Becoming is a powerful journey of self-discovery and personal transformation that allows you to embrace your true potential. Exploring the stages of becoming helps you understand the changes necessary for growth and fulfillment. Dive into the rest of the article to uncover how you can embark on your own path of becoming.
Table of Comparison
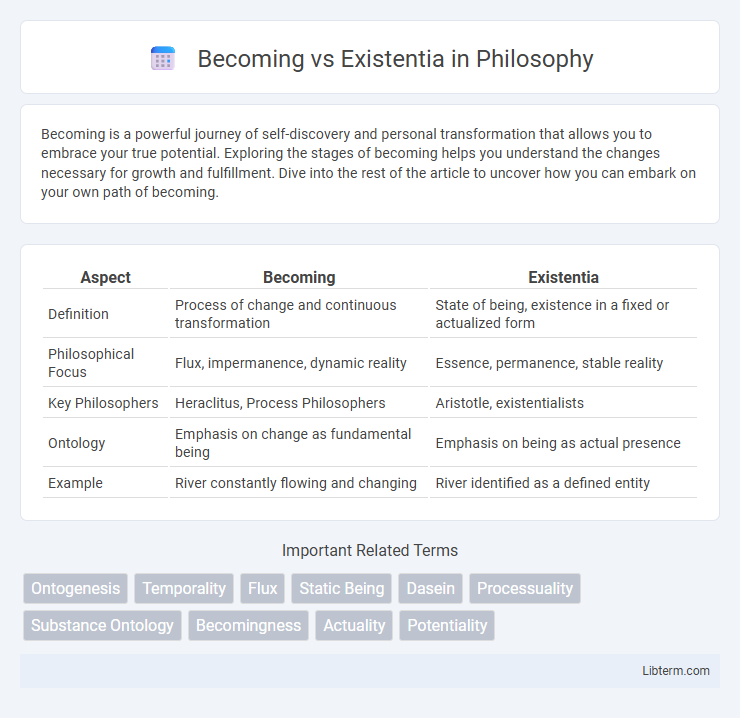
| Aspect | Becoming | Existentia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of change and continuous transformation | State of being, existence in a fixed or actualized form |
| Philosophical Focus | Flux, impermanence, dynamic reality | Essence, permanence, stable reality |
| Key Philosophers | Heraclitus, Process Philosophers | Aristotle, existentialists |
| Ontology | Emphasis on change as fundamental being | Emphasis on being as actual presence |
| Example | River constantly flowing and changing | River identified as a defined entity |
Defining Becoming and Existentia
Becoming refers to the continuous process of change and transformation inherent in existence, emphasizing the dynamic nature of reality as it evolves through time. Existentia, or existence, denotes the state of being actual or present, highlighting the static condition of entities as they are perceived in a given moment. Together, these concepts underscore the philosophical tension between flux and permanence in understanding the nature of being.
Philosophical Roots: Becoming in Ancient Thought
Becoming in ancient philosophy is deeply rooted in Heraclitus's doctrine of flux, which asserts that everything is in constant change and nothing remains static. This contrasts with Parmenides' concept of Existentia, emphasizing an unchanging, eternal reality. The philosophical tension between Becoming and Existentia forms the foundation of metaphysical debates on the nature of reality and existence.
The Essence of Existentia in Philosophy
The essence of Existentia in philosophy centers on the inherent reality and presence of being as it manifests in concrete existence, contrasting with the transient and dynamic nature of Becoming. Existentia emphasizes the fixed and enduring qualities that define an entity's true nature beyond temporal changes. Philosophers like Heidegger explore Existentia as the authentic mode of being, grounding identity in presence rather than continuous flux.
Key Differences: Process vs. State
Becoming emphasizes continuous change and dynamic processes, highlighting transformation and development over time, while Existentia refers to a stable, enduring state of being or existence. The key difference lies in Becoming as movement toward a future condition, contrasted with Existentia as the present reality or actualized state. Understanding these concepts is crucial in philosophy, especially in metaphysics and ontology, where process versus state analysis informs interpretations of existence and identity.
Major Thinkers on Becoming
Major thinkers on Becoming, such as Heraclitus, emphasize the constant flux and transformation inherent in existence, asserting that reality is characterized by perpetual change rather than fixed being. Friedrich Nietzsche further develops this concept by highlighting the dynamic process of becoming as essential to life, opposing static notions of identity and emphasizing self-overcoming and continuous growth. Henri Bergson introduces the idea of elan vital, a vital force driving evolution and creativity, underscoring the primacy of becoming in the unfolding of life and consciousness.
Existentialism and the Concept of Existentia
Existentialism emphasizes the concept of Existentia, referring to the concrete, lived experience of being, which contrasts with the abstract potentiality of Becoming. Existentia involves the individual's authentic existence, defined through choices and actions that give meaning to life in an otherwise indifferent universe. This philosophy centers on the tension between the fluidity of Becoming and the fixed reality of Existentia, highlighting personal responsibility and self-definition.
Real-World Implications: Change vs. Being
Becoming emphasizes dynamic transformation, reflecting the continuous evolution in natural and social systems where adaptation drives progress. Existentia centers on stability and the essence of being, providing a foundation for identity and persistence amid change. Understanding the balance between becoming and existentia informs decision-making in fields such as psychology, organizational development, and philosophy of science, highlighting the tension between growth and preservation.
How Becoming Shapes Identity
Becoming shapes identity by emphasizing continuous growth and transformation rather than static existence, highlighting the fluid nature of selfhood. This process-driven view underlines how experiences, choices, and external influences actively construct and reconstruct personal identity over time. The dynamic interplay between potentiality and actualization in becoming challenges fixed notions of identity, fostering adaptability and self-awareness.
The Role of Existentia in Human Experience
Existentia anchors human experience by providing a stable foundation of being from which personal identity and consciousness arise. This state of existence shapes perception, grounding individuals in reality and enabling meaningful interaction with their environment. Understanding Existentia is crucial for exploring concepts of self-awareness and the continuity of human life.
Bridging the Divide: Integrating Becoming and Existentia
Bridging the divide between Becoming and Existentia requires synthesizing dynamic change with static being to create a holistic understanding of existence. Integrating the transformative processes of Becoming with the stable essence of Existentia enables a framework where identity evolves while maintaining continuity. This fusion fosters a dialectical approach that reconciles flux and permanence crucial for philosophical and ontological discourse.
Becoming Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com