Pragmatic ambiguity occurs when a sentence or phrase can be interpreted in multiple ways depending on the context or the speaker's intentions. This type of ambiguity challenges clear communication because the meaning relies heavily on situational factors and shared knowledge between the speaker and listener. Explore the rest of the article to understand how pragmatic ambiguity influences everyday language and strategies to minimize misunderstandings.
Table of Comparison
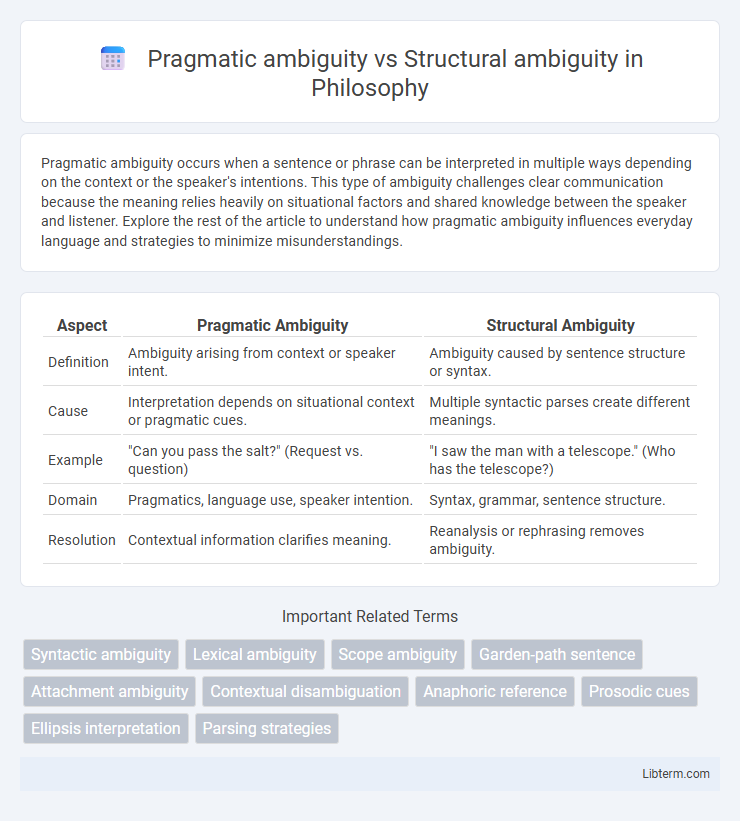
| Aspect | Pragmatic Ambiguity | Structural Ambiguity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ambiguity arising from context or speaker intent. | Ambiguity caused by sentence structure or syntax. |
| Cause | Interpretation depends on situational context or pragmatic cues. | Multiple syntactic parses create different meanings. |
| Example | "Can you pass the salt?" (Request vs. question) | "I saw the man with a telescope." (Who has the telescope?) |
| Domain | Pragmatics, language use, speaker intention. | Syntax, grammar, sentence structure. |
| Resolution | Contextual information clarifies meaning. | Reanalysis or rephrasing removes ambiguity. |
Introduction to Ambiguity in Language
Ambiguity in language arises when a word, phrase, or sentence has multiple interpretations, impacting clarity and meaning. Pragmatic ambiguity occurs due to context-dependent interpretations, where the intended meaning varies based on situational factors or speaker intention. Structural ambiguity stems from syntactic variations, where sentence construction leads to multiple parsing possibilities, influencing how information is understood.
Defining Pragmatic Ambiguity
Pragmatic ambiguity occurs when a sentence's meaning is unclear due to context or speaker intention, rather than its grammatical structure. It arises from multiple possible interpretations based on real-world knowledge or the communicative situation. In contrast, structural ambiguity stems from sentence syntax, where different parses create distinct meanings.
Defining Structural Ambiguity
Structural ambiguity occurs when a sentence's syntax allows multiple interpretations because its components can be grouped in different ways, leading to more than one possible meaning. This type of ambiguity arises from the sentence structure rather than the individual words. In contrast, pragmatic ambiguity involves the context or implied meanings influencing how a statement is understood.
Key Differences Between Pragmatic and Structural Ambiguity
Pragmatic ambiguity arises when a sentence's meaning depends on the context or speaker intention, making it unclear which interpretation applies. Structural ambiguity occurs due to sentence syntax, where different grammatical structures create multiple possible meanings. Key differences include pragmatic ambiguity relying on external situational factors, while structural ambiguity stems solely from the linguistic form and sentence construction.
Real-World Examples of Pragmatic Ambiguity
Pragmatic ambiguity arises when the intended meaning depends on context, such as the sentence "Can you pass the salt?" which can be a question about ability or a polite request. Structural ambiguity occurs due to sentence syntax, like "I saw the man with the telescope," where it is unclear who has the telescope. Real-world examples of pragmatic ambiguity include statements like "I'm cold," which could express discomfort or a request to close a window depending on the situation.
Illustrative Cases of Structural Ambiguity
Structural ambiguity arises when a sentence can be parsed in multiple ways due to its syntactic structure, leading to different interpretations. Illustrative cases include the phrase "I saw the man with the telescope," which can mean either using a telescope to see the man or seeing a man who possesses a telescope. Another example is "Flying planes can be dangerous," ambiguous between the act of flying planes and planes that are flying posing danger.
Impact on Communication and Interpretation
Pragmatic ambiguity arises when context influences the meaning of a phrase, leading to multiple interpretations based on real-world knowledge, while structural ambiguity stems from sentence syntax allowing for different grammatical parses. The impact on communication includes potential misunderstanding or misinterpretation, as listeners may assign incorrect meaning without clear contextual clues or disambiguating syntactic cues. Effective interpretation requires discerning speaker intent and contextual information to resolve ambiguity and ensure accurate message comprehension.
Ambiguity in Linguistics Research
Pragmatic ambiguity arises when a sentence's meaning is unclear due to context or speaker intention, while structural ambiguity occurs from multiple possible syntactic interpretations within the sentence itself. Linguistics research often analyzes these ambiguities to understand how language users disambiguate meaning through context or grammatical structure. Studies emphasize parsing models and contextual cues as essential tools in resolving both pragmatic and structural ambiguities efficiently.
Resolving Pragmatic and Structural Ambiguity
Resolving pragmatic ambiguity involves interpreting meaning based on context, speaker intent, and background knowledge, enabling disambiguation of sentences with multiple plausible meanings that depend on situational factors. Structural ambiguity, also known as syntactic ambiguity, is resolved by analyzing sentence syntax and parsing different possible grammatical structures to determine the correct interpretation. Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques like part-of-speech tagging, parsing algorithms, and semantic role labeling enhance the resolution of both pragmatic and structural ambiguities in computational linguistics.
Conclusion: Implications for Language Understanding
Pragmatic ambiguity arises from context-dependent meanings, while structural ambiguity stems from multiple syntactic interpretations of a sentence. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for improving natural language processing systems, as it enables more accurate disambiguation and interpretation of human language. Effective handling of both types enhances machine comprehension, leading to better communication and information extraction in AI applications.
Pragmatic ambiguity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com