Censorship restricts access to information, often shaping public opinion and controlling what can be shared or seen. It impacts freedom of expression and can influence societal beliefs and behaviors. Explore how censorship affects your daily life and the broader implications by reading the rest of the article.
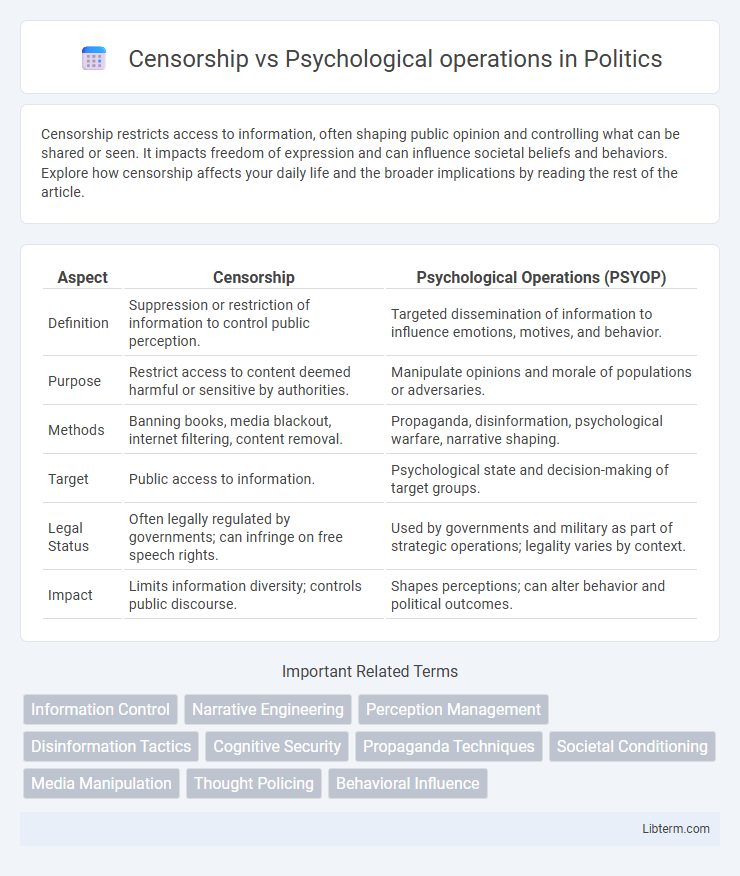
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Censorship | Psychological Operations (PSYOP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Suppression or restriction of information to control public perception. | Targeted dissemination of information to influence emotions, motives, and behavior. |
| Purpose | Restrict access to content deemed harmful or sensitive by authorities. | Manipulate opinions and morale of populations or adversaries. |
| Methods | Banning books, media blackout, internet filtering, content removal. | Propaganda, disinformation, psychological warfare, narrative shaping. |
| Target | Public access to information. | Psychological state and decision-making of target groups. |
| Legal Status | Often legally regulated by governments; can infringe on free speech rights. | Used by governments and military as part of strategic operations; legality varies by context. |
| Impact | Limits information diversity; controls public discourse. | Shapes perceptions; can alter behavior and political outcomes. |
Introduction: Defining Censorship and Psychological Operations
Censorship involves the deliberate suppression or restriction of information, ideas, or content by authorities to control public access and perception. Psychological operations (PSYOPS) refer to strategic communication techniques designed to influence emotions, motives, and behavior of target audiences, often used in military or political contexts. Both mechanisms manipulate information flow but differ in intent and application, with censorship primarily restricting content and PSYOPS actively shaping attitudes and actions.
Historical Context: Evolution of Information Control
Historical context reveals that censorship and psychological operations (PSYOPs) evolved as strategic tools in information control to influence public perception and behavior. Censorship systematically suppresses or alters information, while PSYOPs actively disseminate targeted messages to manipulate attitudes during conflicts and political shifts. The development of mass media and digital platforms has intensified these practices, shaping how governments and organizations manage and control information flow.
Objectives: Goals of Censorship vs. Psychological Operations
Censorship aims to control or suppress information to prevent dissent, maintain social order, or protect government interests by limiting public access to specific content. Psychological operations (PSYOPS) seek to influence the emotions, motives, and behavior of target audiences to achieve strategic objectives, often by disseminating persuasive propaganda or misinformation. While censorship restricts information flow to mitigate threats, PSYOPS actively shape perceptions and attitudes to manipulate public opinion and decision-making processes.
Methods and Tactics Employed
Censorship employs methods such as information suppression, content filtering, and blacklisting to control the flow of information and limit public access to dissenting views. Psychological operations (PSYOPS) utilize tactics like propaganda dissemination, disinformation campaigns, and targeted psychological manipulation to influence attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors of specific audiences. Both approaches leverage digital surveillance, media control, and psychological profiling to enhance effectiveness in shaping perception and controlling narratives.
Targets: Who is Affected and Why
Censorship predominantly targets the general public by restricting access to information deemed harmful or sensitive, aiming to control societal narratives and maintain political or social order. Psychological operations (PSYOPS) focus on specific groups such as enemy combatants, foreign populations, or domestic factions, using tailored messages to influence emotions, attitudes, and behaviors for strategic advantage. Both strategies affect individuals differently based on their roles, beliefs, and access to information, with censorship suppressing knowledge while PSYOPS actively manipulate perceptions.
Impact on Society and Public Perception
Censorship shapes public perception by controlling the flow of information, often creating a limited or biased understanding of events, which can lead to social conformity or dissent suppression. Psychological operations manipulate emotions and beliefs through targeted messaging, significantly influencing individual and collective attitudes within society. Both tactics impact social trust and democratic processes by altering reality in ways that can either unify or polarize populations.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Censorship involves legally restricting information to protect public order or national security, while psychological operations employ strategic communication techniques to influence perceptions and behavior, often within military contexts. Legal frameworks like the First Amendment in the U.S. emphasize free speech protections, yet allow for limitations when speech incites violence or poses threats to safety. Ethical considerations demand transparency, respect for individual rights, and avoidance of manipulation or coercion, raising ongoing debates about the balance between security and freedom in both censorship and psychological operations.
Case Studies: Notable Examples from Around the World
Case studies of censorship versus psychological operations reveal distinct approaches in controlling information and influencing public perception globally. China's Great Firewall exemplifies state censorship by restricting internet access and suppressing dissenting content, while Russia's use of disinformation campaigns during the Ukraine conflict demonstrates psychological operations aimed at manipulating beliefs and behavior. North Korea combines both censorship and psychological tactics to maintain regime stability through strict media control and propaganda dissemination.
Countermeasures and Resistance Strategies
Countermeasures against censorship and psychological operations include enhancing digital literacy, implementing encryption technologies, and promoting open-source communication platforms to safeguard information integrity. Resistance strategies emphasize grassroots mobilization, awareness campaigns, and international coalition-building to expose manipulation tactics and uphold freedom of expression. Leveraging artificial intelligence for detecting disinformation and employing legal frameworks to challenge unjust restrictions further fortify defenses against psychological and informational control.
Future Trends in Information Warfare
Future trends in information warfare increasingly blur the lines between censorship and psychological operations, leveraging AI-driven content filtering and deepfake technologies to manipulate public perception. Advanced algorithms enable state and non-state actors to control narratives by selectively suppressing or amplifying information, shaping cognitive biases on a massive scale. The integration of neurotechnology promises more personalized psychological operations, targeting individual vulnerabilities to influence behavior and decision-making in real time.
Censorship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com