A proxy ballot allows a voter to authorize another person to cast their vote on their behalf, ensuring participation even when unable to attend in person. This method is commonly used in corporate meetings and shareholder elections to maintain fair representation. Discover how proxy ballots work and why they're essential for your voting rights by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
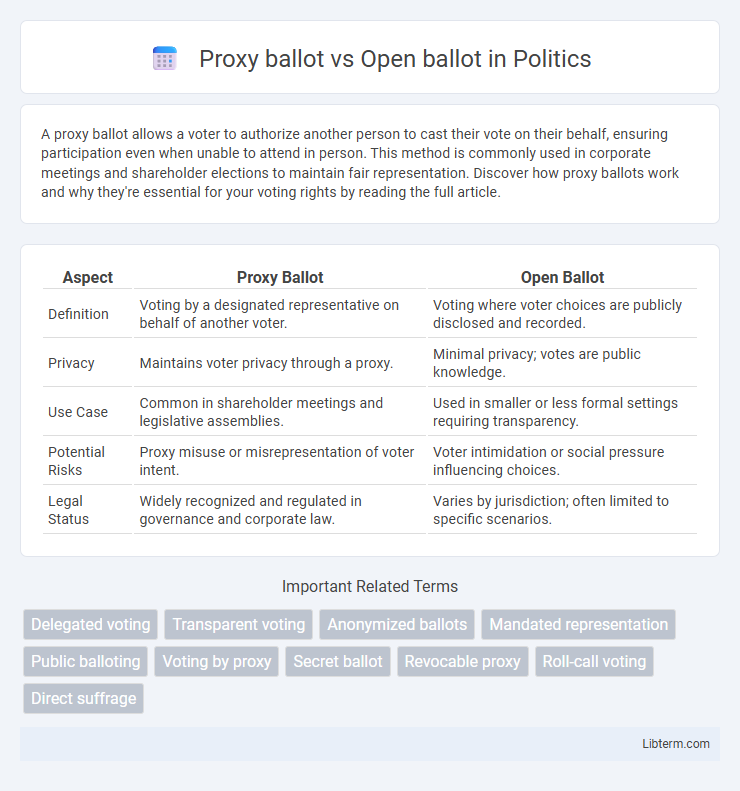
| Aspect | Proxy Ballot | Open Ballot |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voting by a designated representative on behalf of another voter. | Voting where voter choices are publicly disclosed and recorded. |
| Privacy | Maintains voter privacy through a proxy. | Minimal privacy; votes are public knowledge. |
| Use Case | Common in shareholder meetings and legislative assemblies. | Used in smaller or less formal settings requiring transparency. |
| Potential Risks | Proxy misuse or misrepresentation of voter intent. | Voter intimidation or social pressure influencing choices. |
| Legal Status | Widely recognized and regulated in governance and corporate law. | Varies by jurisdiction; often limited to specific scenarios. |
Understanding Proxy Ballot and Open Ballot
Proxy ballots empower voters to delegate their voting power to a trusted individual, allowing representation in decision-making without physical presence. Open ballots, characterized by transparent voting processes, enable voters' choices to be visible, ensuring accountability and deterring fraud. Understanding the mechanics of proxy and open ballots highlights the trade-off between voter convenience and election transparency.
Key Differences Between Proxy and Open Ballot
Proxy ballots allow voters to designate a representative to cast votes on their behalf, ensuring participation when they cannot attend in person. Open ballots require voters to cast their votes publicly, often during meetings where choices are visible to all participants, which enhances transparency but may reduce privacy. The key differences lie in the level of voter presence, confidentiality, and the method of vote collection, with proxy ballots focusing on absentee voting and open ballots emphasizing in-person, transparent voting processes.
Advantages of Proxy Ballot Systems
Proxy ballot systems enable voters to delegate their voting power to trusted representatives, ensuring participation even when individuals cannot attend in person. This method enhances voter turnout and inclusivity by accommodating absentee voters, thereby strengthening democratic processes. Proxy ballots also maintain vote confidentiality and reduce the risk of coercion compared to open ballot systems.
Benefits of Open Ballot Voting
Open ballot voting enhances transparency and accountability by allowing voters' choices to be visible, reducing the risk of electoral fraud and manipulation. It fosters community trust as results are openly verifiable, ensuring legitimacy in the election process. Voters are encouraged to make decisions responsibly, knowing their selections are publicly observed, which can lead to more informed and conscientious participation.
Drawbacks of Proxy Ballots
Proxy ballots often raise concerns about voter authenticity and the potential for coercion, as the designated proxy may not accurately represent the voter's true intentions. The process lacks transparency and can lead to increased opportunities for fraud or manipulation, compromising election integrity. Unlike open ballots that allow direct voter participation, proxy ballots reduce accountability and hinder verification of individual votes.
Challenges of Open Ballot Elections
Open ballot elections face significant challenges such as voter intimidation and lack of privacy, which can compromise the integrity of the voting process. The transparency of open ballots may deter honest voting, leading to potential manipulation and coercion by influential parties. Unlike proxy ballots, open ballots struggle to ensure voter confidentiality, impacting free and fair election outcomes.
Security and Transparency Concerns
Proxy ballots raise significant security concerns due to potential manipulation and unauthorized voting, as proxies may not always act in the voter's true interest. Open ballots enhance transparency by allowing votes to be publicly verified, but this compromises voter privacy and increases the risk of coercion. Balancing these factors, election systems must implement stringent authentication for proxy ballots and secure methods to maintain anonymity in open ballots.
Impact on Voter Privacy
Proxy ballots risk compromising voter privacy as they require voters to entrust their vote to a proxy, increasing the chance of influence or coercion. Open ballots expose voter choices publicly, eliminating secrecy and potentially subjecting voters to social pressure or retaliation. Maintaining voter privacy is crucial for free and fair elections, making secret or confidential voting methods more effective in protecting individual electoral autonomy.
Best Use Cases for Each Ballot Type
Proxy ballots are best suited for corporate board elections and shareholder meetings where voters cannot attend in person, allowing designated representatives to cast votes on their behalf. Open ballots work effectively in community meetings or informal settings where transparency and immediate vote tallying build trust among participants. Selecting the ideal ballot type depends on the need for secure representation or public disclosure during the voting process.
Choosing the Right Ballot for Your Organization
Selecting the right ballot type is crucial for ensuring effective decision-making and member participation in your organization. Proxy ballots allow members to delegate their voting power to trusted representatives, ideal for large or geographically dispersed groups seeking efficiency and convenience. Open ballots promote transparency and direct engagement, better suited for smaller organizations emphasizing accountability and open communication.
Proxy ballot Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com