Approval voting allows voters to select all candidates they find acceptable, rather than choosing just one, promoting a more representative election outcome. This system reduces the impact of vote splitting and helps ensure that the candidate with the broadest support wins. Discover how approval voting can improve your next election by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
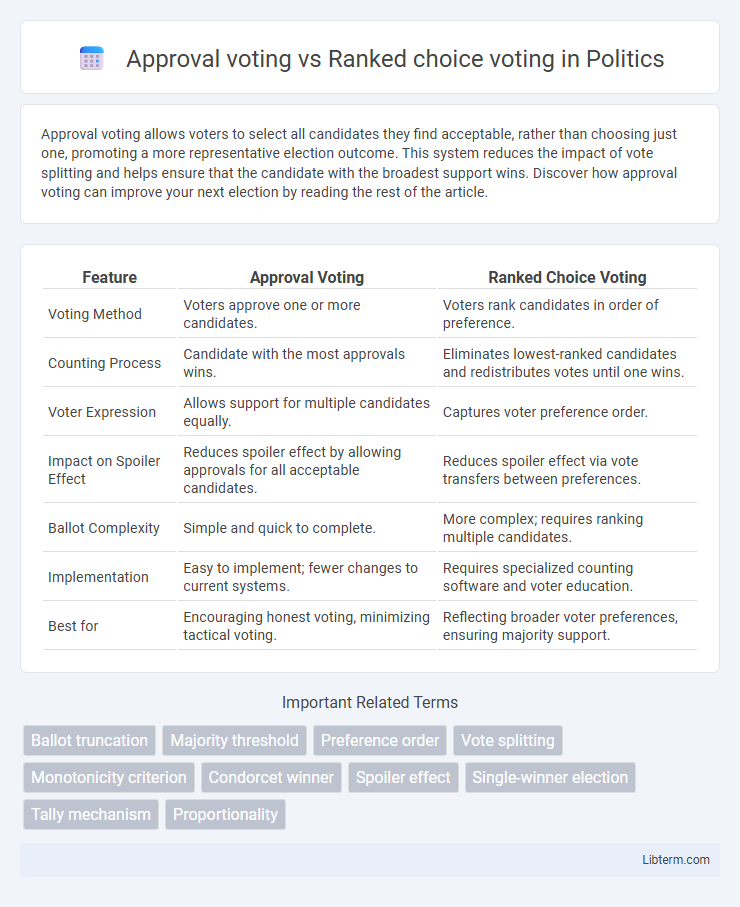
| Feature | Approval Voting | Ranked Choice Voting |
|---|---|---|
| Voting Method | Voters approve one or more candidates. | Voters rank candidates in order of preference. |
| Counting Process | Candidate with the most approvals wins. | Eliminates lowest-ranked candidates and redistributes votes until one wins. |
| Voter Expression | Allows support for multiple candidates equally. | Captures voter preference order. |
| Impact on Spoiler Effect | Reduces spoiler effect by allowing approvals for all acceptable candidates. | Reduces spoiler effect via vote transfers between preferences. |
| Ballot Complexity | Simple and quick to complete. | More complex; requires ranking multiple candidates. |
| Implementation | Easy to implement; fewer changes to current systems. | Requires specialized counting software and voter education. |
| Best for | Encouraging honest voting, minimizing tactical voting. | Reflecting broader voter preferences, ensuring majority support. |
Introduction to Voting Systems
Approval voting allows voters to select all candidates they approve of, maximizing expressiveness and minimizing the spoiler effect, while ranked-choice voting requires voters to rank candidates by preference, enabling instant runoff and majority support. Approval voting simplifies ballot counting by tallying approval marks, whereas ranked-choice voting uses multiple rounds of elimination and redistribution to determine the winner. Both systems aim to produce more representative outcomes compared to plurality voting, with ranked-choice emphasizing consensus and approval voting prioritizing voter honesty.
What Is Approval Voting?
Approval voting allows voters to select all candidates they find acceptable rather than just one, enabling a more expressive and flexible voting method. This system increases the likelihood of consensus winners by counting each approved candidate's total votes, rather than ranking preferences as in ranked choice voting. Approval voting reduces the vote-splitting problem common in plurality elections and encourages honest voting without strategic compromise.
What Is Ranked Choice Voting?
Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) is an electoral system allowing voters to rank candidates by preference rather than selecting a single choice, promoting majority support for elected officials. Unlike Approval Voting, where voters approve any number of candidates, RCV eliminates the need for separate runoff elections by redistributing votes from the least popular candidates in successive rounds. This method enhances voter expression and reduces strategic voting, leading to outcomes that better reflect voter preferences.
How Approval Voting Works
Approval Voting allows voters to select any number of candidates they approve of, rather than restricting them to a single choice. Each candidate that receives approval votes is counted equally, and the candidate with the most approvals wins the election. This method simplifies voting and reduces the impact of vote splitting compared to Ranked Choice Voting, where voters rank candidates in order of preference.
How Ranked Choice Voting Works
Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) allows voters to rank candidates in order of preference, ensuring that the winning candidate has broad support. If no candidate receives more than 50% of first-choice votes, the candidate with the fewest votes is eliminated, and those votes are redistributed based on the next preferences until someone secures a majority. This system reduces the likelihood of vote splitting and promotes majority consensus without the need for a runoff election.
Advantages of Approval Voting
Approval voting allows voters to select all candidates they find acceptable, increasing the likelihood of electing broadly supported winners and reducing the spoiler effect. It simplifies the ballot and counting process compared to ranked choice voting, minimizing voter errors and administrative costs. The system promotes honest voting by enabling sincere expression of preferences without strategic ranking complexities inherent in ranked choice methods.
Advantages of Ranked Choice Voting
Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) allows voters to rank candidates in order of preference, which reduces the spoiler effect and encourages greater voter participation. It promotes majority support by ensuring the winning candidate has over 50% of the vote through instant runoffs, enhancing the legitimacy of electoral outcomes. RCV also incentivizes positive campaigning, as candidates seek to gain second and third-choice votes from their opponents' supporters.
Key Differences Between Approval and Ranked Choice Voting
Approval voting allows voters to select any number of candidates they approve of, with the candidate receiving the most approvals winning, while ranked choice voting requires voters to rank candidates in order of preference, and the winner is determined through successive rounds of vote redistribution until a candidate achieves a majority. Approval voting simplifies ballot design and tallying, reducing voter error and ballot exhaustion, whereas ranked choice voting provides a more nuanced expression of voter preferences and aims to ensure majority support for the winner. The main difference lies in approval voting treating each vote independently and equally, contrasting with ranked choice's iterative elimination and transfer process.
Real-World Examples and Adoption
Approval voting has been adopted in several organizations like the University of California Student Association and experienced use in Fargo, North Dakota's local elections, illustrating its simplicity and effectiveness in multi-candidate races. Ranked choice voting (RCV) has a broader adoption footprint, utilized in cities such as San Francisco, Minneapolis, and states like Maine, enhancing voter expression by allowing ranking preferences and reducing the need for separate runoff elections. Both systems aim to better reflect voter intentions, but RCV's complexity has led to more extensive public education efforts, while approval voting's straightforward ballot design fosters quicker implementation in varying electoral contexts.
Which System Is Best for Fair Elections?
Approval voting allows voters to select all candidates they find acceptable, which can reduce vote splitting and promote majority support. Ranked choice voting enables voters to rank candidates by preference, ensuring winners have broad support through instant runoffs. Both systems enhance fairness by capturing voter intent more accurately than plurality voting, but approval voting is simpler to implement and understand, while ranked choice voting offers nuanced expression of preferences.
Approval voting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com