Centralized leadership consolidates decision-making authority within a single individual or small group, enabling swift and consistent direction across an organization. This approach often results in clear accountability and streamlined communication channels, which can improve efficiency in executing strategies. Explore the rest of the article to understand how centralized leadership can impact your organization's performance and when it might be the right fit.
Table of Comparison
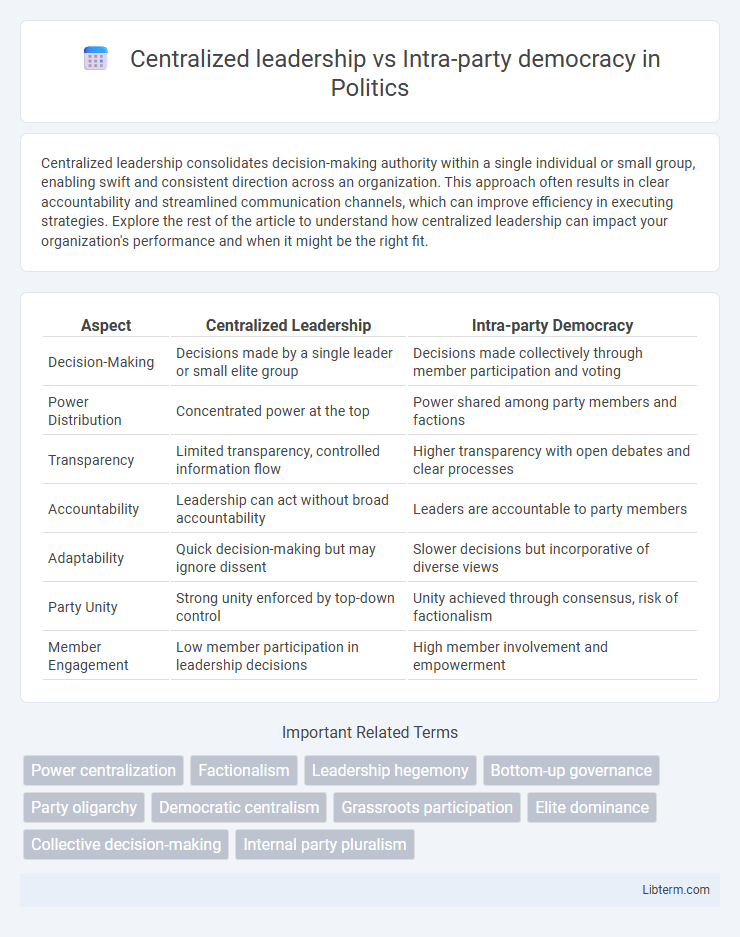
| Aspect | Centralized Leadership | Intra-party Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Decisions made by a single leader or small elite group | Decisions made collectively through member participation and voting |
| Power Distribution | Concentrated power at the top | Power shared among party members and factions |
| Transparency | Limited transparency, controlled information flow | Higher transparency with open debates and clear processes |
| Accountability | Leadership can act without broad accountability | Leaders are accountable to party members |
| Adaptability | Quick decision-making but may ignore dissent | Slower decisions but incorporative of diverse views |
| Party Unity | Strong unity enforced by top-down control | Unity achieved through consensus, risk of factionalism |
| Member Engagement | Low member participation in leadership decisions | High member involvement and empowerment |
Introduction to Party Governance Models
Centralized leadership in party governance concentrates decision-making power within a narrow group or single leader, streamlining direction but limiting broader member input. In contrast, intra-party democracy emphasizes participatory mechanisms, enabling rank-and-file members to influence policy choices and leadership selection through structured voting and debate. These governance models significantly impact party cohesion, policy responsiveness, and adaptability in political landscapes.
Defining Centralized Leadership
Centralized leadership concentrates decision-making authority within a single leader or a small group at the top of the hierarchy, ensuring uniform policy implementation and strategic direction. This model often features streamlined communication channels and reduced internal conflict by limiting dissent and debate. Key characteristics include hierarchical control, top-down directives, and a focus on maintaining organizational cohesion through strong leadership.
Explaining Intra-party Democracy
Intra-party democracy refers to the process within political parties that promotes member participation in decision-making, candidate selection, and policy formulation. This system enhances transparency and accountability by allowing party members to influence leadership choices and party direction through voting or open debates. Unlike centralized leadership, which consolidates power among a few top leaders, intra-party democracy distributes authority more broadly, fostering inclusiveness and internal organizational legitimacy.
Historical Contexts and Evolution
Centralized leadership in political parties often emerged during periods of revolutionary movements or authoritarian regimes, where unified command structures ensured rapid decision-making and control over party ideology. Intra-party democracy evolved as a response to demands for transparency and member participation, gaining prominence in post-war democracies and social movements aiming to balance authority with accountability. Historical shifts such as the fall of totalitarian states and the rise of social democratic parties highlight the ongoing tension and adaptation between centralized control and democratic inclusivity within political organizations.
Advantages of Centralized Leadership
Centralized leadership ensures swift decision-making and coherent strategic direction, which is critical for maintaining organizational focus and effective crisis management. It enhances accountability by clearly defining leadership roles and responsibilities, reducing ambiguity within the party hierarchy. This concentration of authority facilitates consistency in policy implementation and strengthens the party's ability to respond decisively to external challenges.
Benefits of Intra-party Democracy
Intra-party democracy enhances political accountability by enabling active member participation in decision-making processes, fostering transparency and responsiveness to constituents' needs. It promotes policy innovation and adaptability through diverse viewpoints, increasing party legitimacy and strengthening democratic norms within the political system. Empowering grassroots members creates a more inclusive political culture, which can result in greater voter engagement and long-term party stability.
Risks and Drawbacks of Centralization
Centralized leadership often risks suppressing diverse viewpoints, leading to groupthink and reduced innovation within the party. Concentration of power can foster authoritarian tendencies, increasing the likelihood of corruption and alienating grassroots members. Such centralization may undermine intra-party democracy by limiting transparency and accountability, ultimately weakening the party's adaptability and legitimacy.
Challenges in Implementing Intra-party Democracy
Implementing intra-party democracy faces challenges such as resistance from centralized leadership accustomed to controlling decision-making processes, which can lead to internal power struggles and factionalism. The lack of transparent mechanisms and uneven member participation hinder equal representation and accountability within party structures. Moreover, cultural norms and institutional rigidities often limit open debate and critical feedback, undermining the democratic ethos intended in intra-party governance.
Case Studies: Global Political Parties
Centralized leadership in political parties often results in streamlined decision-making but can suppress grassroots participation, as seen in Russia's United Russia party where top-down control consolidates power. In contrast, intra-party democracy promotes member engagement and candidate competition, exemplified by the UK's Labour Party, which implements internal elections and debates to reflect diverse member views. Comparative case studies reveal that while centralized leadership may enhance efficiency in authoritarian contexts, intra-party democracy tends to strengthen legitimacy and adaptability in multiparty democratic systems.
Striking a Balance: Hybrid Approaches
Hybrid approaches to leadership in political parties integrate centralized decision-making with intra-party democracy to enhance responsiveness and cohesion. Structured mechanisms like consultative committees and participatory forums enable member input while maintaining strategic control by central leadership. This balance fosters organizational unity, improves policy effectiveness, and mitigates factionalism within parties.
Centralized leadership Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com