Relativism asserts that truth and morality vary based on individual perspectives or cultural contexts, challenging absolute standards. This philosophy explores how beliefs and values are influenced by social, historical, or personal factors shaping human understanding. Discover how relativism impacts your worldview and the complexities it introduces by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
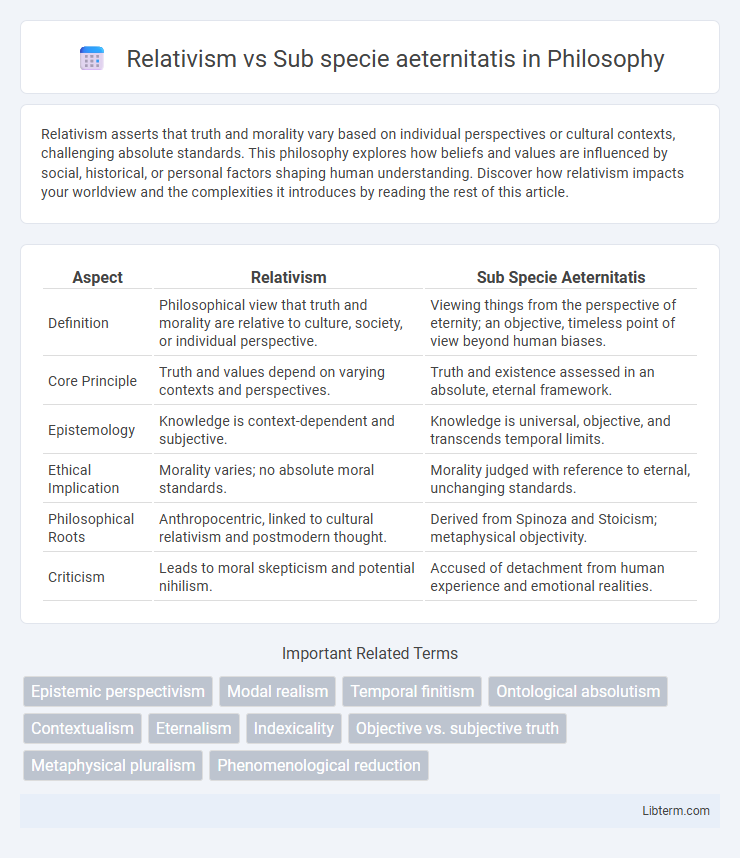
| Aspect | Relativism | Sub Specie Aeternitatis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical view that truth and morality are relative to culture, society, or individual perspective. | Viewing things from the perspective of eternity; an objective, timeless point of view beyond human biases. |
| Core Principle | Truth and values depend on varying contexts and perspectives. | Truth and existence assessed in an absolute, eternal framework. |
| Epistemology | Knowledge is context-dependent and subjective. | Knowledge is universal, objective, and transcends temporal limits. |
| Ethical Implication | Morality varies; no absolute moral standards. | Morality judged with reference to eternal, unchanging standards. |
| Philosophical Roots | Anthropocentric, linked to cultural relativism and postmodern thought. | Derived from Spinoza and Stoicism; metaphysical objectivity. |
| Criticism | Leads to moral skepticism and potential nihilism. | Accused of detachment from human experience and emotional realities. |
Understanding Relativism: Core Concepts
Relativism asserts that truth and moral values depend on cultural, individual, or situational contexts, rejecting absolute or universal standards. It challenges fixed epistemological frameworks by emphasizing the variability of perspectives influenced by historical, social, or personal conditions. In contrast, sub specie aeternitatis seeks objective, timeless understanding, viewing reality from an eternal or cosmic viewpoint beyond subjective limitations.
Defining Sub Specie Aeternitatis: The Eternal Perspective
Sub specie aeternitatis, a Latin phrase meaning "under the aspect of eternity," refers to viewing reality from an eternal, timeless perspective that transcends subjective experiences and relativistic interpretations. Unlike relativism, which emphasizes context-dependent truths shaped by individual or cultural viewpoints, the eternal perspective seeks objective, unchanging truths unaffected by temporal or personal biases. This metaphysical concept encourages understanding existence and moral values as part of a greater, universal framework beyond immediate human perception.
Historical Roots: Relativism and Philosophical Tradition
Relativism, with roots tracing back to Protagoras and the Sophists of ancient Greece, challenges the notion of absolute truth by emphasizing the variability of knowledge across different cultures and perspectives. The philosophical tradition of sub specie aeternitatis, popularized by Baruch Spinoza in the 17th century, opposes this by advocating a viewpoint from "under the aspect of eternity," seeking objective truth beyond subjective human experience. This dichotomy highlights a longstanding tension between subjective interpretations of reality and the pursuit of immutable truths within Western philosophy.
Sub Specie Aeternitatis in Classical and Modern Thought
Sub specie aeternitatis, a philosophical concept originating with Baruch Spinoza, emphasizes viewing reality from the perspective of eternity, offering an absolute, universal standpoint beyond subjective and temporal human experiences. In classical thought, it served as a lens to comprehend existence and morality through immutable truths and divine reason, contrasting sharply with relativism which underscores the dependence of truth on individual or cultural perspectives. Modern interpretations often integrate sub specie aeternitatis with scientific and metaphysical frameworks, promoting a holistic understanding of objective reality that challenges relativistic interpretations dominated by context-dependent or personal viewpoints.
Relativism vs Absolute Truth: Main Differences
Relativism asserts that truth varies based on perspectives, cultures, or contexts, rejecting universal absolutes, whereas the concept of Sub specie aeternitatis emphasizes viewing truth from an eternal, objective perspective beyond temporal and subjective influences. Relativism promotes flexibility and situational understanding, while Sub specie aeternitatis advocates for fixed, unchanging truths accessible through reason or divine insight. This fundamental difference highlights the contrast between multiplicity of truths in relativism and the unity of truth in absolute or eternal frameworks.
The Role of Perspective in Human Understanding
Relativism emphasizes that human understanding is shaped by individual or cultural perspectives, asserting that truth varies based on context and subjective experience. In contrast, sub specie aeternitatis advocates viewing reality from an eternal, objective standpoint that transcends temporal and personal biases, aiming for universal and unchanging truths. The role of perspective is crucial in distinguishing between these approaches, as relativism highlights diverse, context-dependent viewpoints while sub specie aeternitatis seeks a detached, holistic comprehension beyond human limitation.
Ethics and Morality: Relativism versus Eternal Viewpoints
Ethical relativism asserts that moral principles vary across cultures and situations, emphasizing context-dependent values without absolute standards. In contrast, the sub specie aeternitatis perspective views morality from an eternal, objective standpoint, suggesting universal ethical truths that transcend individual and cultural differences. This eternal viewpoint challenges relativism by grounding morality in unchanging principles accessible through reason and timeless reflection.
Relativism and the Limits of Subjectivity
Relativism asserts that truth and moral values are contingent upon individual perspectives, cultures, or historical contexts, emphasizing the limits of subjectivity in understanding reality. It challenges the notion of absolute or universal truths, suggesting that knowledge is inherently shaped by subjective experiences and social frameworks. However, this perspective encounters criticism for potentially undermining objective standards and fostering ethical ambiguity.
Sub Specie Aeternitatis: Implications for Meaning and Purpose
Sub specie aeternitatis, a perspective emphasizing eternal, objective truth, challenges relativism by asserting that meaning and purpose exist independently of subjective interpretations. This viewpoint encourages examining human existence from a timeless vantage, revealing universal values and goals beyond cultural or personal biases. Embracing sub specie aeternitatis fosters a sense of permanent significance, grounding ethical frameworks and life's purpose in enduring cosmic realities rather than transient beliefs.
Reconciling Relativism and the Eternal Perspective: Is Integration Possible?
Reconciling relativism and the eternal perspective involves examining whether subjective truth claims can coexist with timeless, objective values under sub specie aeternitatis, a Platonic view emphasizing the eternal nature of reality. Philosophers argue integration is possible through frameworks like contextualism, which allows truths to be valid relative to context while accepting overarching, immutable principles. This synthesis advances dialogue between flexible moral relativism and fixed cosmic viewpoints, fostering nuanced understanding across epistemological divides.
Relativism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com