Ontological exploration delves into the very nature of being, existence, and reality, seeking to understand the fundamental categories that define what is. This branch of philosophy examines concepts such as being, essence, and identity to clarify how entities relate within a broader framework. Discover how ontological principles can deepen your understanding by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
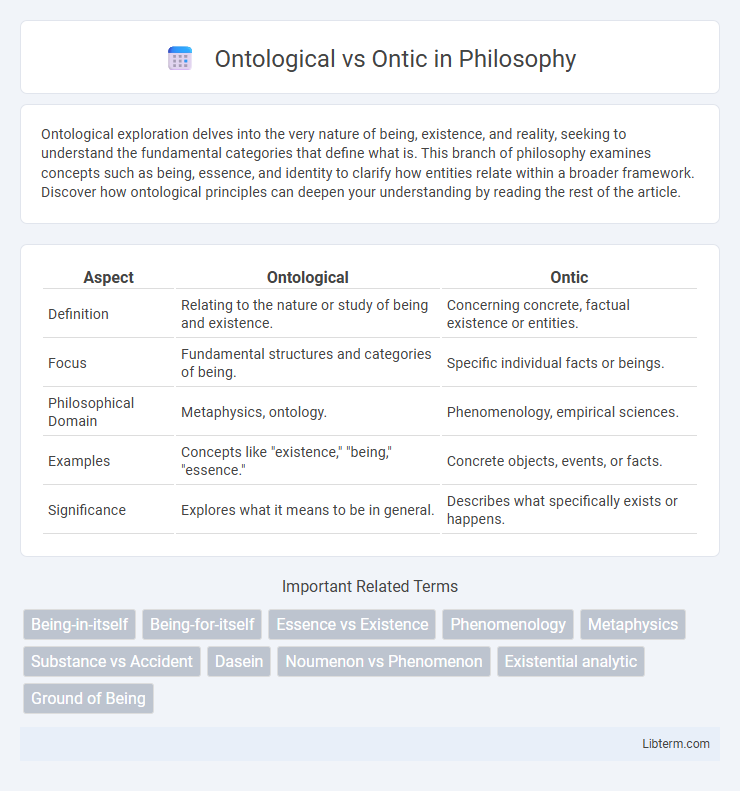
| Aspect | Ontological | Ontic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relating to the nature or study of being and existence. | Concerning concrete, factual existence or entities. |
| Focus | Fundamental structures and categories of being. | Specific individual facts or beings. |
| Philosophical Domain | Metaphysics, ontology. | Phenomenology, empirical sciences. |
| Examples | Concepts like "existence," "being," "essence." | Concrete objects, events, or facts. |
| Significance | Explores what it means to be in general. | Describes what specifically exists or happens. |
Introduction to Ontological and Ontic Concepts
Ontological concepts pertain to the nature of being and existence, exploring categories and relationships that define reality's fundamental structure. Ontic refers to the actual entities, facts, or states of affairs within the world, emphasizing concrete and specific instances of existence. Understanding the distinction between ontological frameworks and ontic realities is crucial for philosophical analysis, metaphysics, and hermeneutics.
Defining Ontology: The Nature of Being
Ontology, a fundamental branch of metaphysics, concerns the study of the nature of being, existence, and reality, focusing on categorizing entities and their relationships. The ontological perspective analyzes the essential qualities and structures that define what it means to exist, while the ontic dimension addresses the specific facts and particulars of existence. Differentiating ontological inquiry from ontic examination allows philosophers to explore abstract frameworks of reality versus concrete instances of being.
What Does Ontic Mean? Scope and Usage
Ontic refers to the aspects of existence that pertain to specific, concrete entities and their actual states or conditions in reality. Its scope includes the particular facts and properties that define individual beings, as distinct from the broader, abstract structures or categories studied in ontology. The term is commonly used in philosophy, especially phenomenology and metaphysics, to analyze the real, empirical details of being rather than conceptual frameworks.
Historical Background: Ontology vs Ontic in Philosophy
Ontology, rooted in ancient Greek philosophy, originated with Aristotle's exploration of being and reality, defining categories of existence and the nature of entities. The ontic, a concept developed later in phenomenology by philosophers like Heidegger, focuses on concrete particulars and factual existence, distinguishing specific beings from the broader ontological framework. The historical evolution highlights ontology as the study of being in general, while the ontic addresses the actual details and instances of being within that philosophical context.
Key Differences between Ontological and Ontic
Ontological pertains to the study of being and existence at the most abstract and universal level, focusing on the nature and categories of reality. Ontic relates to the concrete factual aspects or entities that exist in the world, emphasizing individual instances and actual occurrences. The key difference lies in ontological addressing the theoretical framework of existence, while ontic concerns specific, empirical realities.
Ontological Questions: Exploring Existential Properties
Ontological questions explore the nature of existence and the fundamental categories that define reality, focusing on what kinds of things can be said to exist. These inquiries examine existential properties such as being, substance, and essence, aiming to understand how entities are structured and related within the framework of being. Ontological analysis contrasts with ontic concerns, which address specific instances or facts about individual entities rather than the general conditions of existence.
Ontic Questions: Investigating Concrete Entities
Ontic questions focus on the nature and existence of concrete entities, examining the specific properties and facts that characterize individual objects or phenomena in reality. Unlike ontological inquiries that explore the general nature or categories of being, ontic investigations delve into particular instances and empirical details that define real-world entities. This approach is essential in fields like metaphysics, physics, and ontology, where understanding the tangible aspects of existence informs the interpretation of phenomena.
Applications in Contemporary Philosophy
Ontological analysis in contemporary philosophy examines the nature and categories of being, shaping metaphysical frameworks used in fields like cognitive science and artificial intelligence. Ontic considerations address the concrete entities themselves, influencing empirical investigations and the interpretation of physical reality in philosophy of mind and existentialism. The distinction clarifies debates on existence and reality, enhancing theoretical precision in ontology-driven research and practical applications across interdisciplinary studies.
Ontological and Ontic in Science and Metaphysics
Ontological considerations in science and metaphysics address the nature and categories of being, focusing on what entities fundamentally exist and how they can be classified. Ontic aspects pertain to the concrete, factual existence or particular states of entities within reality, emphasizing individual instances rather than abstract categories. The distinction influences scientific modeling and metaphysical inquiry by separating the study of existence's conditions (ontological) from the study of actual entities and their properties (ontic).
Conclusion: Synthesizing Ontological and Ontic Perspectives
Ontological analysis examines the nature and categories of being, while ontic study focuses on actual entities and their concrete existence. Synthesizing ontological and ontic perspectives enables a comprehensive understanding by integrating abstract structural frameworks with empirical realities. This fusion facilitates deeper insights into both the essence of phenomena and their practical manifestations.
Ontological Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com