognizing the predictable structure of regular forms compared to exceptions requiring memorization or specialized knowledge. Key definitions highlight the importance of identifying these distinctions for effective communication and comprehension in linguistic contexts.
Common Examples of Irregular and Normal Patterns
Common examples of irregular patterns include verbs like "go" (went, gone), "buy" (bought, bought), and "see" (saw, seen), which deviate from standard conjugation rules. Normal patterns follow predictable rules, such as adding "-ed" to form the past tense in "walk" (walked) and "play" (played). Understanding these distinctions helps in mastering English verb conjugation and improving communication accuracy.
Causes and Factors Influencing Irregularity
Irregular patterns often stem from unpredictable causes such as human error, inconsistent data entry, or environmental fluctuations that disrupt normal processes. Factors influencing irregularity include system complexity, lack of standardized protocols, and external variables like market volatility or natural disasters. Understanding these drivers helps in designing more robust systems that minimize irregular occurrences and improve overall reliability.
Impact of Irregular vs Normal on Daily Life
Irregular patterns in daily routines disrupt circadian rhythms, leading to decreased productivity and increased stress levels compared to normal, consistent schedules. Maintaining regular habits enhances mental clarity, physical health, and overall well-being by stabilizing sleep cycles and hormone regulation. Studies show individuals with stable routines experience better focus and resilience in managing daily tasks and unexpected challenges.
Identifying Irregularities: Tips and Techniques
Identifying irregularities involves recognizing patterns that deviate from standard forms, such as irregular verbs that do not follow typical conjugation rules. Techniques include memorizing common irregular forms, using contextual clues within sentences, and practicing with frequent exposure to irregular patterns in reading and speaking. Analytical methods like comparing base forms to past tense or plural variations help in distinguishing irregularities from normal forms effectively.
Benefits of Maintaining Normal Patterns
Maintaining normal patterns in daily activities supports consistent circadian rhythms, enhancing sleep quality and overall cognitive function. Stable routines promote metabolic health, reducing risks of obesity and diabetes by regulating hormone levels and appetite control. Regular behavioral patterns also improve mental resilience, minimizing stress and anxiety through predictable and balanced lifestyle habits.
Health Implications: Irregular vs Normal
Irregular health patterns, such as inconsistent sleep schedules or erratic eating habits, can lead to increased risks of chronic illnesses like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and obesity. Normal, regular routines support optimal metabolic function, hormone regulation, and immune system efficiency. Maintaining consistent health behaviors promotes long-term well-being and reduces the likelihood of developing lifestyle-related health conditions.
Strategies for Managing Irregular Patterns
Effective strategies for managing irregular patterns involve identifying and categorizing exceptions early to create customized rules that accommodate variability. Leveraging machine learning algorithms can improve the accuracy of recognizing irregularities by analyzing large datasets and adapting to new patterns. Maintaining comprehensive databases of irregular instances supports ongoing refinement of predictive models and enhances overall pattern management efficiency.
When to Seek Help for Irregularities
Seek help for irregularities when symptoms such as unexpected bleeding, prolonged cycles beyond 35 days, or severe pain occur, as these may signal underlying health issues like hormonal imbalances or reproductive disorders. Persistent irregularities disrupting daily life or fertility concerns warrant evaluation by a healthcare provider to diagnose conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid dysfunction. Early intervention improves management outcomes and reduces risks associated with untreated menstrual irregularities.
Conclusion: Striking a Balance Between Irregular and Normal
Striking a balance between irregular and normal patterns enhances linguistic adaptability and comprehension, enabling effective communication across diverse contexts. Regular forms provide consistency and ease of learning, while irregular forms enrich language with historical depth and nuance. Embracing both allows for a dynamic and flexible language system that meets practical usage demands and preserves cultural identity.
Irregular Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com