Existentialism explores the meaning of life by focusing on individual freedom, choice, and responsibility in an often absurd or indifferent universe. This philosophical movement emphasizes authentic living and personal experience as the path to understanding existence. Dive into the rest of this article to discover how existentialism can influence Your perspective on life.
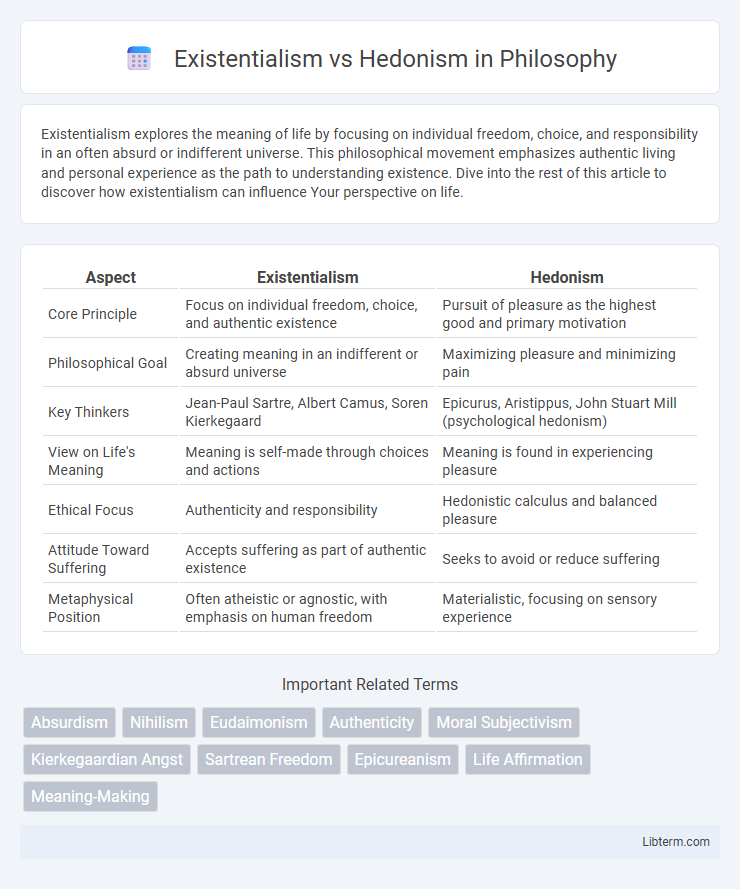
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Existentialism | Hedonism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Focus on individual freedom, choice, and authentic existence | Pursuit of pleasure as the highest good and primary motivation |
| Philosophical Goal | Creating meaning in an indifferent or absurd universe | Maximizing pleasure and minimizing pain |
| Key Thinkers | Jean-Paul Sartre, Albert Camus, Soren Kierkegaard | Epicurus, Aristippus, John Stuart Mill (psychological hedonism) |
| View on Life's Meaning | Meaning is self-made through choices and actions | Meaning is found in experiencing pleasure |
| Ethical Focus | Authenticity and responsibility | Hedonistic calculus and balanced pleasure |
| Attitude Toward Suffering | Accepts suffering as part of authentic existence | Seeks to avoid or reduce suffering |
| Metaphysical Position | Often atheistic or agnostic, with emphasis on human freedom | Materialistic, focusing on sensory experience |
Understanding Existentialism: Core Principles
Existentialism centers on individual freedom, authentic choices, and the search for meaning in an indifferent universe, emphasizing personal responsibility and self-awareness. It rejects predetermined essence, advocating that existence precedes essence, meaning humans define their own nature through actions. Key figures like Jean-Paul Sartre and Soren Kierkegaard highlight existential angst, absurdity, and the imperative to create purpose despite inherent uncertainty.
The Essence of Hedonism: Seeking Pleasure
Hedonism centers on the pursuit of pleasure as the highest good, emphasizing sensory satisfaction and immediate enjoyment as essential to a fulfilling life. This philosophical approach prioritizes experiences that maximize happiness and minimize pain, defining value through personal gratification. Contrasting with existentialism's focus on individual meaning and authentic existence, hedonism measures life's worth by the intensity and quality of pleasurable experiences.
Historical Roots of Existentialism
Existentialism originated in the 19th and early 20th centuries, deeply influenced by philosophers such as Soren Kierkegaard, Friedrich Nietzsche, and later Jean-Paul Sartre and Martin Heidegger. This philosophical movement centers on individual freedom, choice, and the search for meaning in an indifferent or absurd universe. In contrast to hedonism's focus on pleasure as the highest good, existentialism emphasizes authentic existence and personal responsibility as fundamental human concerns.
The Evolution of Hedonistic Philosophy
Hedonistic philosophy has evolved from its classical roots in Ancient Greek thought, emphasizing pleasure as the highest good, to modern interpretations that integrate psychological well-being and sustainable happiness. Philosophers like Epicurus redefined hedonism to prioritize long-term mental tranquility over immediate gratification, influencing contemporary debates on pleasure and ethics. This evolution contrasts with existentialism's focus on individual meaning and authentic existence, highlighting differing approaches to human fulfillment.
Key Thinkers: Existentialists vs. Hedonists
Existentialism, championed by key thinkers such as Jean-Paul Sartre, Soren Kierkegaard, and Simone de Beauvoir, emphasizes individual freedom, authenticity, and the search for meaning in an absurd world. In contrast, hedonism, represented by philosophers like Epicurus and Aristippus, prioritizes pleasure as the highest good and the ultimate goal of life. While existentialists explore the complexities of human existence and moral responsibility, hedonists focus on maximizing personal happiness and minimizing pain.
Meaning of Life: Absurdity vs. Enjoyment
Existentialism explores the meaning of life through the lens of absurdity, emphasizing individual responsibility to create purpose in a seemingly meaningless world. Hedonism centers on maximizing pleasure and enjoyment as the primary value guiding life's purpose. While existentialism confronts the paradox of existence without inherent meaning, hedonism seeks fulfillment through sensory and emotional satisfaction.
Freedom and Responsibility in Both Philosophies
Existentialism emphasizes freedom as the individual's capacity to create meaning through authentic choices while bearing full responsibility for their actions and the consequences, highlighting personal accountability in an absurd world. Hedonism prioritizes freedom as the pursuit of pleasure and avoidance of pain, often minimizing long-term responsibility in favor of immediate gratification. The existentialist framework asserts that true freedom requires embracing responsibility, whereas hedonism centers on freedom as liberation from constraints to maximize enjoyment.
Morality and Ethics: Contrasting Perspectives
Existentialism centers on individual freedom, responsibility, and the creation of personal meaning, emphasizing authentic choices based on moral self-awareness rather than external norms. Hedonism prioritizes pleasure as the highest good, often advocating for actions that maximize happiness while potentially disregarding broader ethical implications. These contrasting perspectives highlight a fundamental debate in morality: existentialism upholds ethical authenticity and self-defined values, whereas hedonism challenges traditional moral constraints by focusing on the pursuit of happiness.
Modern Relevance: Existentialism and Hedonism Today
Existentialism emphasizes individual freedom, authenticity, and finding meaning in a seemingly indifferent world, resonating with modern struggles around purpose and identity in an increasingly complex society. Hedonism's focus on maximizing pleasure and minimizing pain appeals to contemporary consumer culture, where instant gratification and well-being are often prioritized. Both philosophies influence current debates on mental health, lifestyle choices, and personal fulfillment, highlighting a tension between seeking deeper meaning and pursuing immediate happiness.
Choosing a Path: Integrating Existential and Hedonistic Ideas
Choosing a path that integrates existentialism and hedonism involves embracing authentic self-discovery while seeking pleasure and fulfillment. Existentialism emphasizes personal responsibility and creating meaning through choices, while hedonism prioritizes the pursuit of happiness and sensory enjoyment. Balancing these philosophies encourages living a meaningful life enriched by conscious decisions aligned with both purpose and joy.
Existentialism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com