Centrism advocates for balanced political views that avoid extremes on either side of the spectrum, promoting pragmatic solutions and compromise. This approach seeks to unify diverse perspectives and foster stability in governance by prioritizing common ground over partisan division. Explore the rest of this article to understand how centrism can influence political decision-making and impact Your community.
Table of Comparison
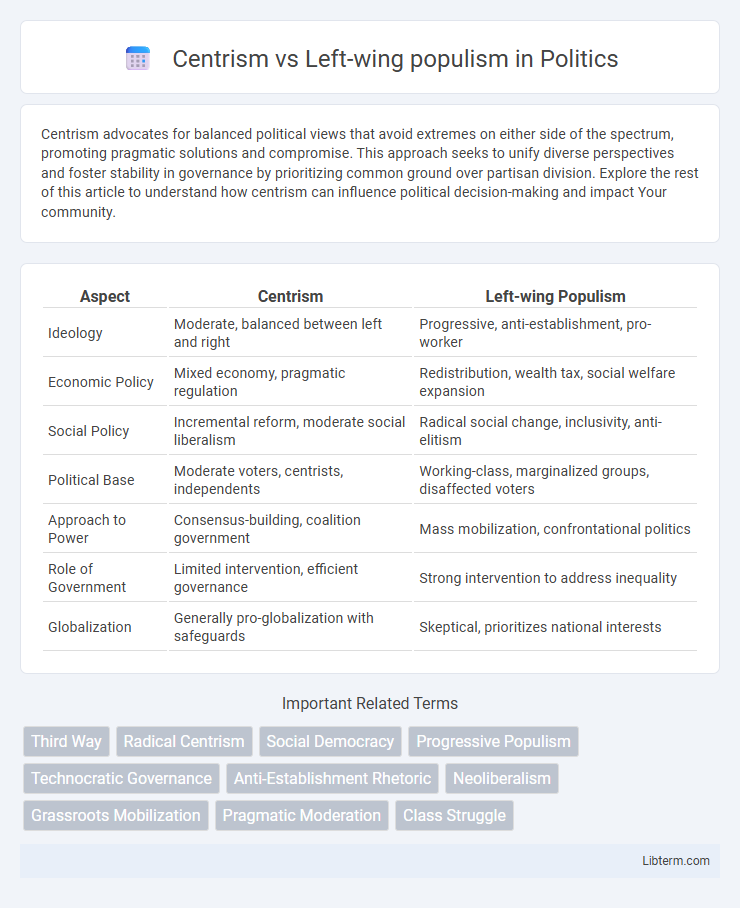
| Aspect | Centrism | Left-wing Populism |
|---|---|---|
| Ideology | Moderate, balanced between left and right | Progressive, anti-establishment, pro-worker |
| Economic Policy | Mixed economy, pragmatic regulation | Redistribution, wealth tax, social welfare expansion |
| Social Policy | Incremental reform, moderate social liberalism | Radical social change, inclusivity, anti-elitism |
| Political Base | Moderate voters, centrists, independents | Working-class, marginalized groups, disaffected voters |
| Approach to Power | Consensus-building, coalition government | Mass mobilization, confrontational politics |
| Role of Government | Limited intervention, efficient governance | Strong intervention to address inequality |
| Globalization | Generally pro-globalization with safeguards | Skeptical, prioritizes national interests |
Understanding Centrism: Core Principles
Centrism emphasizes balanced policies that seek compromise between progressive and conservative viewpoints, promoting pragmatic solutions over ideological extremes. Core principles include political moderation, support for social equality combined with market-friendly economic policies, and a focus on incremental reform rather than radical change. This approach aims to unify diverse constituencies by advocating for stability, inclusivity, and practical governance.
Key Tenets of Left-Wing Populism
Left-wing populism emphasizes economic equality, social justice, and redistribution of wealth through progressive taxation and expanded social programs. It critiques corporate power and advocates for enhanced government intervention to protect workers' rights, public services, and marginalized communities. This approach contrasts with centrism's focus on moderate policies, market-friendly solutions, and incremental reform to balance diverse political interests.
Historical Development of Centrism and Left-Wing Populism
Centrism historically emerged as a pragmatic approach blending elements of both liberalism and conservatism, aiming to balance social stability with progressive reform, notably gaining traction in 19th-century Europe during the rise of parliamentary democracies. Left-wing populism developed in response to economic inequalities and social injustices, drawing on 19th and 20th-century labor movements and socialist ideologies, with key moments such as the formation of the Labour Party in the UK and Latin American populist regimes led by figures like Juan Peron. Both ideologies evolved through reactions to industrialization, economic crises, and shifts in class dynamics, shaping contemporary political spectra worldwide.
Policy Differences: Economy and Welfare
Centrism promotes balanced economic growth through market-friendly policies and moderate welfare programs that aim for sustainability and fiscal responsibility. Left-wing populism advocates for expansive welfare policies, including increased social spending, wealth redistribution, and stronger labor protections to address income inequality. Economic policy in centrism often emphasizes private sector support and gradual reform, while left-wing populism pushes for structural changes and state intervention to achieve social justice.
Approaches to Social Justice and Equality
Centrism advocates for balanced social justice policies that combine market efficiency with targeted social programs, emphasizing incremental reform and institutional stability to achieve equality. Left-wing populism promotes more radical redistribution policies, directly challenging economic elites and systemic structures perceived to perpetuate inequality, often calling for broad societal change and increased state intervention. Both approaches seek social justice but differ in their methods, with centrism favoring pragmatic, moderate reforms and left-wing populism prioritizing transformative, grassroots mobilization.
Leadership Styles and Political Rhetoric
Centrism emphasizes pragmatic leadership focused on consensus-building and moderate policy proposals, often employing measured and inclusive political rhetoric aimed at appealing to a broad electorate. Left-wing populism adopts a confrontational leadership style that champions grassroots mobilization and challenges elite power structures, using emotional and polarizing rhetoric to galvanize support among marginalized groups. The contrast in political rhetoric reflects centrism's preference for nuance and compromise versus left-wing populism's emphasis on stark social and economic inequalities.
Voter Demographics and Support Bases
Centrism typically attracts moderate voters who prioritize stability, pragmatic policies, and incremental change, drawing support from middle-class professionals, suburban families, and older adults. Left-wing populism appeals primarily to working-class populations, younger voters, and marginalized communities, emphasizing economic inequality, social justice, and anti-establishment rhetoric. These distinct voter demographics influence policy priorities, with centrism favoring gradual reforms and left-wing populism pushing for more radical redistribution and systemic change.
Impact on Democratic Institutions
Centrism promotes political stability by advocating for moderate policies that seek compromise and uphold democratic norms, which helps maintain institutional trust and continuity. Left-wing populism challenges established elites by mobilizing grassroots support and emphasizing social justice, potentially revitalizing democratic engagement but also risking polarization and institutional strain. The impact on democratic institutions depends on the balance between fostering inclusiveness and preserving procedural integrity within the political system.
Challenges and Criticisms Faced by Both Ideologies
Centrism faces challenges related to accusations of political indecisiveness and failure to address the demands of polarized electorates, often being criticized for lacking a clear, bold vision. Left-wing populism encounters significant critiques regarding its radical policy proposals, potential economic disruption, and the risk of alienating moderate voters through aggressive rhetoric. Both ideologies struggle with balancing broad appeal and effective governance while navigating increasing political fragmentation and societal divisions.
The Future of Centrism and Left-Wing Populism in Global Politics
The future of centrism in global politics depends on its ability to address increasing polarization by promoting pragmatic policies and inclusive dialogue that bridge ideological divides. Left-wing populism is likely to persist as a significant force by capitalizing on economic inequality, cultural grievances, and demands for social justice, driving transformative changes in welfare and labor policies. Both forces will influence electoral outcomes and policy debates, shaping governance approaches in democracies worldwide amid shifting social and economic realities.
Centrism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com