Syntax governs the structure of sentences, determining how words combine to convey clear meaning. Understanding syntax enhances your ability to communicate effectively and interpret complex texts. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge of syntactic rules and applications.
Table of Comparison
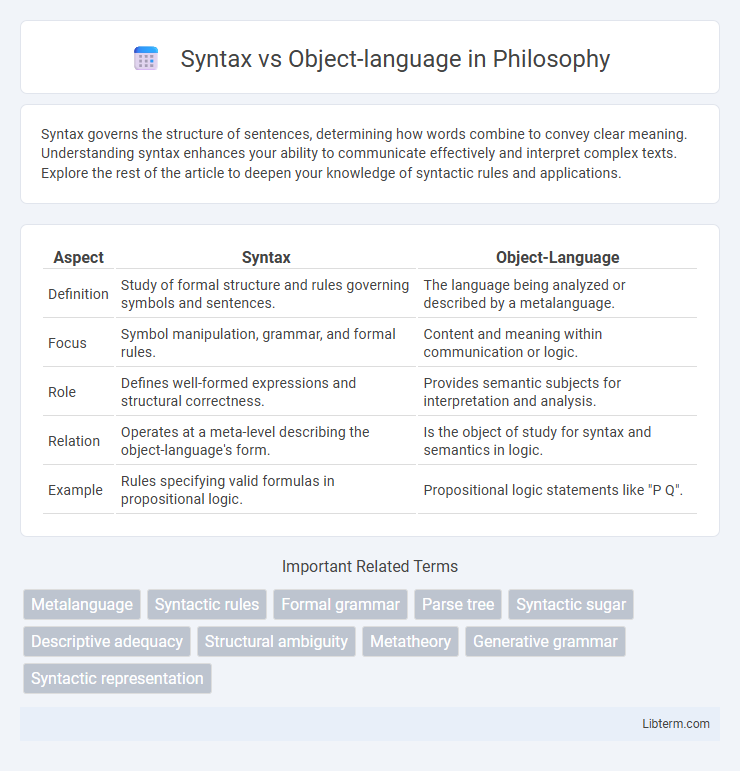
| Aspect | Syntax | Object-Language |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of formal structure and rules governing symbols and sentences. | The language being analyzed or described by a metalanguage. |
| Focus | Symbol manipulation, grammar, and formal rules. | Content and meaning within communication or logic. |
| Role | Defines well-formed expressions and structural correctness. | Provides semantic subjects for interpretation and analysis. |
| Relation | Operates at a meta-level describing the object-language's form. | Is the object of study for syntax and semantics in logic. |
| Example | Rules specifying valid formulas in propositional logic. | Propositional logic statements like "P Q". |
Introduction to Syntax and Object-Language
Syntax refers to the set of rules and principles that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, enabling the formation of grammatically correct statements. Object-language is the language being studied or described within a formal system, while syntax provides the framework for analyzing its formal properties and expressions. Understanding the distinction between syntax and object-language is fundamental in fields such as linguistics, logic, and computer science for parsing, interpreting, and constructing meaningful language models.
Defining Syntax in Linguistics and Logic
Syntax in linguistics and logic refers to the structured set of rules and principles governing the arrangement of symbols and words within a language, defining how expressions can be correctly formed. It deals with the formal relationships between symbols in a system without considering their meanings, distinguishing it from semantics. Object-language is the language being described or analyzed, while syntax provides the framework for understanding its structural formation independent of interpretation or meaning.
What is Object-Language?
Object-language is the language that is being described or analyzed within a formal system, serving as the subject of study for its syntax and semantics. It contrasts with the metalanguage, which is the language used to discuss or define the object-language, enabling precise formulation of rules and interpretations. Understanding object-language is fundamental in logic and linguistics for constructing formal proofs and clarifying meaning.
Key Distinctions between Syntax and Object-Language
Syntax concerns the formal rules and structures governing the arrangement of symbols within a language, defining how expressions are correctly formed without regard to their meaning. Object-language refers to the language being studied or analyzed, encompassing its vocabulary, grammar, and semantics as elements subject to syntactic rules. Key distinctions between syntax and object-language lie in syntax's role as the meta-level framework regulating symbol manipulation, while object-language constitutes the actual linguistic system these rules apply to.
The Role of Syntax in Language Analysis
Syntax serves as the structural framework of object-language by defining the formal rules that govern the arrangement of symbols and phrases. It enables precise language analysis through the identification of valid sentence constructions, ensuring consistent interpretation and logical coherence. The distinction between syntax and object-language highlights how syntactic rules operate at the meta-level to describe and regulate the formation of expressions within the object-language itself.
Object-Language in Logical Frameworks
Object-language in logical frameworks refers to the formal language that is directly manipulated within the system, serving as the subject of syntactic and semantic analysis. It encompasses the precise symbols, expressions, and rules governed by the framework's formal grammar, enabling rigorous reasoning and proof construction. Understanding object-language is essential for encoding mathematical statements and properties within logical frameworks, facilitating automated theorem proving and formal verification.
Syntax vs Object-Language: Common Confusions
Syntax pertains to the formal rules and structure governing sentences within a language, while object-language refers to the language being analyzed or described. A frequent confusion arises when the metalanguage, used to discuss syntax, is mistaken for the object-language itself, blurring the distinction between discussing language rules and the language in use. Clarifying this separation is crucial for accurate linguistic analysis and avoids conflating the language system with its descriptive framework.
Applications in Philosophy and Computer Science
Syntax refers to the formal rules governing the structure of statements in a language, while object-language is the language being analyzed or discussed within a meta-language framework. In philosophy, distinguishing syntax from object-language aids in clarifying arguments about logical form, semantic theories, and metalogical properties. In computer science, syntax rules define programming languages' grammar, enabling compilers and interpreters to process code, whereas the object-language represents the instructions executed or analyzed by software systems.
Real-World Examples Illustrating Syntax and Object-Language
Syntax governs the structural rules that define how symbols and sentences are formed in a formal language, as seen in programming languages where correct syntax ensures code compiles successfully. Object-language refers to the language being studied or manipulated, such as English sentences used in linguistic analysis or mathematical expressions evaluated in algebra. Real-world examples include computer code written in Python representing object-language, while the syntax dictates the proper arrangement of functions, variables, and operators to execute commands correctly.
Conclusion: Understanding Their Interplay
Syntax governs the formal structure and rules within a language system, while object-language refers to the language being studied or described. Understanding their interplay is crucial for distinguishing between the metalanguage used to discuss linguistic elements and the object-language itself, enabling clearer analysis and communication in fields like logic and linguistics. Mastery of this relationship enhances precision in language theory and the development of formal systems.
Syntax Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com