Syntactic ambiguity occurs when a sentence can be interpreted in more than one way due to its structure, leading to multiple possible meanings. This phenomenon often challenges effective communication and requires careful analysis to resolve misunderstandings. Explore the rest of this article to understand how syntactic ambiguity affects language and how you can identify it.
Table of Comparison
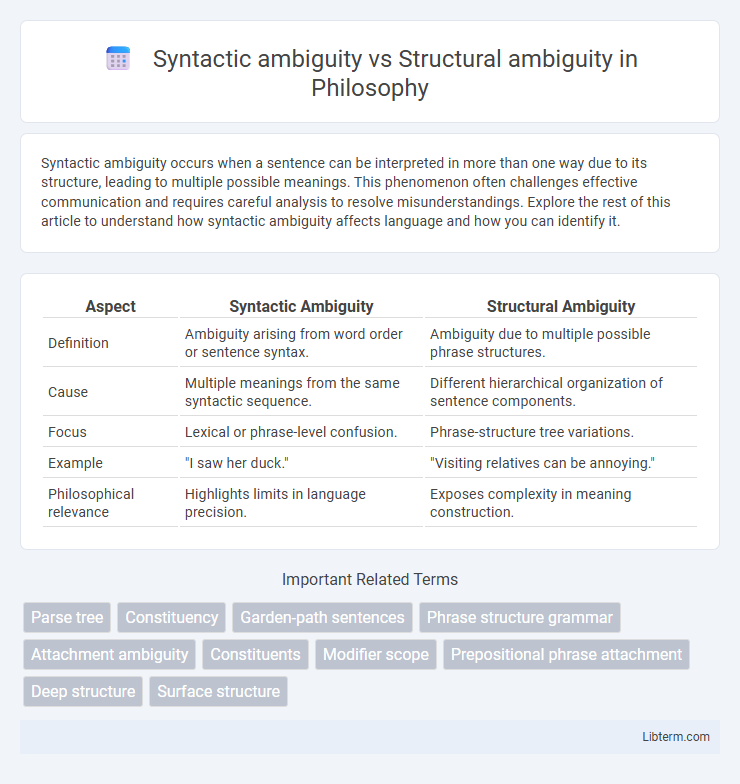
| Aspect | Syntactic Ambiguity | Structural Ambiguity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ambiguity arising from word order or sentence syntax. | Ambiguity due to multiple possible phrase structures. |
| Cause | Multiple meanings from the same syntactic sequence. | Different hierarchical organization of sentence components. |
| Focus | Lexical or phrase-level confusion. | Phrase-structure tree variations. |
| Example | "I saw her duck." | "Visiting relatives can be annoying." |
| Philosophical relevance | Highlights limits in language precision. | Exposes complexity in meaning construction. |
Introduction to Ambiguity in Linguistics
Syntactic ambiguity occurs when a sentence can be interpreted in multiple ways due to the ambiguous arrangement of words, while structural ambiguity arises from unclear sentence structure impacting meaning. Both forms of ambiguity highlight challenges in parsing sentences, emphasizing the complexity of language processing in linguistics. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for analyzing how meaning is derived and resolved in natural language.
Defining Syntactic Ambiguity
Syntactic ambiguity occurs when a sentence can be interpreted in multiple ways due to its unclear grammatical structure, causing confusion about the relationships between words. This type of ambiguity arises when different syntactic parses yield different meanings, such as in the sentence "I saw the man with the telescope," which can mean either the observer used a telescope or the man had one. Structural ambiguity is a subset of syntactic ambiguity specifically relating to the arrangement of sentence components, influencing how phrases and clauses connect within the overall grammatical framework.
What Is Structural Ambiguity?
Structural ambiguity occurs when a sentence or phrase can be interpreted in multiple ways due to its syntactic structure rather than the meanings of individual words. It arises from different possible arrangements or groupings of words that create distinct interpretations, such as "I saw the man with the telescope," which can mean either seeing a man who has a telescope or using a telescope to see the man. Structural ambiguity contrasts with lexical ambiguity, which involves ambiguous word meanings rather than sentence construction.
Key Differences: Syntactic vs Structural Ambiguity
Syntactic ambiguity arises when a sentence can be parsed in multiple ways due to the arrangement of words, leading to different interpretations, while structural ambiguity specifically refers to ambiguity caused by the sentence's hierarchical structure or phrase attachments. Key differences include syntactic ambiguity's focus on word order and grammatical relations, whereas structural ambiguity emphasizes the underlying tree structure of sentence components. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for natural language processing tasks like parsing and disambiguation.
Common Examples of Syntactic Ambiguity
Common examples of syntactic ambiguity arise when a sentence's word order or phrasing allows multiple interpretations, such as "I saw the man with the telescope," where it is unclear who possesses the telescope. Another frequent case is "Flying planes can be dangerous," which ambiguously suggests either the act of piloting planes or planes that are airborne. Structural ambiguity occurs when different syntactic structures cause confusion, but syntactic ambiguity specifically refers to ambiguity within the sentence's word arrangement and phrase attachment.
Structural Ambiguity in Everyday Language
Structural ambiguity occurs when a sentence can be interpreted in multiple ways due to its syntactic structure rather than the meaning of individual words. Everyday language frequently exhibits structural ambiguity in phrases like "I saw the man with the telescope," where it is unclear whether the man has the telescope or it was used to see him. Understanding structural ambiguity is crucial for natural language processing and communication clarity because it affects how information is parsed and understood in various contexts.
Causes and Sources of Ambiguity
Syntactic ambiguity arises when a sentence's syntax allows multiple interpretations due to unclear attachment or coordination of words, often caused by homonyms or polysemous words. Structural ambiguity stems from the arrangement or parsing of sentence elements, especially when phrases or clauses can be grouped differently, leading to multiple plausible meanings. Both types of ambiguity commonly originate from the flexibility and complexity of natural language grammar, including phrase boundary confusion and lexical ambiguity.
Effects of Ambiguity on Communication
Syntactic ambiguity occurs when a sentence can be interpreted in multiple ways due to ambiguous word order or sentence structure, while structural ambiguity arises from unclear relationships between sentence components. Both types of ambiguity can hinder clear communication by causing misunderstandings or multiple interpretations, leading to confusion in conveying intended meanings. Effective resolution of these ambiguities through precise syntax and context is crucial for successful information exchange in language processing and communication.
Resolving and Analyzing Ambiguous Sentences
Syntactic ambiguity arises when a sentence allows multiple grammatical interpretations due to unclear word order or phrase structure, while structural ambiguity involves multiple ways to parse the same sentence components. Resolving ambiguous sentences requires analyzing sentence constituents through parsing algorithms, context evaluation, and semantic role labeling to determine the intended meaning. Disambiguation techniques such as probabilistic parsing and dependency grammar models enhance accuracy in interpreting complex syntactic structures and improving natural language processing outcomes.
Conclusion: Addressing Ambiguity in Linguistic Analysis
Syntactic ambiguity arises when a sentence can be parsed in multiple ways due to ambiguous word order or phrase structure, whereas structural ambiguity involves uncertainty in the hierarchical organization of sentence components. Effective linguistic analysis requires distinguishing these types of ambiguity to enhance parsing accuracy and improve natural language processing systems. Addressing both syntactic and structural ambiguities is crucial for developing robust language models that accurately interpret and generate human language.
Syntactic ambiguity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com