Lobbying firms specialize in influencing government policy and legislation on behalf of clients by leveraging strategic communication and advocacy techniques. These firms navigate complex regulatory environments to effectively represent your interests, ensuring lawmakers understand the impact of proposed laws. Discover how partnering with a skilled lobbying firm can advance your agenda by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
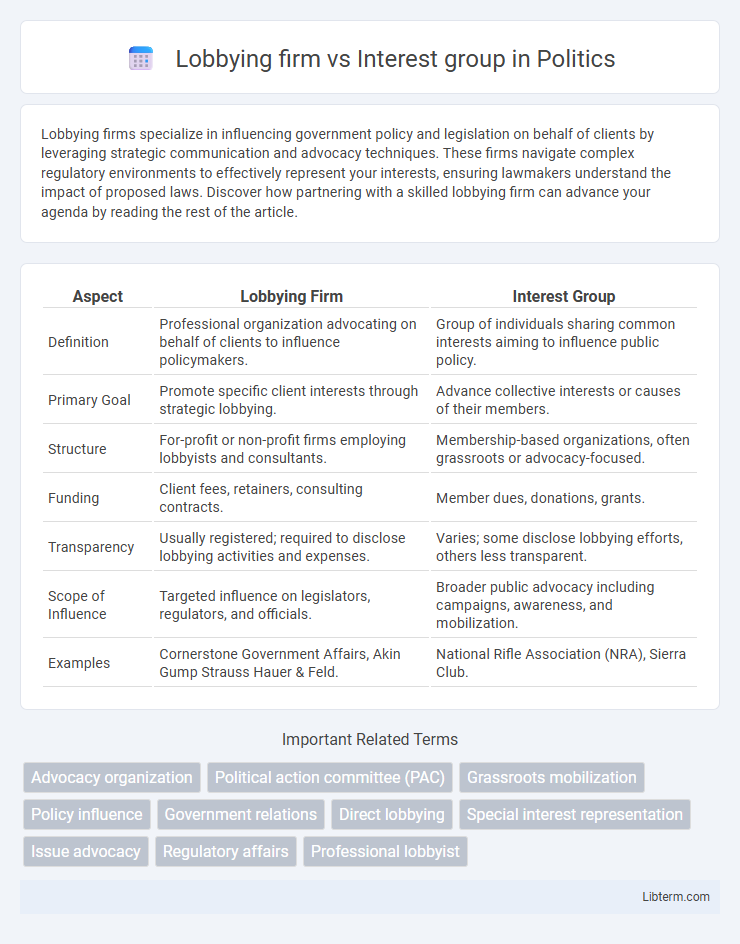
| Aspect | Lobbying Firm | Interest Group |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Professional organization advocating on behalf of clients to influence policymakers. | Group of individuals sharing common interests aiming to influence public policy. |
| Primary Goal | Promote specific client interests through strategic lobbying. | Advance collective interests or causes of their members. |
| Structure | For-profit or non-profit firms employing lobbyists and consultants. | Membership-based organizations, often grassroots or advocacy-focused. |
| Funding | Client fees, retainers, consulting contracts. | Member dues, donations, grants. |
| Transparency | Usually registered; required to disclose lobbying activities and expenses. | Varies; some disclose lobbying efforts, others less transparent. |
| Scope of Influence | Targeted influence on legislators, regulators, and officials. | Broader public advocacy including campaigns, awareness, and mobilization. |
| Examples | Cornerstone Government Affairs, Akin Gump Strauss Hauer & Feld. | National Rifle Association (NRA), Sierra Club. |
Introduction to Lobbying Firms and Interest Groups
Lobbying firms are professional organizations that advocate on behalf of clients by influencing policymakers and government officials to support specific legislation or regulations. Interest groups consist of individuals or organizations united by shared concerns or goals, mobilizing resources to promote their agenda through various advocacy efforts. Both entities play critical roles in shaping public policy, with lobbying firms providing specialized strategic services while interest groups represent collective views and grassroots mobilization.
Defining Lobbying Firms
Lobbying firms are professional organizations hired to influence public policy and legislation on behalf of clients by directly interacting with government officials and policymakers. These firms use strategic communication, research, and advocacy techniques to shape decisions in favor of their clients' interests, often representing multiple clients across various industries. Unlike interest groups, which are membership-based entities advocating for a specific cause or public interest, lobbying firms operate as paid service providers focusing on targeted legislative outcomes.
Understanding Interest Groups
Interest groups are organizations formed to represent specific interests by influencing public policy and decision-making processes, often through advocacy, education, and grassroots mobilization. Lobbying firms, on the other hand, are professional entities hired by interest groups or other clients to directly engage with lawmakers and government officials to promote specific legislative outcomes. Understanding interest groups involves recognizing their role in aggregating member preferences, shaping public opinion, and supporting political candidates aligned with their goals.
Core Functions and Objectives
Lobbying firms specialize in influencing legislation and policy decisions by directly engaging lawmakers and government officials to advance their clients' interests. Interest groups mobilize members and the public to promote specific policy goals, focusing on advocacy, awareness, and grassroots campaigns. Both entities aim to shape public policy but differ in tactics, with lobbying firms providing expert negotiation and strategic counsel, while interest groups prioritize collective action and public support.
Organizational Structures Compared
Lobbying firms operate as specialized entities hired by clients to influence public policy, featuring hierarchical organizational structures with dedicated teams for research, strategy, and client relations. Interest groups, often membership-based organizations, rely on distributed leadership and grassroots participation to mobilize supporters and advocate collective interests. The lobbying firm's structure emphasizes professional expertise and client service, whereas interest groups prioritize member involvement and democratic governance.
Methods of Influence and Advocacy
Lobbying firms employ specialized strategies such as direct meetings with policymakers, drafting legislation, and providing expert testimony to influence public policy, leveraging professional networks and detailed research. Interest groups engage in grassroots mobilization, public campaigns, and voter education to build broad-based support and sway public opinion alongside policy decisions. Both utilize targeted communication and advocacy, but lobbying firms focus more on insider tactics while interest groups rely heavily on outsider pressure.
Key Differences Between Lobbying Firms and Interest Groups
Lobbying firms operate as professional service providers hired by clients to influence legislative and regulatory decisions, while interest groups represent collective social, economic, or political interests to shape public policy. Lobbying firms typically engage in targeted advocacy on behalf of multiple clients, leveraging specialized expertise and access to policymakers, whereas interest groups mobilize grassroots support and public opinion to advance their causes. The primary distinction lies in the lobbying firm's client-driven contract model versus the interest group's member-driven mission to advocate for specific issues or constituencies.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks
Lobbying firms operate within a strict legal and regulatory framework that mandates registration, disclosure of activities, and compliance with lobbying laws such as the Lobbying Disclosure Act in the United States. Interest groups, while also subject to regulatory oversight, primarily function as collective entities advocating for policy changes without the same formal requirements as lobbying firms for reporting expenditures or direct lobbying efforts. Both entities must navigate complex legal boundaries to influence legislation, but lobbying firms are more directly accountable to regulatory bodies through detailed transparency and ethical standards.
Impact on Public Policy
Lobbying firms directly influence public policy by engaging with lawmakers, drafting legislation, and providing expert testimony to shape decisions in favor of their clients' interests. Interest groups mobilize public support, conduct advocacy campaigns, and use grassroots efforts to pressure policymakers, creating a broader base of influence on legislative outcomes. Both entities play critical roles in policy formation, with lobbying firms focusing on targeted, strategic interactions and interest groups emphasizing collective action and public opinion.
Choosing the Right Advocacy Approach
Choosing the right advocacy approach depends on understanding the specific roles and strengths of lobbying firms versus interest groups. Lobbying firms specialize in direct influence through professional government relations and targeted legislative strategies, ideal for organizations seeking expert negotiation and regulatory insight. Interest groups mobilize grassroots support and public opinion to drive policy changes, making them effective for broad-based advocacy and community engagement campaigns.
Lobbying firm Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com