Existentialism explores the meaning and purpose of human existence, emphasizing individual freedom, choice, and responsibility in an often ambiguous world. This philosophical movement challenges you to confront anxiety, absurdity, and isolation while creating authentic meaning through personal experience. Discover how existentialism shapes perspectives on identity and life by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
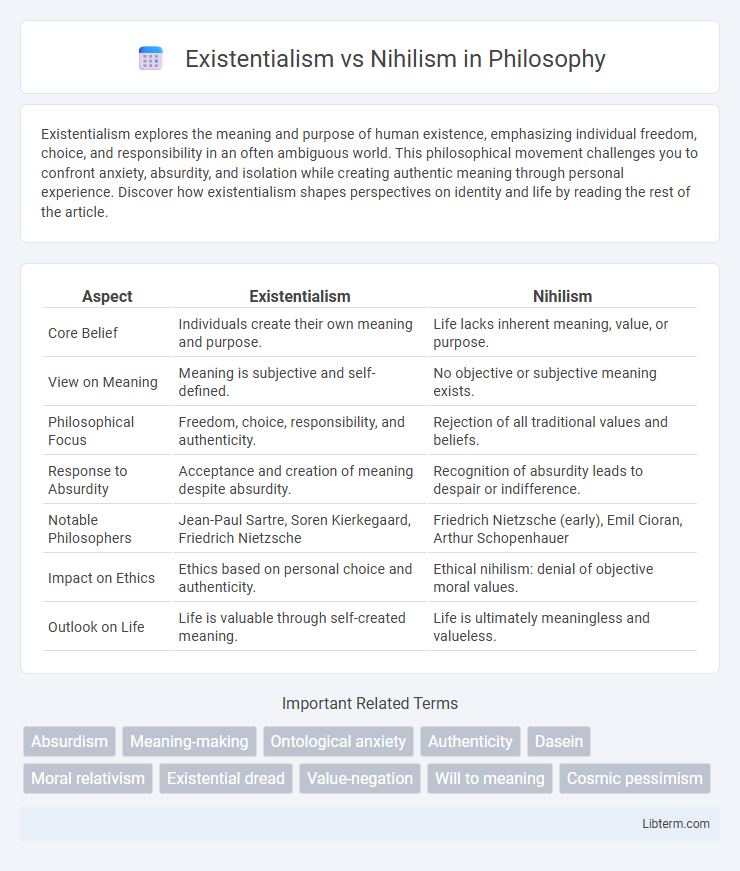
| Aspect | Existentialism | Nihilism |
|---|---|---|
| Core Belief | Individuals create their own meaning and purpose. | Life lacks inherent meaning, value, or purpose. |
| View on Meaning | Meaning is subjective and self-defined. | No objective or subjective meaning exists. |
| Philosophical Focus | Freedom, choice, responsibility, and authenticity. | Rejection of all traditional values and beliefs. |
| Response to Absurdity | Acceptance and creation of meaning despite absurdity. | Recognition of absurdity leads to despair or indifference. |
| Notable Philosophers | Jean-Paul Sartre, Soren Kierkegaard, Friedrich Nietzsche | Friedrich Nietzsche (early), Emil Cioran, Arthur Schopenhauer |
| Impact on Ethics | Ethics based on personal choice and authenticity. | Ethical nihilism: denial of objective moral values. |
| Outlook on Life | Life is valuable through self-created meaning. | Life is ultimately meaningless and valueless. |
Introduction to Existentialism and Nihilism
Existentialism emphasizes individual freedom, choice, and the search for meaning in an inherently meaningless world, highlighting philosophers like Jean-Paul Sartre and Soren Kierkegaard. Nihilism asserts the rejection of inherent meaning, values, and purpose, often associated with Friedrich Nietzsche's critique of traditional moral frameworks. Both philosophies explore human existence and meaning, yet existentialism encourages creating personal significance while nihilism often confronts the void of meaning.
Historical Origins and Key Philosophers
Existentialism emerged in the 19th and 20th centuries with key philosophers such as Soren Kierkegaard, Friedrich Nietzsche, Jean-Paul Sartre, and Martin Heidegger, focusing on individual existence, freedom, and authenticity. Nihilism, primarily associated with Nietzsche, originated in the 19th century and emphasizes the rejection of inherent meaning, values, or purpose in life. Both philosophies respond to the crisis of meaning in modernity but diverge in their conclusions about life's significance and moral frameworks.
Core Principles of Existentialism
Existentialism centers on the belief that individuals create their own meaning and purpose through authentic choices, emphasizing personal freedom, responsibility, and subjective experience. It asserts that while life inherently lacks predetermined meaning, humans must confront this absurdity by actively defining their existence. Unlike nihilism, which rejects all meaning and values as baseless, existentialism encourages embracing the freedom to construct individual significance despite life's inherent uncertainty.
Core Tenets of Nihilism
Nihilism asserts that life lacks inherent meaning, purpose, or intrinsic value, rejecting established moral principles and beliefs. Core tenets include the belief in the absurdity of existence, the denial of objective truth, and the conviction that traditional structures such as religion, morality, and social norms are baseless. This philosophy contrasts with existentialism by emphasizing emptiness and meaninglessness rather than creating individual purpose despite the void.
Existentialism: Meaning and Individual Responsibility
Existentialism emphasizes the creation of personal meaning through individual choice and responsibility, rejecting the notion that life's purpose is predetermined or inherent. It asserts that humans define their essence by actions, confronting the inherent absurdity of existence with authentic engagement and self-awareness. This philosophy advocates embracing freedom and accountability to forge a meaningful life despite existential uncertainty.
Nihilism: The Rejection of Meaning
Nihilism asserts that life lacks intrinsic meaning, purpose, or value, challenging traditional moral and existential frameworks. It rejects universal truths and posits that any imposed meaning is arbitrary and subjective. This philosophy contrasts with Existentialism, which, despite acknowledging life's inherent meaninglessness, encourages individuals to create personal significance and authentic purpose.
Major Differences Between Existentialism and Nihilism
Existentialism emphasizes individual freedom, meaning, and authentic choice despite an inherently meaningless universe, while nihilism asserts that life lacks any objective purpose, value, or meaning altogether. Existentialists argue that meaning is personally created through actions and decisions, contrasting with nihilists' belief in the absence of any inherent or constructed meaning. Key thinkers like Jean-Paul Sartre and Friedrich Nietzsche illustrate these distinctions, with existentialism promoting self-determined meaning and nihilism highlighting existential despair or rejection of all values.
Impact on Modern Thought and Culture
Existentialism profoundly shapes modern thought by emphasizing individual freedom, choice, and the search for meaning in an indifferent universe, influencing literature, psychology, and art. Nihilism challenges traditional values by asserting the absence of inherent meaning or purpose, often prompting cultural skepticism and critiques of authority. The interplay between existentialist affirmation of personal meaning and nihilist rejection of objective values continues to drive contemporary philosophical debates and cultural expressions.
Criticisms and Misconceptions
Existentialism often faces criticism for its perceived focus on individual angst and subjective meaning, which some argue leads to solipsism or moral relativism, while nihilism is frequently misunderstood as mere pessimism or despair rather than a rejection of inherent meaning. Critics of existentialism highlight the challenge of creating authentic values without objective foundations, whereas nihilism is often mischaracterized as advocating hopelessness instead of questioning traditional beliefs. Both philosophies are frequently conflated, yet existentialism seeks to construct meaning despite absurdity, contrasting with nihilism's assertion that life lacks intrinsic purpose.
Conclusion: Relevance in Contemporary Life
Existentialism offers a framework for finding personal meaning and authentic existence despite inherent absurdities, fostering resilience and self-awareness in contemporary life. Nihilism, by contrast, challenges the notion of inherent purpose but can lead to a liberating re-evaluation of values and beliefs in a rapidly changing world. Both philosophies remain relevant as they address fundamental questions about meaning, identity, and human freedom in the context of modern societal complexity.
Existentialism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com