Sharp power manipulates information and distorts democratic processes to influence public opinion and political environments covertly. This form of power exploits media and cultural channels to undermine transparency and manipulate perceptions without direct confrontation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how sharp power shapes global politics and impacts your society.
Table of Comparison
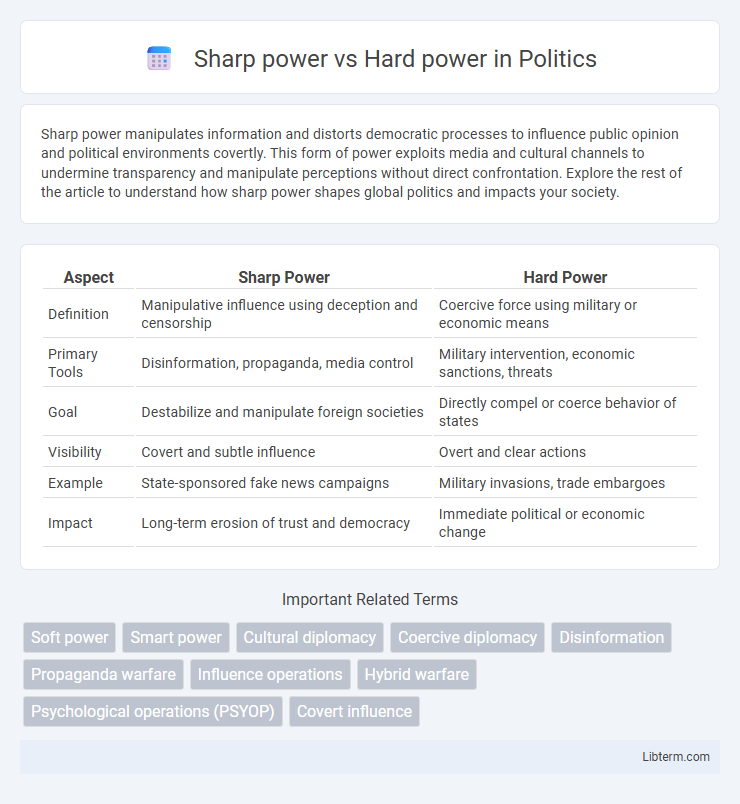
| Aspect | Sharp Power | Hard Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manipulative influence using deception and censorship | Coercive force using military or economic means |
| Primary Tools | Disinformation, propaganda, media control | Military intervention, economic sanctions, threats |
| Goal | Destabilize and manipulate foreign societies | Directly compel or coerce behavior of states |
| Visibility | Covert and subtle influence | Overt and clear actions |
| Example | State-sponsored fake news campaigns | Military invasions, trade embargoes |
| Impact | Long-term erosion of trust and democracy | Immediate political or economic change |
Understanding Sharp Power: Definition and Origins
Sharp power refers to the strategic use of manipulative information and cultural influence by authoritarian states to shape public opinion and undermine democratic institutions beyond their borders. Originating from the analysis of authoritarian interference in Western democracies, sharp power contrasts with hard power's reliance on military or economic coercion by emphasizing covert media, disinformation, and political subversion. Understanding sharp power involves recognizing its role in distorting political narratives and eroding trust within targeted societies without direct confrontation.
Hard Power Explained: Traditional Tools of Influence
Hard power refers to a country's use of military force and economic sanctions to influence the behavior of other nations, relying on coercion and tangible threats. Traditional tools of hard power include military intervention, defense alliances, and economic embargoes that compel compliance through direct pressure. This form of power contrasts with soft power by emphasizing concrete resources and authoritative measures to achieve strategic objectives.
Key Differences Between Sharp Power and Hard Power
Sharp power manipulates information and media to influence public opinion and political environments covertly, often through censorship, disinformation, and propaganda. Hard power relies on military force, economic sanctions, and coercion to achieve foreign policy goals through overt means, including direct intervention or threats. The key difference lies in sharp power's focus on shaping perceptions and attitudes stealthily, while hard power emphasizes visible, tangible pressure and enforcement.
Historical Examples of Hard Power in Action
Hard power historically manifests through military force and economic sanctions used to impose a nation's will, such as the U.S. interventions in Vietnam and Iraq where direct military action aimed to achieve strategic objectives. The Soviet Union's invasion of Afghanistan in 1979 exemplifies hard power through armed occupation to maintain influence over satellite states during the Cold War. Economic blockades and embargoes, including the U.S. embargo against Cuba, highlight hard power tactics designed to coerce governments into policy changes by restricting resources and trade.
Modern Manifestations of Sharp Power
Modern manifestations of sharp power include disinformation campaigns, cyberattacks, and cultural influence operations designed to manipulate public opinion and undermine democratic institutions. These tactics exploit digital platforms and media ecosystems to covertly spread propaganda and censorship while avoiding direct military confrontation common in hard power. Sharp power often targets vulnerable societies through psychological and informational means, contrasting with the overt coercion and military force characteristic of hard power.
Sharp Power Tactics: Manipulation, Media, and Misinformation
Sharp power tactics exploit manipulation, media control, and misinformation to influence foreign populations by distorting facts and promoting propaganda. Authoritarian regimes often deploy these strategies through cyber operations, controlled news outlets, and social media campaigns to undermine democratic institutions and sow discord. This covert approach contrasts with traditional hard power, which relies on military force and economic sanctions to achieve geopolitical objectives.
Military Might vs. Media Influence: Comparing Impact
Military might, characterized by the deployment of armed forces and advanced weaponry, exerts direct and immediate influence over geopolitical outcomes through coercion and force. Media influence, as an aspect of sharp power, shapes perceptions and controls narratives across borders by manipulating information and censoring dissent, thereby achieving strategic objectives without physical confrontation. While military power commands respect through fear and defense capabilities, media influence subtly alters public opinion and policy decisions, reflecting a modern shift towards information-centric dominance in global power dynamics.
Global Case Studies: Sharp Power vs. Hard Power Usage
Sharp power, employed by countries like China and Russia, manipulates information and media to influence public opinion and political environments in democratic nations, exemplified by China's state-controlled media campaigns in Taiwan and Russia's interference in the 2016 US elections. Hard power, demonstrated by the United States and Saudi Arabia, relies on military force, economic sanctions, and coercive diplomacy, as seen in US-led interventions in Iraq and Saudi Arabia's military involvement in Yemen. Global case studies reveal sharp power's subtle, covert persuasion contrasts with hard power's overt, forceful strategies in shaping international relations.
The Risks and Challenges of Sharp Power Strategies
Sharp power strategies pose significant risks including the erosion of democratic institutions, manipulation of public opinion, and the spread of misinformation that undermines trust in media and government. Unlike hard power, which relies on overt military or economic coercion, sharp power operates covertly, making it challenging to identify and counteract effectively. The clandestine nature of sharp power complicates diplomatic relations and can escalate tensions by fostering distrust and suspicion among nations.
Future Trends: Evolving Power Dynamics in International Relations
Sharp power leverages information manipulation, cyber tactics, and covert influence to shape perceptions and disrupt democracies, reflecting the growing importance of digital and informational domains in global politics. Hard power relies on traditional military force and economic sanctions to coerce or compel state behavior, remaining central but increasingly constrained by emerging asymmetric threats and technological advancements. Future trends indicate a fusion of sharp and hard power strategies, emphasizing hybrid approaches that integrate cyber warfare, disinformation campaigns, and targeted military actions to achieve geopolitical objectives in a multipolar world.
Sharp power Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com