Phenomenological research focuses on exploring and understanding human experiences from a first-person perspective, emphasizing the meaning individuals attach to their lived experiences. It is widely used in psychology, sociology, and education to gather deep insights into how people perceive and make sense of their worlds. Discover how phenomenology can enhance your approach by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
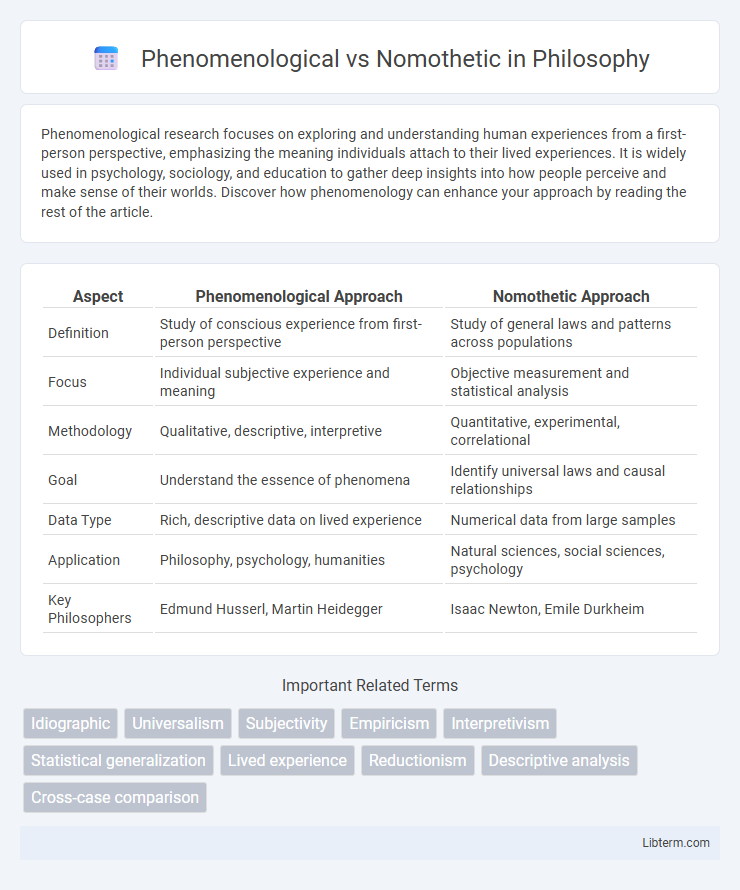
| Aspect | Phenomenological Approach | Nomothetic Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of conscious experience from first-person perspective | Study of general laws and patterns across populations |
| Focus | Individual subjective experience and meaning | Objective measurement and statistical analysis |
| Methodology | Qualitative, descriptive, interpretive | Quantitative, experimental, correlational |
| Goal | Understand the essence of phenomena | Identify universal laws and causal relationships |
| Data Type | Rich, descriptive data on lived experience | Numerical data from large samples |
| Application | Philosophy, psychology, humanities | Natural sciences, social sciences, psychology |
| Key Philosophers | Edmund Husserl, Martin Heidegger | Isaac Newton, Emile Durkheim |
Introduction to Phenomenological and Nomothetic Approaches
Phenomenological approaches emphasize understanding individual experiences and subjective realities by exploring consciousness and lived phenomena. Nomothetic approaches prioritize establishing general laws and objective patterns through quantifiable data and statistical analysis. Both methodologies provide complementary insights, with phenomenology focusing on depth and meaning, while nomothetic research targets breadth and prediction.
Defining the Phenomenological Approach
The phenomenological approach centers on exploring individuals' lived experiences to understand the essence of phenomena from a first-person perspective, emphasizing subjective perception and meaning-making. It seeks to uncover how people consciously experience events, emotions, and relationships, prioritizing qualitative data over quantitative measures. This method contrasts with nomothetic approaches by focusing on depth and context rather than generalizable laws or statistical patterns.
Understanding the Nomothetic Approach
The nomothetic approach emphasizes the search for general laws and principles that apply across large populations by using quantitative methods such as surveys and experiments. It prioritizes objectivity, measurement, and statistical analysis to identify patterns and causal relationships in behavior or phenomena. This approach is central to disciplines like psychology and sociology, where establishing predictive models and universal truths is essential for scientific advancement.
Historical Background and Development
Phenomenological approaches originated in the early 20th century through Edmund Husserl's work, emphasizing the study of conscious experience and subjective perception. Nomothetic methods trace back to natural sciences and aim to establish general laws and objective principles, influenced by thinkers like Francis Bacon and later positivists. Both frameworks have evolved to address human behavior, with phenomenology focusing on individual meaning and nomothetic research seeking universal patterns.
Key Differences Between Phenomenological and Nomothetic Methods
Phenomenological methods emphasize in-depth exploration of individual lived experiences and subjective meanings, focusing on qualitative data derived from personal perspectives. Nomothetic approaches prioritize generalization by identifying common laws or patterns across larger populations through quantitative data and statistical analysis. The key difference lies in phenomenology's aim to understand unique, contextual phenomena versus nomothetic methods' goal to establish universal principles applicable across cases.
Applications in Psychological Research
Phenomenological approaches in psychological research prioritize in-depth exploration of individual subjective experiences, making them essential for qualitative studies on perception, consciousness, and mental health. Nomothetic methods emphasize identifying general laws and patterns through quantitative data, facilitating large-scale surveys and experimental research to establish universal psychological principles. Integrating both approaches enhances understanding by combining rich personal insights with broad applicability in fields like clinical psychology and cognitive science.
Strengths and Limitations of the Phenomenological Approach
The phenomenological approach excels in exploring subjective human experiences and capturing rich, detailed insights into individual consciousness, providing depth and context often missed by quantitative methods. Its strength lies in understanding meanings and perspectives that shape human behavior, making it invaluable in psychology and qualitative research. However, limitations include challenges in generalizing findings due to small, non-representative samples and the potential for researcher bias in interpreting personal experiences.
Strengths and Limitations of the Nomothetic Approach
The nomothetic approach excels in identifying general laws and patterns through large-scale data and statistical analysis, making it valuable for predicting behavior and establishing standardized measures. However, it often overlooks individual differences and the depth of personal experience, limiting its ability to capture the complexity of subjective human phenomena. Its focus on quantifiable variables can result in reductionism, potentially ignoring contextual or nuanced factors that are crucial in psychological understanding.
Integrating Phenomenological and Nomothetic Perspectives
Integrating phenomenological and nomothetic perspectives enhances psychological research by combining subjective individual experiences with generalizable laws. Phenomenological methods explore personal consciousness and lived experiences, while nomothetic approaches identify patterns and predict behaviors across populations. This integration fosters a comprehensive understanding of human behavior, balancing depth with broad applicability in both clinical and experimental settings.
Future Directions and Implications for Research
Future directions in Phenomenological research emphasize deepening qualitative insights into subjective human experiences using advanced interpretative methods and integrating neurophenomenology to bridge first-person perspectives with brain data. Nomothetic approaches increasingly leverage large-scale data analytics and machine learning to identify generalized patterns and causal relationships across populations, enhancing predictive accuracy in psychological and social sciences. Combining Phenomenological depth with Nomothetic breadth promises innovative mixed-method frameworks that improve theoretical models and practical applications in mental health, education, and personalized interventions.
Phenomenological Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com