Self-identity shapes how you perceive your unique traits, beliefs, and experiences, forming the core of personal identity. Personal identity encompasses the continuous sense of self across time, influenced by memory, values, and social interactions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these concepts impact your life and relationships.
Table of Comparison
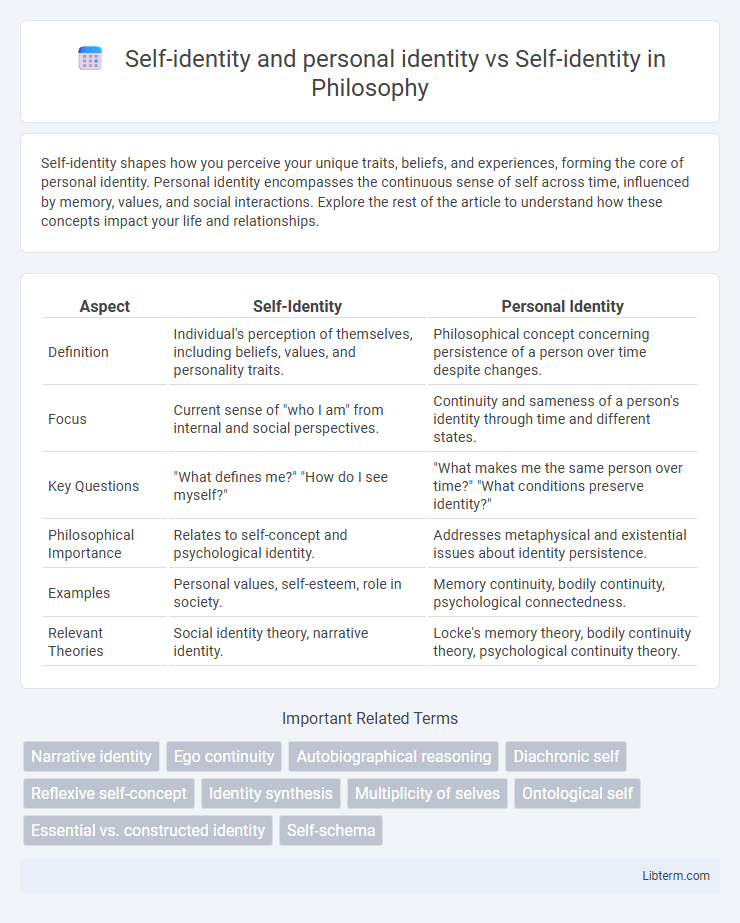
| Aspect | Self-Identity | Personal Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual's perception of themselves, including beliefs, values, and personality traits. | Philosophical concept concerning persistence of a person over time despite changes. |
| Focus | Current sense of "who I am" from internal and social perspectives. | Continuity and sameness of a person's identity through time and different states. |
| Key Questions | "What defines me?" "How do I see myself?" | "What makes me the same person over time?" "What conditions preserve identity?" |
| Philosophical Importance | Relates to self-concept and psychological identity. | Addresses metaphysical and existential issues about identity persistence. |
| Examples | Personal values, self-esteem, role in society. | Memory continuity, bodily continuity, psychological connectedness. |
| Relevant Theories | Social identity theory, narrative identity. | Locke's memory theory, bodily continuity theory, psychological continuity theory. |
Understanding Self-Identity: Core Concepts
Understanding self-identity involves exploring the core concepts of personal identity, which include the continuity of experiences, memories, and values that define an individual over time. Self-identity encompasses the perception of oneself as a distinct entity with unique characteristics, shaped by both internal awareness and external social interactions. The distinction between personal identity and self-identity lies in the former's emphasis on the persistence of the self through time, while the latter focuses more on how individuals consciously construct and express their sense of who they are.
Defining Personal Identity: What Sets It Apart
Personal identity refers to the enduring characteristics and experiences that define an individual over time, encompassing memory, consciousness, and bodily continuity. Self-identity focuses more on the subjective perception and awareness of oneself as a distinct entity in the present moment. The key distinction lies in personal identity's emphasis on persistence and coherence across time, while self-identity centers on present self-recognition and internal sense of being.
Key Differences: Self-Identity vs Personal Identity
Self-identity refers to an individual's perception of who they are based on internal self-concept, including beliefs, values, and experiences. Personal identity encompasses the continuous and coherent sense of self over time, emphasizing the persistence and psychological connectedness that distinguishes one person from another. Key differences lie in scope; self-identity focuses on subjective self-awareness and internal traits, while personal identity addresses the broader continuity and distinctiveness of a person's existence through time.
The Psychological Foundations of Self-Identity
Self-identity refers to an individual's conscious awareness of their own characteristics, beliefs, and values that shape their sense of self, while personal identity encompasses the continuous and coherent sense of being the same person over time despite changes. The psychological foundations of self-identity involve cognitive processes such as self-reflection, memory integration, and the internalization of social roles that contribute to a stable yet evolving self-concept. Understanding these foundations helps clarify how individuals construct their self-narrative and maintain personal continuity within dynamic social contexts.
Social Influences on Self and Personal Identity
Social influences shape both self-identity and personal identity through interactions, cultural norms, and societal expectations, which serve as frameworks for understanding oneself. Social identity theory highlights how group membership impacts self-concept, while personal identity incorporates unique traits and experiences influenced by these external factors. Peer pressure, media representation, and family dynamics play crucial roles in constructing an individual's evolving sense of identity within their social environment.
Identity Formation: Stages and Influencing Factors
Identity formation involves distinct stages including exploration, commitment, and consolidation, where individuals evaluate personal beliefs, values, and roles to establish self-identity. Personal identity emphasizes the continuous sense of self that integrates experiences and social interactions, while self-identity focuses on the individual's internal perception and self-awareness. Influencing factors such as cultural background, social context, and psychological development play critical roles in shaping both self-identity and personal identity throughout the identity formation process.
Culture and Context: Shaping the Sense of Self
Self-identity reflects an individual's evolving sense of who they are, shaped by personal experiences, values, and self-perception, while personal identity concerns the consistent traits and characteristics defining a person over time. Culture and context play a crucial role in shaping self-identity through social norms, traditions, language, and collective memory, influencing how individuals interpret their own existence and roles within a community. Understanding the dynamic interplay between culture, context, and identity reveals the fluid nature of selfhood as it adapts to changing social environments and cultural frameworks.
Challenges in Maintaining Consistent Identity
Maintaining a consistent self-identity often involves navigating conflicts between personal identity, which encompasses deeply held beliefs and values, and social self-identity influenced by external perceptions and roles. Challenges arise from cognitive dissonance when personal authenticity clashes with societal expectations or shifting life circumstances. Psychological resilience and reflective self-awareness are critical for preserving coherence in identity amidst these pressures.
The Role of Self-Reflection in Identity Development
Self-reflection plays a crucial role in the development of both self-identity and personal identity by enabling individuals to evaluate their beliefs, values, and experiences. This introspective process fosters greater self-awareness, helping to differentiate self-identity as an internal sense of who one is from personal identity, which encompasses external social roles and group affiliations. Continuous self-reflection enhances identity coherence and authenticity, allowing for adaptive growth and alignment between internal perceptions and external expressions.
Nurturing Authenticity: Integrating Self and Personal Identity
Nurturing authenticity involves harmonizing self-identity, which reflects one's internal sense of being, with personal identity, encompassing social roles and external characteristics. This integration fosters congruence between inner values and outward expressions, promoting psychological well-being and genuine self-presentation. Emphasizing self-awareness and reflective practices enhances the alignment of self-identity and personal identity, strengthening overall authenticity.
Self-identity and personal identity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com