Propaganda shapes public opinion by spreading biased or misleading information to promote a particular agenda, often manipulating emotions and beliefs. Recognizing propaganda techniques is crucial for developing critical thinking and avoiding misinformation in media consumption. Explore the rest of the article to learn how propaganda influences society and how you can identify it effectively.
Table of Comparison
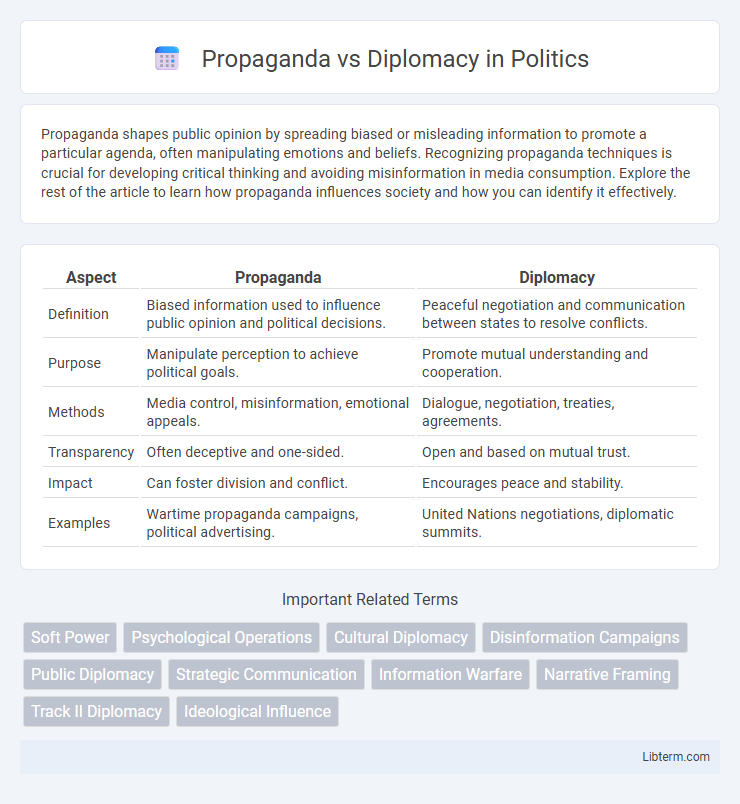
| Aspect | Propaganda | Diplomacy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biased information used to influence public opinion and political decisions. | Peaceful negotiation and communication between states to resolve conflicts. |
| Purpose | Manipulate perception to achieve political goals. | Promote mutual understanding and cooperation. |
| Methods | Media control, misinformation, emotional appeals. | Dialogue, negotiation, treaties, agreements. |
| Transparency | Often deceptive and one-sided. | Open and based on mutual trust. |
| Impact | Can foster division and conflict. | Encourages peace and stability. |
| Examples | Wartime propaganda campaigns, political advertising. | United Nations negotiations, diplomatic summits. |
Understanding Propaganda and Diplomacy
Propaganda manipulates public perception through biased or misleading information to influence opinions and behavior, often targeting large audiences via media channels. Diplomacy involves strategic communication and negotiation between states or organizations to resolve conflicts and build mutual agreements, emphasizing dialogue and compromise. Understanding propaganda requires recognizing its emotional and psychological appeals, while diplomacy relies on rational discourse and adherence to international protocols.
Historical Evolution of Propaganda and Diplomacy
Propaganda and diplomacy have evolved distinctly through history, with propaganda emerging prominently in ancient civilizations as a tool for influencing public opinion and rallying support during wars, especially visible in Roman and Napoleonic eras. Diplomacy, rooted in the formal negotiations of city-states like Athens and Sparta, developed into a structured practice during the Renaissance through the establishment of permanent embassies and codified diplomatic protocols. The 20th century witnessed the refinement of propaganda with mass media and psychological tactics, while diplomacy expanded into multilateral forums such as the League of Nations and the United Nations, reflecting the complex interplay between persuasion and negotiation in international relations.
Key Differences: Propaganda vs Diplomacy
Propaganda focuses on manipulating public opinion through biased or misleading information to achieve political or ideological goals, whereas diplomacy involves negotiation, dialogue, and the peaceful resolution of conflicts between states or organizations. Propaganda often employs emotional appeal and mass communication to influence attitudes, while diplomacy relies on formal protocols, mutual respect, and strategic compromise. The key difference lies in propaganda's intent to persuade and control versus diplomacy's goal to build consensus and maintain international relationships.
Tools and Techniques of Propaganda
Propaganda employs tools such as mass media, symbols, slogans, and emotional appeals to influence public opinion and manipulate attitudes, often using misinformation or biased information to achieve political or ideological goals. Techniques include repetition, fear-mongering, scapegoating, and selective presentation of facts, which contrast with diplomacy's reliance on negotiation, dialogue, and mutual understanding to resolve conflicts. Visual imagery, controlled messaging, and psychological tactics amplify propaganda's impact by targeting subconscious biases and emotions, differentiating it sharply from the reason-based approach of diplomacy.
Diplomatic Strategies and Practices
Diplomatic strategies prioritize dialogue, negotiation, and building mutual trust to resolve conflicts and foster international cooperation. Effective diplomacy employs tact, cultural understanding, and strategic communication to advance national interests while maintaining peaceful relations. Unlike propaganda, which manipulates public perception, diplomacy emphasizes transparency, respect for sovereignty, and long-term relationship building to achieve sustainable agreements.
The Role of Media in Propaganda and Diplomacy
Media serves as a strategic tool in both propaganda and diplomacy by shaping public perception and conveying targeted narratives. Propaganda utilizes media channels to manipulate information, influence mass opinion, and promote specific political agendas, often through biased or misleading content. In diplomacy, media facilitates transparent communication, fosters mutual understanding, and supports the negotiation process by disseminating accurate information to both domestic and international audiences.
Impact on International Relations
Propaganda influences international relations by shaping public opinion and manipulating perceptions, often leading to increased tensions and mistrust between nations. Diplomacy fosters dialogue, negotiation, and mutual understanding, promoting peaceful conflict resolution and cooperative partnerships. The strategic use of propaganda can undermine diplomatic efforts, while effective diplomacy mitigates misinformation and builds stable international alliances.
Case Studies: Propaganda vs Diplomatic Approaches
Case studies reveal stark contrasts between propaganda and diplomatic approaches in international relations, highlighting how propaganda manipulates public perception through biased messaging, while diplomacy seeks mutual understanding and conflict resolution through negotiation. For instance, Cold War-era propaganda campaigns by the United States and Soviet Union intensified ideological divides, whereas diplomatic efforts like the Helsinki Accords facilitated dialogue and eased tensions. Examining these approaches underscores the efficacy of diplomacy in achieving sustainable peace, compared to the short-term influence of propaganda-driven policies.
Consequences of Propaganda on Diplomacy
Propaganda undermines diplomacy by eroding trust between nations, often escalating conflicts through misinformation and hostile narratives. Its dissemination can polarize international relations, making peaceful negotiations difficult and reducing opportunities for compromise. The long-term consequence is a destabilized geopolitical environment where diplomatic efforts are overshadowed by suspicion and aggression.
Navigating the Balance: Modern Perspectives
Navigating the balance between propaganda and diplomacy requires a nuanced understanding of communication strategies in contemporary international relations. Effective diplomacy prioritizes transparency, mutual respect, and fact-based dialogue, while propaganda often manipulates information to influence public opinion or political outcomes. Modern perspectives emphasize ethical considerations and the need for credible messaging to maintain international trust and cooperation.
Propaganda Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com